Behavioral video coding analysis of chronic morphine administration in rats
- PMID: 39345955
- PMCID: PMC11428083
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2024.1856
Behavioral video coding analysis of chronic morphine administration in rats
Abstract
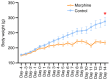
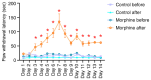
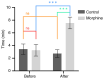
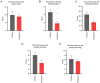
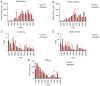
The present study assessed the behavior of morphine-addicted rats using behavioral video coding technology, to evaluate effective methods for identifying morphine addiction. Rats were divided into a control group (n=15) and a morphine addiction group (n=15). The morphine addiction model was established with a 14-day increasing dose scheme, confirmed using a conditional place preference (CPP) experiment. After successful modeling, the rats' behavior was recorded for 12 h, then coded and analyzed using Observer XT behavior analysis software. Compared with the control group, morphine-addicted rats showed increased heat pain tolerance time (P=0.039) and spent more time in the white box during the CPP experiment (P<0.001). Video coding analysis revealed significant behavioral changes in morphine-addicted rats compared to controls. In addition to being lighter, morphine-addicted rats showed decreased water intake, reduced licking of forelimbs and hind limbs, and altered sleeping posture (sleeping curled up) during the day (all P<0.05). In conclusion, chronic morphine administration in rats leads to distinctive behavioral changes, including decreased licking frequency, reduced water intake and altered sleep posture. Video coding analysis, as a safe and non-invasive method, may provide a convenient and efficient approach for studying morphine addiction in rats.
Keywords: addiction; conditional place preference experiment; morphine; rat; video coding.
Copyright: © 2024 Yin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic administration of N-acetylcysteine during the extinction period and on the reinstatement day decreased the maintenance of morphine rewarding properties in the rats.Behav Brain Res. 2021 Sep 10;413:113451. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113451. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34256079
-
Metabolic profiling of urine and blood plasma in rat models of drug addiction on the basis of morphine, methamphetamine, and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Feb;406(5):1339-54. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-7234-1. Epub 2013 Aug 4. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 23912828
-
[Wireless telemetry electrical activity of nucleus accumbens shell in morphine-induced CPP rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Jan;31(1):49-53. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26016239 Chinese.
-
[Influence of acupuncture and moxibustion on conditional position preference and prefrontal cortical ultrastructure in heroin re-addicted rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2009 Apr;34(2):97-100. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2009. PMID: 19685722 Chinese.
-
Inhibition of the reinstatement of morphine-induced place preference in rats by high-frequency stimulation of the bilateral nucleus accumbens.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(10):1939-43. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013. PMID: 23673114
References
-
- Nguyen QN, Chun SG, Chow E, Komaki R, Liao Z, Zacharia R, Szeto BK, Welsh JW, Hahn SM, Fuller CD, et al. Single-Fraction stereotactic vs conventional multifraction radiotherapy for pain relief in patients with predominantly nonspine bone metastases: A Randomized phase 2 trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:872–878. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0192. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

