Cobblestone lissencephaly (Type II), clinical, and neuroimaging: A case report and literature review
- PMID: 39228958
- PMCID: PMC11367506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.07.043
Cobblestone lissencephaly (Type II), clinical, and neuroimaging: A case report and literature review
Abstract
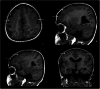
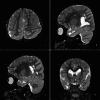
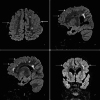
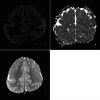
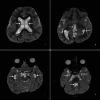
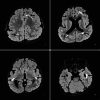
Cobblestone lissencephaly (C-LIS) (TYPE II) is a rare and severe neuronal migration disorder characterized by a smooth brain surface with overmigrated neurons and abnormal formation of cerebral convolutions or gyri during fetal development, resulting in a cobblestone appearance. C-LIS is associated with eye anomalies and muscular dystrophy. This case report presents a detailed clinical and neuroimaging analysis of a patient diagnosed with cobblestone lissencephaly (Type II). It reviews pertinent literature to enhance our understanding of this complex condition. We report a case of a 6-year-old female child with cobblestone lissencephaly (C-LIS) (Type II) severe developmental delays, hypotonia, and recurrent intractable seizures. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a characteristic cobblestone appearance on the brain surface, indicative of abnormal neuronal migration. In addition to the classic findings of Type II Cobblestone lissencephaly, the patient displayed ventriculomegaly and cerebellar hypoplasia, contributing to the overall neurological impairment observed. The literature review highlights the genetic basis of cobblestone lissencephaly, emphasizing the involvement of genes associated with glycosylation processes and basement membrane integrity. Neuroimaging findings, including MRI and computed tomography scans, are crucial for accurate diagnosis and prognostication. Early identification of cobblestone lissencephaly allows for appropriate counseling and management strategies. However, the prognosis remains guarded, and interventions primarily focus on supportive care and seizure management. This case report contributes to the knowledge of cobblestone lissencephaly, shedding light on the clinical spectrum and neuroimaging features associated with this rare disorder. To clarify the underlying genetic mechanisms and possible therapeutic pathways for better patient outcomes, more investigation is necessary.
Keywords: Cerebellar hypoplasia; Cobblestone lissencephaly; Magnetic resonance imaging; Muscular dystrophies; Neurons.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of University of Washington.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Genetic and clinical aspects of lissencephaly].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2007 May;163(5):533-47. doi: 10.1016/s0035-3787(07)90460-9. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2007. PMID: 17571022 Review. French.
-
Cobblestone lissencephaly: neuropathological subtypes and correlations with genes of dystroglycanopathies.Brain. 2012 Feb;135(Pt 2):469-82. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr357. Epub 2012 Feb 9. Brain. 2012. PMID: 22323514
-
[Analysis of the clinical manifestations and magnetic resonance imaging features of 11 patients with lissencephaly].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011 Mar;31(3):482-6. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21421488 Chinese.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis of Lissencephaly Type 2 using Three-dimensional Ultrasound and Fetal MRI: Case Report and Review of the Literature.Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2016 Apr;38(4):201-6. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1582126. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2016. PMID: 27088705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GPR56-related bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria: further evidence for an overlap with the cobblestone complex.Brain. 2010 Nov;133(11):3194-209. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq259. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Brain. 2010. PMID: 20929962
Cited by
-
β-PIX-d, a Member of the ARHGEF7 Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Family, Activates Rac1 and Induces Neuritogenesis in Primary Cortical Neurons.Exp Neurobiol. 2024 Oct 31;33(5):215-224. doi: 10.5607/en24026. Exp Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39568178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dobyns WB. The clinical patterns and molecular genetics of lissencephaly and subcortical band heterotopia. Epilepsia. 2010;51(s1):5–9. - PubMed
-
- Ross ME, Swanson K, Dobyns WB. Lissencephaly with cerebellar hypoplasia (LCH): a heterogeneous group of cortical malformations. Neuropediatrics. 2001;32(5):256–263. - PubMed
-
- Verloes A, Elmaleh M, Gonzales M, Laquerrière A, Gressens P. Lissencéphalies : aspects cliniques et génétiques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2007;163(5):533–547. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


