Update of the clinical guideline for hypertension diagnosis and treatment in Iran
- PMID: 38822442
- PMCID: PMC11143619
- DOI: 10.1186/s40885-024-00269-6
Update of the clinical guideline for hypertension diagnosis and treatment in Iran
Abstract
Background: This article introduces the updated version of the Iranian guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension in adults. The initial version of the national guideline was developed in 2011 and updated in 2014. Among the reasons necessitating the update of this guideline were the passage of time, the incompleteness of the scopes, the limitation of the target group, and more important is the request of the ministry of health in Iran.
Method: The members of the guideline updating group, after reviewing the original version and the new evidence, prepared 10 clinical questions regarding hypertension, and based on the evidence found from the latest scientific documents, provided recommendations or suggestions to answer these questions.
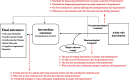
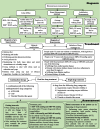
Result: According to the updated guideline, the threshold for office prehypertension diagnosis should be considered the systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 130-139 mmHg and/or the diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 80-89 mmHg, and in adults under 75 years of age without comorbidities, the threshold for office hypertension diagnosis should be SBP ≥ 140 mmHg and or DBP ≥ 90 mmHg. The goal of treatment in adults who lack comorbidities and risk factors is SBP < 140 mmHg and DBP < 90 mmHg. The first-line treatment recommended in people with prehypertension is lifestyle modification, while for those with hypertension, pharmacotherapy along with lifestyle modification. The threshold to start drug therapy is determined at SBP ≥ 140 mmHg and or DBP ≥ 90 mmHg, and the first-line treatment is considered a drug or a combined pill of antihypertensive drugs, including ACEIs, ARBs, thiazide and thiazide-like agents, or CCBs. At the beginning of the pharmacotherapy, the Guideline Updating Group members suggested studying serum electrolytes, creatinine, lipid profile, fasting sugar, urinalysis, and an electrocardiogram. Regarding the visit intervals, monthly visits are suggested at the beginning of the treatment or in case of any change in the type or dosage of the drug until achieving the treatment goal, followed by every 3-to-6-month visits. Moreover, to reduce further complications, it was suggested that healthcare unit employees use telehealth strategies.
Conclusions: In this guideline, specific recommendations and suggestions have been presented for adults and subgroups like older people or those with cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, and COVID-19.
Keywords: Blood Pressure; Clinical practice Guideline; Diagnosis; Hypertension; Treatment; Updating.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The 2010 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 2 - therapy.Can J Cardiol. 2010 May;26(5):249-58. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(10)70379-2. Can J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20485689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for deliberately altering blood pressure in acute stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Oct 28;2014(10):CD000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000039.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25353321 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 2009 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: Part 2--therapy.Can J Cardiol. 2009 May;25(5):287-98. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(09)70492-1. Can J Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19417859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 2008 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for the management of hypertension: part 2 - therapy.Can J Cardiol. 2008 Jun;24(6):465-75. doi: 10.1016/s0828-282x(08)70620-2. Can J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18548143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening for Hypertension in Children and Adolescents: Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force [Internet].Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Nov. Report No.: 20-05261-EF-1. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2020 Nov. Report No.: 20-05261-EF-1. PMID: 33284560 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Steinberg E, Greenfield S, Wolman DM, Mancher M, Graham R. Clinical practice guidelines we can trust. Washington, D.C: National Academies Press; 2011. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources