Screening of gastric cancer diagnostic biomarkers in the homologous recombination signaling pathway and assessment of their clinical and radiomic correlations
- PMID: 39206620
- PMCID: PMC11358765
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70153
Screening of gastric cancer diagnostic biomarkers in the homologous recombination signaling pathway and assessment of their clinical and radiomic correlations
Abstract
Background: Homologous recombination plays a vital role in the occurrence and drug resistance of gastric cancer. This study aimed to screen new gastric cancer diagnostic biomarkers in the homologous recombination pathway and then used radiomic features to construct a prediction model of biomarker expression to guide the selection of chemotherapy regimens.
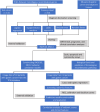
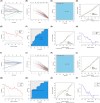
Methods: Gastric cancer transcriptome data were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. Machine learning methods were used to screen for diagnostic biomarkers of gastric cancer and validate them experimentally. Computed Tomography image data of gastric cancer patients and corresponding clinical data were downloaded from The Cancer Imaging Archive and our imaging centre, and then the Computed Tomography images were subjected to feature extraction, and biomarker expression prediction models were constructed to analyze the correlation between the biomarker radiomics scores and clinicopathological features.
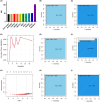
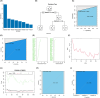
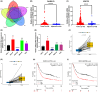
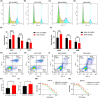
Results: We screened RAD51D and XRCC2 in the homologous recombination pathway as biomarkers for gastric cancer diagnosis by machine learning, and the expression of RAD51D and XRCC2 was significantly positively correlated with pathological T stage, N stage, and TNM stage. Homologous recombination pathway blockade inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation, promotes apoptosis, and reduces the sensitivity of gastric cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs. Our predictive RAD51D and XRCC2 expression models were constructed using radiomics features, and all the models had high accuracy. In the external validation cohort, the predictive models still had decent accuracy. Moreover, the radiomics scores of RAD51D and XRCC2 were also significantly positively correlated with the pathologic T, N, and TNM stages.
Conclusions: The gastric cancer diagnostic biomarkers RAD51D and XRCC2 that we screened can, to a certain extent, reflect the expression status of genes through radiomic characteristics, which is of certain significance in guiding the selection of chemotherapy regimens for gastric cancer patients.
Keywords: RAD51D; XRCC2; gastric cancer; homologous recombination; radiomics.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Validation of a Computed Tomography-Based Model for Noninvasive Prediction of the T Stage in Gastric Cancer: Multicenter Retrospective Study.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Oct 9;26:e56851. doi: 10.2196/56851. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39382960 Free PMC article.
-
RAD51D splice variants and cancer-associated mutations reveal XRCC2 interaction to be critical for homologous recombination.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Apr;76:99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 30836272 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics signature of computed tomography imaging for prediction of survival and chemotherapeutic benefits in gastric cancer.EBioMedicine. 2018 Oct;36:171-182. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 14. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 30224313 Free PMC article.
-
Landscape of homologous recombination deficiency in gastric cancer and clinical implications for first-line chemotherapy.Gastric Cancer. 2024 Nov;27(6):1273-1286. doi: 10.1007/s10120-024-01542-1. Epub 2024 Aug 7. Gastric Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39110344
-
Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics predicts preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis to support surgical decisions and is associated with tumor microenvironment in invasive breast cancer: A machine learning, multicenter study.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jul;69:103460. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103460. Epub 2021 Jul 4. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34233259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229‐263. - PubMed
-
- Wang YX, Shao QS, Yang Q, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of early gastric cancer after gastrectomy. Chin Med J. 2012;125:770‐774. - PubMed
-
- Molinari C, Tedaldi G, Rebuzzi F, et al. Early gastric cancer: identification of molecular markers able to distinguish submucosa‐penetrating lesions with different prognosis. Gastric Cancer. 2021;24:392‐401. - PubMed
-
- Shitara K, Yatabe Y, Matsuo K, et al. Prognosis of patients with advanced gastric cancer by HER2 status and trastuzumab treatment. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16:261‐267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


