Analysis of microbial gene transcripts in environmental samples
- PMID: 16000831
- PMCID: PMC1168992
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.7.4121-4126.2005
Analysis of microbial gene transcripts in environmental samples
Abstract
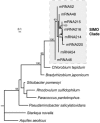
We analyzed gene expression in marine and freshwater bacterioplankton communities by the direct retrieval and analysis of microbial transcripts. Environmental mRNA, obtained from total RNA by subtractive hybridization of rRNA, was reverse transcribed, amplified with random primers, and cloned. Approximately 400 clones were analyzed, of which approximately 80% were unambiguously mRNA derived. mRNAs appeared to be from diverse taxonomic groups, including both Bacteria (mainly alpha- and gamma-Proteobacteria) and Archaea (mainly Euryarchaeota). Many transcripts could be linked to environmentally important processes such as sulfur oxidation (soxA), assimilation of C1 compounds (fdh1B), and acquisition of nitrogen via polyamine degradation (aphA). Environmental transcriptomics is a means of exploring functional gene expression within natural microbial communities without bias toward known sequences, and provides a new approach for obtaining community-specific variants of key functional genes.
Figures
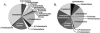
Similar articles
-
Development and quantitative analyses of a universal rRNA-subtraction protocol for microbial metatranscriptomics.ISME J. 2010 Jul;4(7):896-907. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.18. Epub 2010 Mar 11. ISME J. 2010. PMID: 20220791
-
Characterization of microbial community structure in Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates: comparative analysis of DNA- and RNA-derived clone libraries.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jun;71(6):3235-47. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3235-3247.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15933026 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic diversity of bacterial and archaeal communities in the anoxic zone of the Cariaco Basin.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Apr;67(4):1663-74. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.4.1663-1674.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11282619 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Bacterioplankton Seasonal Succession Dynamics.Trends Microbiol. 2017 Jun;25(6):494-505. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.12.013. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Trends Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28108182 Review.
-
A multiomics approach to study the microbiome response to phytoplankton blooms.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;101(12):4863-4870. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8330-5. Epub 2017 May 19. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28526980 Review.
Cited by
-
Modern microbiology: Embracing complexity through integration across scales.Cell. 2024 Sep 19;187(19):5151-5170. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.028. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39303684 Review.
-
Analysis of Culturable Bacterial Diversity of Pangong Tso Lake via a 16S rRNA Tag Sequencing Approach.Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 17;12(2):397. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020397. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399801 Free PMC article.
-
Using metatranscriptomics to better understand the role of microbial nitrogen cycling in coastal sediment benthic flux denitrification efficiency.Environ Microbiol Rep. 2023 Aug;15(4):308-323. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.13148. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36992633 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse engineering environmental metatranscriptomes clarifies best practices for eukaryotic assembly.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 3;24(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-05121-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36869298 Free PMC article.
-
MetaGT: A pipeline for de novo assembly of metatranscriptomes with the aid of metagenomic data.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 28;13:981458. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.981458. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36386613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Béjà, O., M. T. Suzuki, E. V. Koonin, L. Aravind, A. Hadd, L. P. Nguyen, R. Villacorta, M. Amjadi, C. Garrigues, S. B. Jovanovich, R. A. Feldman, and E. F. DeLong. 2000. Construction and analysis of bacterial artificial chromosome libraries from a marine microbial assemblage. Environ. Microbiol. 2:516-529. - PubMed
-
- Belasco, J. G., and G. Brawerman. 1993. Control of messenger RNA stability. Academic Press, San Diego, Calif.
-
- Felsenstein, J. 1989. PHYLIP, phylogenetic inference package (version 3.2). Cladistics 5:164-166.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


