Genome-wide association study identifies five new schizophrenia loci
- PMID: 21926974
- PMCID: PMC3303194
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.940
Genome-wide association study identifies five new schizophrenia loci
Abstract
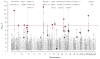
We examined the role of common genetic variation in schizophrenia in a genome-wide association study of substantial size: a stage 1 discovery sample of 21,856 individuals of European ancestry and a stage 2 replication sample of 29,839 independent subjects. The combined stage 1 and 2 analysis yielded genome-wide significant associations with schizophrenia for seven loci, five of which are new (1p21.3, 2q32.3, 8p23.2, 8q21.3 and 10q24.32-q24.33) and two of which have been previously implicated (6p21.32-p22.1 and 18q21.2). The strongest new finding (P = 1.6 × 10(-11)) was with rs1625579 within an intron of a putative primary transcript for MIR137 (microRNA 137), a known regulator of neuronal development. Four other schizophrenia loci achieving genome-wide significance contain predicted targets of MIR137, suggesting MIR137-mediated dysregulation as a previously unknown etiologic mechanism in schizophrenia. In a joint analysis with a bipolar disorder sample (16,374 affected individuals and 14,044 controls), three loci reached genome-wide significance: CACNA1C (rs4765905, P = 7.0 × 10(-9)), ANK3 (rs10994359, P = 2.5 × 10(-8)) and the ITIH3-ITIH4 region (rs2239547, P = 7.8 × 10(-9)).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: details accompany the full-text HTML version of the paper at
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loci with genome-wide associations with schizophrenia in the Han Chinese population.Br J Psychiatry. 2015 Dec;207(6):490-4. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.114.150490. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Br J Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26206863
-
Large-scale genome-wide association analysis of bipolar disorder identifies a new susceptibility locus near ODZ4.Nat Genet. 2011 Sep 18;43(10):977-83. doi: 10.1038/ng.943. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21926972 Free PMC article.
-
A rare functional noncoding variant at the GWAS-implicated MIR137/MIR2682 locus might confer risk to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.Am J Hum Genet. 2014 Dec 4;95(6):744-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Am J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 25434007 Free PMC article.
-
Suggestion of roles for both common and rare risk variants in genome-wide studies of schizophrenia.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010 Jul;67(7):667-73. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.69. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20603448 Review. No abstract available.
-
What is the impact of genome-wide supported risk variants for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder on brain structure and function? A systematic review.Psychol Med. 2015;45(12):2461-80. doi: 10.1017/S0033291715000537. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Psychol Med. 2015. PMID: 25858580 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene-environment interactions in the influence of maternal education on adolescent neurodevelopment using ABCD study.Sci Adv. 2024 Nov 15;10(46):eadp3751. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adp3751. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39546599 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor 4 expression in the developing non-human primate brain: a comparative analysis with the mouse brain.Front Neuroanat. 2024 Oct 22;18:1478689. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2024.1478689. eCollection 2024. Front Neuroanat. 2024. PMID: 39502395 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a high-throughput screening system targeting the protein-protein interactions between PRL and CNNM.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25432. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76269-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455715 Free PMC article.
-
Analyses of GWAS signal using GRIN identify additional genes contributing to suicidal behavior.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 21;7(1):1360. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06943-7. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39433874 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic dysfunction in postmortem dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: implications for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia and affective disorders.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Sep 24;18:1440834. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1440834. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39381500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 MH085515/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078075/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH085812/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM047845/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH074543/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH071681/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G1000708/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0800509/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080403/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068921/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM047845-21/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082659/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH074027/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K23 MH001760/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH085518/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH085520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079800/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH058693/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082659-12/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084098/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH077139/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH068881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G1000718/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH079470/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH085548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083094/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U01 MH094421/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA142538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous


