Pathway analysis of GWAS provides new insights into genetic susceptibility to 3 inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 19956648
- PMCID: PMC2778995
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008068
Pathway analysis of GWAS provides new insights into genetic susceptibility to 3 inflammatory diseases
Abstract
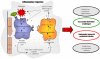
Although the introduction of genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have greatly increased the number of genes associated with common diseases, only a small proportion of the predicted genetic contribution has so far been elucidated. Studying the cumulative variation of polymorphisms in multiple genes acting in functional pathways may provide a complementary approach to the more common single SNP association approach in understanding genetic determinants of common disease. We developed a novel pathway-based method to assess the combined contribution of multiple genetic variants acting within canonical biological pathways and applied it to data from 14,000 UK individuals with 7 common diseases. We tested inflammatory pathways for association with Crohn's disease (CD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and type 1 diabetes (T1D) with 4 non-inflammatory diseases as controls. Using a variable selection algorithm, we identified variants responsible for the pathway association and evaluated their use for disease prediction using a 10 fold cross-validation framework in order to calculate out-of-sample area under the Receiver Operating Curve (AUC). The generalisability of these predictive models was tested on an independent birth cohort from Northern Finland. Multiple canonical inflammatory pathways showed highly significant associations (p 10(-3)-10(-20)) with CD, T1D and RA. Variable selection identified on average a set of 205 SNPs (149 genes) for T1D, 350 SNPs (189 genes) for RA and 493 SNPs (277 genes) for CD. The pattern of polymorphisms at these SNPS were found to be highly predictive of T1D (91% AUC) and RA (85% AUC), and weakly predictive of CD (60% AUC). The predictive ability of the T1D model (without any parameter refitting) had good predictive ability (79% AUC) in the Finnish cohort. Our analysis suggests that genetic contribution to common inflammatory diseases operates through multiple genes interacting in functional pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
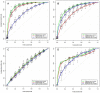
 ) removed. Red curves show the predictive performance of the models formed only by the previously excluded SNPs (significant hits and SNPs in LD). In T1D (A) the area under the average ROC curves is 91%, 71% and 84%, in RA (B) it is 85%, 81%, 70% and in CD (C) 60%, 56%, 58% for the pathway-derived models (green-curves), the pathway-derived models excluding the significant hits (blue curves) and the significant-hit models (red-curves) respectively. In (D) the AUC of the green, blue and red ROC is 0.79, 0.71 and 0.76 respectively.
) removed. Red curves show the predictive performance of the models formed only by the previously excluded SNPs (significant hits and SNPs in LD). In T1D (A) the area under the average ROC curves is 91%, 71% and 84%, in RA (B) it is 85%, 81%, 70% and in CD (C) 60%, 56%, 58% for the pathway-derived models (green-curves), the pathway-derived models excluding the significant hits (blue curves) and the significant-hit models (red-curves) respectively. In (D) the AUC of the green, blue and red ROC is 0.79, 0.71 and 0.76 respectively.
Similar articles
-
Biological function integrated prediction of severe radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a nested case control study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Oct 25;19(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1414-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29065906 Free PMC article.
-
A systems genetics approach provides a bridge from discovered genetic variants to biological pathways in rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25389. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025389. Epub 2011 Sep 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21980439 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated enrichment analysis of variants and pathways in genome-wide association studies indicates central role for IL-2 signaling genes in type 1 diabetes, and cytokine signaling genes in Crohn's disease.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(10):e1003770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003770. Epub 2013 Oct 3. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24098138 Free PMC article.
-
The genetic architecture of type 1 diabetes mellitus.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018 Dec 5;477:70-80. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2018.06.002. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29913182 Review.
-
The current state of genetic risk models for the development of kidney cancer: a review and validation.BJU Int. 2022 Nov;130(5):550-561. doi: 10.1111/bju.15752. Epub 2022 May 7. BJU Int. 2022. PMID: 35460182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Applications of Regulatory T cells in Adoptive Cell Therapies.Cell Gene Ther Insights. 2018 Jan;4(1):405-429. doi: 10.18609/cgti.2018.042. Cell Gene Ther Insights. 2018. PMID: 34984106 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of CD4+ T-cell subtypes using single cell RNA sequencing and the impact of cell number and sequencing depth.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 13;10(1):19825. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76972-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33188258 Free PMC article.
-
A zebrafish functional genomics model to investigate the role of human A20 variants in vivo.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 5;10(1):19085. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75917-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33154446 Free PMC article.
-
TAK1: a potent tumour necrosis factor inhibitor for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.Open Biol. 2020 Sep;10(9):200099. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200099. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 32873150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analyzing Genome-Wide Association Study Dataset Highlights Immune Pathways in Lip Bone Mineral Density.Front Genet. 2020 Mar 10;11:4. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00004. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32211016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hunter DJ, Kraft P. Drinking from the fire hose–statistical issues in genomewide association studies. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:436–439. - PubMed
-
- Kruglyak L. The road to genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:314–318. - PubMed
-
- Wray NR, Goddard ME, Visscher PM. Prediction of individual genetic risk of complex disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18:257–263. - PubMed
-
- van der Poll T, Opal SM. Host-pathogen interactions in sepsis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:32–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


