Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Insight into Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Benefits of Chinese Herbal Medicines
- PMID: 39051370
- PMCID: PMC11270433
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines11070014
Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Insight into Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Benefits of Chinese Herbal Medicines
Abstract
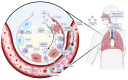
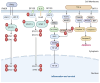
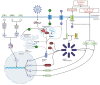
Cytokine storm (CS) is the main driver of SARS-CoV-2-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in severe coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19). The pathological mechanisms of CS are quite complex and involve multiple critical molecular targets that turn self-limited and mild COVID-19 into a severe and life-threatening concern. At present, vaccines are strongly recommended as safe and effective treatments for preventing serious illness or death from COVID-19. However, effective treatment options are still lacking for people who are at the most risk or hospitalized with severe disease. Chinese herbal medicines have been shown to improve the clinical outcomes of mild to severe COVID-19 as an adjunct therapy, particular preventing the development of mild to severe ARDS. This review illustrates in detail the pathogenesis of CS-involved ARDS and its associated key molecular targets, cytokines and signalling pathways. The therapeutic targets were identified particularly in relation to the turning points of the development of COVID-19, from mild symptoms to severe ARDS. Preclinical and clinical studies were reviewed for the effects of Chinese herbal medicines together with conventional therapies in reducing ARDS symptoms and addressing critical therapeutic targets associated with CS. Multiple herbal formulations, herbal extracts and single bioactive phytochemicals with or without conventional therapies demonstrated strong anti-CS effects through multiple mechanisms. However, evidence from larger, well-designed clinical trials is lacking and their detailed mechanisms of action are yet to be well elucidated. More research is warranted to further evaluate the therapeutic value of Chinese herbal medicine for CS in COVID-19-induced ARDS.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute respiratory distress syndrome; curcumin; cytokine storm; integrative Chinese medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of phytochemical compounds of Fagopyrum dibotrys and their targets by metabolomics, network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Heliyon. 2023 Mar;9(3):e14029. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14029. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36911881 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine: Fighting SARS-CoV-2 infection on all fronts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113869. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113869. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33485973 Free PMC article.
-
[Treatment strategy and thought on classical herbal formulae for coronavirus disease 2019].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Jan;46(2):494-503. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200603.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33645139 Chinese.
-
Cytokine Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Elderly.J Inflamm Res. 2020 Oct 20;13:737-747. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S276091. eCollection 2020. J Inflamm Res. 2020. PMID: 33116752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2.Clin Chim Acta. 2020 Oct;509:280-287. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.017. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32531256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kirby R. Sepsis: An important treatable illness, but susceptible to hype. Trends Urol. Men’s Health. 2021;12:21–23a. doi: 10.1002/tre.794. - DOI
-
- Liang Y., Wang M.-L., Chien C.-S., Yarmishyn A.A., Yang Y.-P., Lai W.-Y., Luo Y.-H., Lin Y.-T., Chen Y.-J., Chang P.-C. Highlight of immune pathogenic response and hematopathologic effect in SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:1022. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


