Abstract
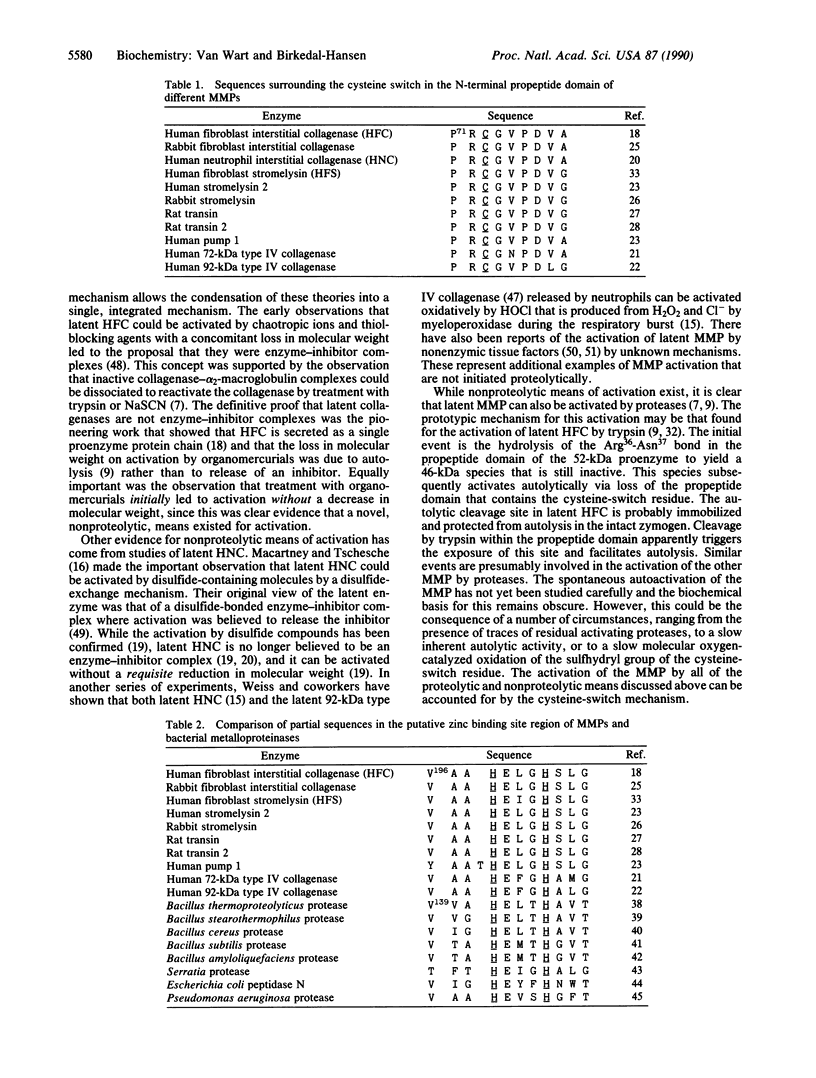
The general applicability of the "cysteine-switch" activation mechanism to the members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene family is examined here. All currently known members of the MMP gene family share the characteristic that they are synthesized in a latent, inactive, form. Recent evidence suggests that this latency in human fibroblast collagenase (HFC) is the result of formation of an intramolecular complex between the single cysteine residue in its propeptide domain and the essential zinc atom in the catalytic domain, a complex that blocks the active site. Latent HFC can be activated by multiple means, all of which effect the dissociation of the cysteine residue from the complex. This is referred to as the "cysteine-switch" mechanism of activation. The propeptide domain that contains the critical cysteine residue and the catalytic domain that contains the zinc-binding site are the only two domains common to all of the MMPs. The amino acid sequences surrounding both the critical cysteine residue and a region of the protein chains containing two of the putative histidine zinc-binding ligands are highly conserved in all of the MMPs. A survey of the literature shows that many of the individual MMPs can be activated by the multiple means observed for latent HFC. These observations support the view that the cysteine-switch mechanism is applicable to all members of this gene family. This mechanism is unprecedented in enzymology as far as we know and offers the opportunity for multiple modes of physiological activation of these important enzymes. Since conditions in different cells and tissues may match those necessary to effect one of these activation modes for a given MMP, this may offer metabolic flexibility in the control of MMP activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe S., Shinmei M., Nagai Y. Synovial collagenase and joint diseases: the significancy of latent collagenase with special reference to rheumatoid arthritis. J Biochem. 1973 May;73(5):1007–1011. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer E. A., Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. Collagenase production by human skin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):232–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bever R. A., Iglewski B. H. Molecular characterization and nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa elastase structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4309–4314. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4309-4314.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen B., Moore W. G., Taylor R. E., Bhown A. S., Birkedal-Hansen H. Monoclonal antibodies to human fibroblast procollagenase. Inhibition of enzymatic activity, affinity purification of the enzyme, and evidence for clustering of epitopes in the NH2-terminal end of the activated enzyme. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6751–6758. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H. Catabolism and turnover of collagens: collagenases. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:140–171. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkedal-Hansen H., Taylor R. E. Detergent-activation of latent collagenase and resolution of its component molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug 31;107(4):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Matrisian L. M., Gesnel M. C., Staub A., Leroy P. Sequences coding for part of oncogene-induced transin are highly conserved in a related rat gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1139–1151. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier I. E., Wilhelm S. M., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Seltzer J. L., Kronberger A., He C. S., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE-1) secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6579–6587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fini M. E., Karmilowicz M. J., Ruby P. L., Beeman A. M., Borges K. A., Brinckerhoff C. E. Cloning of a complementary DNA for rabbit proactivator. A metalloproteinase that activates synovial cell collagenase, shares homology with stromelysin and transin, and is coordinately regulated with collagenase. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1254–1264. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fini M. E., Plucinska I. M., Mayer A. S., Gross R. H., Brinckerhoff C. E. A gene for rabbit synovial cell collagenase: member of a family of metalloproteinases that degrade the connective tissue matrix. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6156–6165. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglino M., Gharbi S., Lazdunski A. Nucleotide sequence of the pepN gene encoding aminopeptidase N of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;49(3):303–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujishima A., Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature. 1972 Jul 7;238(5358):37–38. doi: 10.1038/238037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Wilhelm S. M., Kronberger A., Bauer E. A., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z. Human fibroblast collagenase. Complete primary structure and homology to an oncogene transformation-induced rat protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6600–6605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Roswit W. T., Goldberg G. I. The activation of human skin fibroblast procollagenase. Sequence identification of the major conversion products. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5886–5889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A. R. Molecular structure of an aspartic proteinase zymogen, porcine pepsinogen, at 1.8 A resolution. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):33–38. doi: 10.1038/319033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Bouvier J., Bairoch A. A unique signature identifies a family of zinc-dependent metallopeptidases. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 2;242(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassell B., Kay J. Zymogens of proteolytic enzymes. Science. 1973 Jun 8;180(4090):1022–1027. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4090.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knäuper V., Krämer S., Reinke H., Tschesche H. Characterization and activation of procollagenase from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. N-terminal sequence determination of the proenzyme and various proteolytically activated forms. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacko A. G., Neurath H. Studies on procarboxypeptidase A and carboxypeptidase A of the spiny pacific dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4680–4690. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus G. S., Daniels J. R., Lian J., Burleigh M. C. Role of granulocyte collagenase in collagen degradation. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):565–578. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy P. L., Pangburn M. K., Burstein Y., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Evidence of homologous relationship between thermolysin and neutral protease A of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindy S., Sorsa T., Suomalainen K., Turto H. Gold sodium thiomalate activates latent human leukocyte collagenase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):23–25. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macartney H. W., Tschesche H. Lantent collagenase from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes and activation to collagenase by removal of a inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):327–332. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80282-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macartney H. W., Tschesche H. Latent and active human polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenases. Isolation, purification and characterisation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Glaichenhaus N., Gesnel M. C., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor and oncogenes induce transcription of the same cellular mRNA in rat fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1435–1440. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKerrow J. H. Human fibroblast collagenase contains an amino acid sequence homologous to the zinc-binding site of Serratia protease. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):5943–5943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Quantin B., Gesnel M. C., Millon-Collard R., Abecassis J., Breathnach R. The collagenase gene family in humans consists of at least four members. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 1;253(1):187–192. doi: 10.1042/bj2530187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Bretz U., Baggiolini M., Reynolds J. J. The latent collagenase and gelatinase of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil leucocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):517–525. doi: 10.1042/bj1920517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama K., Yoshimura K., Marumoto R., Kikuchi M., Lee I. S., Hase T., Matsubara H. Cloning and sequencing of Serratia protease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5843–5855. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppin G. J., Weiss S. J. Activation of the endogenous metalloproteinase, gelatinase, by triggered human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Murphy G., Breathnach R. Pump-1 cDNA codes for a protein with characteristics similar to those of classical collagenase family members. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 27;28(13):5327–5334. doi: 10.1021/bi00439a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Lopez R., Nicholson R., Gesnel M. C., Matrisian L. M., Breathnach R. Structure-function relationships in the collagenase family member transin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11892–11899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers A., Cartwright E., Murphy G., Reynolds J. J. Evidence that latent collagenases are enzyme-inhibitor complexes. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):303–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1630303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidler W., Niederer E., Suter F., Zuber H. The primary structure of Bacillus cereus neutral proteinase and comparison with thermolysin and Bacillus subtilis neutral proteinase. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Jul;367(7):643–657. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinucci C., Zucker S., Wieman J. M., Lysik R. M., Imhof B., Ramamurthy N., Liotta L. A., Nagase H. Purification of a gelatin-degrading type IV collagenase secreted by ras oncogene-transformed fibroblasts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Nov 2;80(17):1416–1420. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.17.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springman E. B., Angleton E. L., Birkedal-Hansen H., Van Wart H. E. Multiple modes of activation of latent human fibroblast collagenase: evidence for the role of a Cys73 active-site zinc complex in latency and a "cysteine switch" mechanism for activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):364–368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler-Stevenson W. G., Krutzsch H. C., Wacher M. P., Margulies I. M., Liotta L. A. The activation of human type IV collagenase proenzyme. Sequence identification of the major conversion product following organomercurial activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1353–1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Roswit W. T., Eisen A. Z. Human skin fibroblast procollagenase: mechanisms of activation by organomercurials and trypsin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):61–68. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Kossiakoff A. A., Chambers J. L. Mechanisms of zymogen activation. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:177–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi M., Imanaka T., Aiba S. Nucleotide sequence and promoter region for the neutral protease gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):824–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.824-831.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschesche H., Macartney H. W. A new principle of regulation of enzymic activity. Activation and regulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenase via disulfide-thiol exchange as catalysed by the glutathione cycle in a peroxidase-coupled reaction to glucose metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyree B., Seltzer J. L., Halme J., Jeffrey J. J., Eisen A. Z. The stoichiometric activation of human skin fibroblast pro-collagenase by factors present in human skin and rat uterus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 May;208(2):440–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Auld D. S. Active-site zinc ligands and activated H2O of zinc enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):220–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Auld D. S. Short and long spacer sequences and other structural features of zinc binding sites in zinc enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):138–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81805-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasantha N., Thompson L. D., Rhodes C., Banner C., Nagle J., Filpula D. Genes for alkaline protease and neutral protease from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens contain a large open reading frame between the regions coding for signal sequence and mature protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):811–819. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.811-819.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Peppin G., Ortiz X., Ragsdale C., Test S. T. Oxidative autoactivation of latent collagenase by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):747–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2982211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Mainardi C. L., Vater C. A., Harris E. D., Jr Endogenous activiation of latent collagenase by rheumatoid synovial cells. Evidence for a role of plasminogen activator. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 5;296(18):1017–1023. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705052961801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitham S. E., Murphy G., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Smith B. J., Lyons A., Harris T. J., Reynolds J. J., Herrlich P., Docherty A. J. Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2400913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Kronberger A., Eisen A. Z., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Bauer E. A., Goldberg G. I. Human skin fibroblast stromelysin: structure, glycosylation, substrate specificity, and differential expression in normal and tumorigenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6725–6729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm S. M., Collier I. E., Marmer B. L., Eisen A. Z., Grant G. A., Goldberg G. I. SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92-kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17213–17221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wize J., Abgarowicz T., Wojtecka-Lukasik E., Ksiezny S., Dancewicz A. M. Activation of human leucocyte procollagenase by rheumatoid synovial tissue culture medium. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Dec;34(6):520–523. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.6.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




