Mussel-Derived and Bioclickable Peptide Mimic for Enhanced Interfacial Osseointegration via Synergistic Immunomodulation and Vascularized Bone Regeneration
- PMID: 38922775
- PMCID: PMC11348244
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202401833
Mussel-Derived and Bioclickable Peptide Mimic for Enhanced Interfacial Osseointegration via Synergistic Immunomodulation and Vascularized Bone Regeneration
Abstract
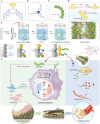
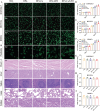
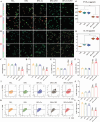
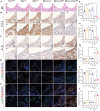
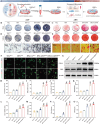
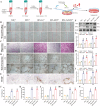
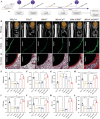
Inadequate osseointegration at the interface is a key factor in orthopedic implant failure. Mechanistically, traditional orthopedic implant interfaces fail to precisely match natural bone regeneration processes in vivo. In this study, a novel biomimetic coating on titanium substrates (DPA-Co/GFO) through a mussel adhesion-mediated ion coordination and molecular clicking strategy is engineered. In vivo and in vitro results confirm that the coating exhibits excellent biocompatibility and effectively promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Crucially, the biomimetic coating targets the integrin α2β1 receptor to promote M2 macrophage polarization and achieves a synergistic effect between immunomodulation and vascularized bone regeneration, thereby maximizing osseointegration at the interface. Mechanical push-out tests reveal that the pull-out strength in the DPA-Co/GFO group is markedly greater than that in the control group (79.04 ± 3.20 N vs 31.47 ± 1.87 N, P < 0.01) and even surpasses that in the sham group (79.04 ± 3.20 N vs 63.09 ± 8.52 N, P < 0.01). In summary, the novel biomimetic coating developed in this study precisely matches the natural process of bone regeneration in vivo, enhancing interface-related osseointegration and showing considerable potential for clinical translation and applications.
Keywords: bone regeneration; immunomodulatory; mussel adhesion; orthopedic implant; tissue adaptation.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biomimetic HA-GO implant coating for enhanced osseointegration via macrophage M2 polarization-induced osteo-immunomodulation.J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2024 Jan-Dec;22:22808000241266665. doi: 10.1177/22808000241266665. J Appl Biomater Funct Mater. 2024. PMID: 39129373
-
Biomolecular surface coating to enhance orthopaedic tissue healing and integration.Biomaterials. 2007 Jul;28(21):3228-35. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.04.003. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Biomaterials. 2007. PMID: 17448533 Free PMC article.
-
Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine Coating: A General Strategy To Enhance Osteogenic Differentiation and Osseointegration for Diverse Implants.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019 Feb 20;11(7):7615-7625. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b21558. Epub 2019 Feb 8. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019. PMID: 30689334
-
The Effect of Antibacterial-Osteogenic Surface Modification on the Osseointegration of Titanium Implants: A Static and Dynamic Strategy.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024 Jul 8;10(7):4093-4113. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01756. Epub 2024 Jun 3. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024. PMID: 38829538 Review.
-
Biomaterial strategies for engineering implants for enhanced osseointegration and bone repair.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Nov 1;94:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.03.013. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 25861724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferguson R. J., Palmer A. J., Taylor A., Porter M. L., Malchau H., Glyn‐Jones S., Lancet 2018, 392, 1662. - PubMed
-
- Corcuera‐Flores J. R., Alonso‐Domínguez A. M., Serrera‐Figallo M., Torres‐Lagares D., Castellanos‐Cosano L., Machuca‐Portillo G., J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 14. - PubMed
-
- Takeshita F., Murai K., Iyama S., Ayukawa Y., Suetsugu T., J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 314. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

