Mapping the Neural Basis of Neuroeconomics with Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Narrative Literature Review
- PMID: 38790489
- PMCID: PMC11120557
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14050511
Mapping the Neural Basis of Neuroeconomics with Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
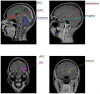
Neuroeconomics merges neuroscience, economics, and psychology to investigate the neural basis of decision making. Decision making involves assessing outcomes with subjective value, shaped by emotions and experiences, which are crucial in economic decisions. Functional MRI (fMRI) reveals key areas of the brain, including the ventro-medial prefrontal cortex, that are involved in subjective value representation. Collaborative interdisciplinary efforts are essential for advancing the field of neuroeconomics, with implications for clinical interventions and policy design. This review explores subjective value in neuroeconomics, highlighting brain regions identified through fMRI studies.
Keywords: brain; fMRI; neuroeconomics; subjective value.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The neuroeconomics of alcohol demand: an initial investigation of the neural correlates of alcohol cost-benefit decision making in heavy drinking men.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Jul;39(8):1988-95. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.47. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24584331 Free PMC article.
-
The neural basis of economic decision-making in the Ultimatum Game.Science. 2003 Jun 13;300(5626):1755-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1082976. Science. 2003. PMID: 12805551
-
The neural bases underlying social risk perception in purchase decisions.Neuroimage. 2014 May 1;91:120-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.01.036. Epub 2014 Jan 26. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24473098
-
Molecular neuroimaging of emotional decision-making.Neurosci Res. 2013 Apr;75(4):269-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2013.01.011. Epub 2013 Feb 15. Neurosci Res. 2013. PMID: 23419862 Review.
-
Do Political and Economic Choices Rely on Common Neural Substrates? A Systematic Review of the Emerging Neuropolitics Literature.Front Psychol. 2016 Feb 25;7:264. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00264. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 26941703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Camerer C.F. Neuroeconomics. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2009. Behavioral Game Theory and the Neural Basis of Strategic Choice; pp. 193–206.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


