Too little or too much nocturnal movements in Parkinson's disease: A practical guide to managing the unseen
- PMID: 38845753
- PMCID: PMC11153921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2024.100258
Too little or too much nocturnal movements in Parkinson's disease: A practical guide to managing the unseen
Abstract
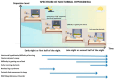
Nocturnal and sleep-related motor disorders in people with Parkinson's disease (PD) have a wide spectrum of manifestations and present a complex clinical picture. Problems can arise due to impaired movement ability (hypokinesias), e.g. nocturnal hypokinesia or early-morning akinesia, or to excessive movement (hyperkinesias), e.g. end-of-the-day dyskinesia, parasomnias, periodic limb movement during sleep and restless legs syndrome. These disorders can have a significant negative impact on the sleep, daytime functional ability, and overall quality of life of individuals with PD and their carers. The debilitating motor issues are often accompanied by a combination of non-motor symptoms, including pain and cramping, which add to the overall burden. Importantly, nocturnal motor disorders encompass a broader timeline than just the period of sleep, often starting in the evening, as well as occurring throughout the night and on awakening, and are not just limited to problems of insomnia or sleep fragmentation. Diagnosis can be challenging as, in many cases, the 'gold standard' assessment method is video polysomnography, which may not be available in all settings. Various validated questionnaires are available to support evaluation, and alternative approaches, using wearable sensors and digital technology, are now being developed to facilitate early diagnosis and monitoring. This review sets out the parameters of what can be considered normal nocturnal movement and describes the clinical manifestations, usual clinical or objective assessment methods, and evidence for optimal management strategies for the common nocturnal motor disorders that neurologists will encounter in people with PD in their clinical practice.
Keywords: Evening dyskinesia; Nocturnal hypokinesia; Nocturnal movement disorders; Parkinson’s disease; Periodic limb movement disorders; Sleep-related movement disorders.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Shedding Light on Nocturnal Movements in Parkinson's Disease: Evidence from Wearable Technologies.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Sep 10;20(18):5171. doi: 10.3390/s20185171. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32927816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How well do Parkinson's disease patients turn in bed? Quantitative analysis of nocturnal hypokinesia using multisite wearable inertial sensors.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Feb;23:10-6. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016. PMID: 26683743
-
Sleep in Parkinson's disease.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Jan;45(1):121-128. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0448-y. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31234200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time for a strategy in night-time dopaminergic therapy? An objective sensor-based analysis of nocturnal hypokinesia and sleeping positions in Parkinson's disease.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Feb 15;373:244-248. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2016.12.045. Epub 2016 Dec 28. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28131197
-
Getting a good night sleep? The importance of recognizing and treating nocturnal hypokinesia in Parkinson's disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018 May;50:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.01.008. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018. PMID: 29336905 Review.
References
-
- Bhidayasiri R., Sringean J., Trenkwalder C. Mastering nocturnal jigsaws in Parkinson's disease: a dusk-to-dawn review of night-time symptoms. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2020;127:763–777. - PubMed
-
- Klingelhoefer L., Sokolov E., Chaudhuri K.R. Therapeutic options for nocturnal problems in Parkinson's disease and atypical parkinsonian disorders. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 2014;121(Suppl 1):S25–S31. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya A., Lenka A., Stezin A., Kamble N., Pal P.K. Overview of sleep disturbances and their management in Parkinson plus disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020;415 - PubMed
-
- Mao C.J., Yang Y.P., Chen J.P., Wang F., Chen J., Zhang J.R., Zhang H.J., Zhuang S., Xiong Y.T., Gu C.C., Yuan W., Huang J.Y., Fay A., Zhong C.K., Liu C.F. Poor nighttime sleep is positively associated with dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018;48:68–73. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


