In Vitro Assessment of the Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Polyphenols Against Tau Phosphorylation, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 39519499
- PMCID: PMC11547808
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16213667
In Vitro Assessment of the Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Polyphenols Against Tau Phosphorylation, Neuroinflammation, and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, at both the systemic and the central level, are critical early events in atherosclerosis and Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Purpose: To investigate the oxidative stress-, inflammation-, and Tau-phosphorylation-lowering effects of pomegranate polyphenols (PPs) (punicalagin, ellagic acid, peel, and aril extracts).
Methods: We used flow cytometry to quantify the protein expression of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory mediators (IL-10) in THP-1 macrophages, as well as M1/M2 cell-specific marker (CD86 and CD163) expression in human microglia HMC3 cells. The IL-10 protein expression was also quantified in U373-MG human astrocytes. The effect of PPs on human amyloid beta 1-42 (Aβ1-42)-induced oxidative stress was assessed in the microglia by measuring ROS generation and lipid peroxidation, using 2',7'-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) tests, respectively. Neuronal viability and cell apoptotic response to Aβ1-42 toxicity were assayed using the MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazolyl-2)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) assay and the annexin-V-FITC apoptosis detection kit, respectively. Finally, flow cytometry analysis was also performed to evaluate the ability of PPs to modulate Aβ1-42-induced Tau-181 phosphorylation (pTau-181).
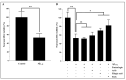
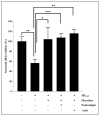
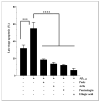
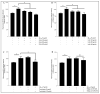
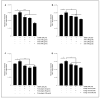
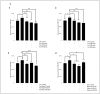
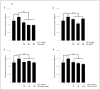
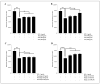
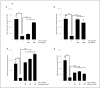
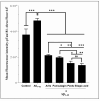
Results: Our data indicate that PPs are significantly (p < 0.05) effective in countering Aβ1-42-induced inflammation through increasing the anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10) in U373-MG astrocytes and THP1 macrophages and decreasing proinflammatory marker (IL-1β) expression in THP1 macrophages. The PPs were also significantly (p < 0.05) effective in inducing the phenotypic transition of THP-1 macrophages and microglial cells from M1 to M2 by decreasing CD86 and increasing CD163 surface receptor expression. Moreover, our treatments have a significant (p < 0.05) beneficial impact on oxidative stress, illustrated in the reduction in TBARS and ROS generation. Our treatments have significant (p < 0.05) cell viability improvement capacities and anti-apoptotic effects on human H4 neurons. Furthermore, our results suggest that Aβ1-42 significantly (p < 0.05) increases pTau-181. This effect is significantly (p < 0.05) attenuated by arils, peels, and punicalagin and drastically reduced by the ellagic acid treatment.
Conclusion: Overall, our results attribute to PPs anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and anti-Tau-pathology potential. Future studies should aim to extend our knowledge of the potential role of PPs in Aβ1-42-induced neurodegeneration, particularly concerning its association with the tauopathy involved in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-beta; ellagic acid; microglia; neuroinflammation; oxidative stress; phospho-Tau-181; pomegranate (Punica granatum L.); punicalagin.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Ton Bunt was employed by the company Izumi Biosciences, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Piper sarmentosum Roxb. confers neuroprotection on beta-amyloid (Aβ)-induced microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 May 10;217:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.025. Epub 2018 Feb 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29462698
-
Pomegranate polyphenols and extract inhibit nuclear factor of activated T-cell activity and microglial activation in vitro and in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease.J Nutr. 2013 May;143(5):597-605. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.169516. Epub 2013 Mar 6. J Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23468550 Free PMC article.
-
Vanillic acid attenuates Aβ1-42-induced oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 18;7:40753. doi: 10.1038/srep40753. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28098243 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 17;24(3):1856. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031856. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-COVID-19 Potential of Ellagic Acid and Polyphenols of Punica granatum L.Molecules. 2023 Apr 27;28(9):3772. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093772. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175181 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials


