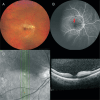
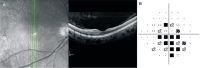
Unilateral branch retinal artery occlusion in association with COVID-19: a case report
- PMID: 38638251
- PMCID: PMC10988083
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2024.04.25
Unilateral branch retinal artery occlusion in association with COVID-19: a case report
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Inomata T, reports non-financial support from Lion Corporation and Sony Network Communications Inc., grants from Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc., Kandenko, Co., Ltd., Yuimedi, Inc., Rohto Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kobayashi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kandenko Co., Ltd., and Fukoku Co., Ltd., personal fees from Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., InnoJin, Inc., and Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., outside the submitted work; Okumura Y and Nagino K, report personal fees from InnoJin, Inc., outside the submitted work; Nakao S, reports grants from Kowa Company. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Alcon Japan, Ltd., Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Machida Endoscope Co., Ltd., Wakamoto Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd., Senju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Hoya Corporation, and Novartis Pharma K.K., outside the submitted work; Hirosawa K, None; Sung J, None; Morooka Y, None; Huang T, None; Akasaki Y, None; Omori K, None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of underdiagnosed concurrent branch retinal artery occlusion in a patient with central retinal vein occlusion using spectral domain optical coherence tomography.BMC Ophthalmol. 2014 Jul 12;14:91. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-14-91. BMC Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25015220 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone implant (ozurdex) in a case with unilateral simultaneous central retinal vein and branch retinal artery occlusion.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2015 Feb 23;6(1):76-81. doi: 10.1159/000377668. eCollection 2015 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25873891 Free PMC article.
-
Unilateral branch retinal arterial occlusion following administration of bevacizumab for branch retinal vein occlusion.Int Ophthalmol. 2013 Oct;33(5):549-52. doi: 10.1007/s10792-012-9679-1. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Int Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23179231
-
BRANCH RETINAL ARTERY OCCLUSION ASSOCIATED WITH PARACENTRAL ACUTE MIDDLE MACULOPATHY IN A PATIENT WITH LIVEDO RETICULARIS.Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2017 Fall;11(4):356-360. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000370. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2017. PMID: 27490977 Review.
-
Transient branch retinal artery occlusion in a 15-year-old girl and review of the literature.Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015 Sep;159(3):508-11. doi: 10.5507/bp.2015.031. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015. PMID: 26160228 Review.
References
-
- Biousse V, Nahab F, Newman NJ. Management of acute retinal ischemia: follow the guidelines! Ophthalmology. 2018;125(10):1597–1607. - PubMed
-
- Lang GE, Spraul CW. Risk factors for retinal occlusive diseases. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1997;211(4):217–226. - PubMed
-
- Feltgen N, Pielen A. Retinal artery occlusion. Ophthalmologe. 2017;114(2):177–190. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

