How the brain integrates costs and benefits during decision making
- PMID: 21118983
- PMCID: PMC3003102
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0908104107
How the brain integrates costs and benefits during decision making
Abstract
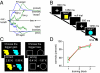
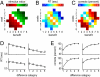
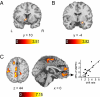
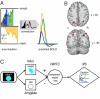
When we make decisions, the benefits of an option often need to be weighed against accompanying costs. Little is known, however, about the neural systems underlying such cost-benefit computations. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging and choice modeling, we show that decision making based on cost-benefit comparison can be explained as a stochastic accumulation of cost-benefit difference. Model-driven functional MRI shows that ventromedial and left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex compare costs and benefits by computing the difference between neural signatures of anticipated benefits and costs from the ventral striatum and amygdala, respectively. Moreover, changes in blood oxygen level dependent (BOLD) signal in the bilateral middle intraparietal sulcus reflect the accumulation of the difference signal from ventromedial prefrontal cortex. In sum, we show that a neurophysiological mechanism previously established for perceptual decision making, that is, the difference-based accumulation of evidence, is fundamental also in value-based decisions. The brain, thus, weighs costs against benefits by combining neural benefit and cost signals into a single, difference-based neural representation of net value, which is accumulated over time until the individual decides to accept or reject an option.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neural computations underlying action-based decision making in the human brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Oct 6;106(40):17199-204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901077106. Epub 2009 Sep 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19805082 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Decision-Making with Predictions of Others' Likely and Unlikely Choices in the Human Brain.J Neurosci. 2024 Sep 11;44(37):e2236232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2236-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39179384 Free PMC article.
-
Decision value computation in DLPFC and VMPFC adjusts to the available decision time.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Apr;35(7):1065-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08076.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22487036 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cortico-limbic-striatal circuits subserving different forms of cost-benefit decision making.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2008 Dec;8(4):375-89. doi: 10.3758/CABN.8.4.375. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19033236 Review.
-
Value, pleasure and choice in the ventral prefrontal cortex.Trends Cogn Sci. 2011 Feb;15(2):56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2010.12.004. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Trends Cogn Sci. 2011. PMID: 21216655 Review.
Cited by
-
Emotion-Driven Moral Evaluation: A Mechanistic Study Based on the Drift-Diffusion Model.Brain Sci. 2024 Oct 4;14(10):1005. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14101005. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39452019 Free PMC article.
-
Exaggerated frontoparietal control over cognitive effort-based decision-making in young women with anorexia nervosa.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Aug 28. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02712-4. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39198684
-
Online cancer information seeking and colorectal cancer screening in China: Considering threat and coping Appraisals, and cancer fatalism.Prev Med Rep. 2024 Jul 14;45:102824. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102824. eCollection 2024 Sep. Prev Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39132579 Free PMC article.
-
Multiattribute Decision-making in Macaques Relies on Direct Attribute Comparisons.J Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Sep 1;36(9):1879-1897. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_02208. J Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38940740 Free PMC article.
-
Synergizing habits and goals with variational Bayes.Nat Commun. 2024 May 25;15(1):4461. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48577-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38796491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knutson B, Cooper JC. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of reward prediction. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005;18:411–417. - PubMed
-
- Heekeren HR, Marrett S, Ungerleider LG. The neural systems that mediate human perceptual decision making. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2008;9:467–479. - PubMed
-
- Gold JI, Shadlen MN. Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli. Trends Cogn Sci. 2001;5:10–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


