Nanoscale dynamics of the cadherin-catenin complex bound to vinculin revealed by neutron spin echo spectroscopy
- PMID: 39298480
- PMCID: PMC11441495
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2408459121
Nanoscale dynamics of the cadherin-catenin complex bound to vinculin revealed by neutron spin echo spectroscopy
Abstract
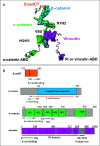
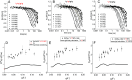
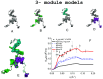
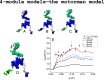
We report a neutron spin echo (NSE) study of the nanoscale dynamics of the cell-cell adhesion cadherin-catenin complex bound to vinculin. Our measurements and theoretical physics analyses of the NSE data reveal that the dynamics of full-length α-catenin, β-catenin, and vinculin residing in the cadherin-catenin-vinculin complex become activated, involving nanoscale motions in this complex. The cadherin-catenin complex is the central component of the cell-cell adherens junction (AJ) and is fundamental to embryogenesis, tissue wound healing, neuronal plasticity, cancer metastasis, and cardiovascular health and disease. A highly dynamic cadherin-catenin-vinculin complex provides the molecular dynamics basis for the flexibility and elasticity that are necessary for the AJs to function as force transducers. Our theoretical physics analysis provides a way to elucidate these driving nanoscale motions within the complex without requiring large-scale numerical simulations, providing insights not accessible by other techniques. We propose a three-way "motorman" entropic spring model for the dynamic cadherin-catenin-vinculin complex, which allows the complex to function as a flexible and elastic force transducer.
Keywords: adherens junction; mechanotransduction; nonequilibrium statistical mechanics; protein dynamics; quasielastic neutron scattering.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activated nanoscale actin-binding domain motion in the catenin-cadherin complex revealed by neutron spin echo spectroscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Mar 30;118(13):e2025012118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2025012118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33753508 Free PMC article.
-
An ensemble of flexible conformations underlies mechanotransduction by the cadherin-catenin adhesion complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 22;116(43):21545-21555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911489116. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31591245 Free PMC article.
-
An autoinhibited structure of α-catenin and its implications for vinculin recruitment to adherens junctions.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 31;288(22):15913-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.453928. Epub 2013 Apr 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23589308 Free PMC article.
-
Actin filament association at adherens junctions.J Med Invest. 2017;64(1.2):14-19. doi: 10.2152/jmi.64.14. J Med Invest. 2017. PMID: 28373611 Review.
-
Dynamics between actin and the VE-cadherin/catenin complex: novel aspects of the ARP2/3 complex in regulation of endothelial junctions.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(2):125-35. doi: 10.4161/cam.28243. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 24621569 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mezei F., “The principles of neutron spin echo” in Neutron Spin Echo: Proceedings of a Laue-Langevin Institut Workshop, Mezei F., Eds. (Springer, Heidelberg, 1980), pp. 1–26.
-
- Farago B., et al. , The IN15 upgrade. Neutron News 26, 15 (2015).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


