A meta-analysis of MRI radiomics-based diagnosis for BI-RADS 4 breast lesions
- PMID: 38748373
- PMCID: PMC11096203
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-024-05697-3
A meta-analysis of MRI radiomics-based diagnosis for BI-RADS 4 breast lesions
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to conduct a systematic evaluation of the diagnostic efficacy of Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4 benign and malignant breast lesions using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) radiomics.
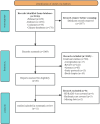
Methods: A systematic search identified relevant studies. Eligible studies were screened, assessed for quality, and analyzed for diagnostic accuracy. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses explored heterogeneity, while publication bias, clinical relevance and threshold effect were evaluated.
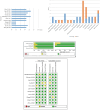
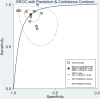
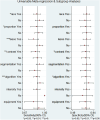
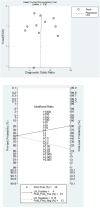
Results: This study analyzed a total of 11 studies involving 1,915 lesions in 1,893 patients with BI-RADS 4 classification. The results showed that the combined sensitivity and specificity of MRI radiomics for diagnosing BI-RADS 4 lesions were 0.88 (95% CI 0.83-0.92) and 0.79 (95% CI 0.72-0.84). The positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative likelihood ratio (NLR), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were 4.2 (95% CI 3.1-5.7), 0.15 (95% CI: 0.10-0.22), and 29.0 (95% CI 15-55). The summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) analysis yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.90 (95% CI 0.87-0.92), indicating good diagnostic performance. The study found no significant threshold effect or publication bias, and heterogeneity among studies was attributed to various factors like feature selection algorithm, radiomics algorithms, etc. Overall, the results suggest that MRI radiomics has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of BI-RADS 4 lesions and enhance patient outcomes.
Conclusion: MRI-based radiomics is highly effective in diagnosing BI-RADS 4 benign and malignant breast lesions, enabling improving patients' medical outcomes and quality of life.
Keywords: BI-RADS 4; Breast cancer; Breast lesions; MRI; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Photoacoustic Imaging Radiomics to Identify Breast Cancer in BI-RADS 4 or 5 Lesions.Clin Breast Cancer. 2024 Jul;24(5):e379-e388.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2024.02.017. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Clin Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38548517
-
High-temporal resolution DCE-MRI improves assessment of intra- and peri-breast lesions categorized as BI-RADS 4.BMC Med Imaging. 2023 Apr 19;23(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12880-023-01015-4. BMC Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37076817 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Predicting Breast Cancer in Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Ultrasound Category 4 or 5 Lesions: A Nomogram Combining Radiomics and BI-RADS.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 15;9(1):11921. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48488-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31417138 Free PMC article.
-
Breast lesions classified as probably benign (BI-RADS 3) on magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2018 May;28(5):1919-1928. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5127-y. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29168006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diagnostic performance of ultrafast MRI to differentiate benign from malignant breast lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Oct;34(10):6285-6295. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10690-y. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38512492 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


