Large language models could change the future of behavioral healthcare: a proposal for responsible development and evaluation
- PMID: 38609507
- PMCID: PMC10987499
- DOI: 10.1038/s44184-024-00056-z
Large language models could change the future of behavioral healthcare: a proposal for responsible development and evaluation
Abstract
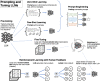
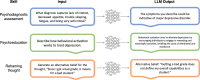
Large language models (LLMs) such as Open AI's GPT-4 (which power ChatGPT) and Google's Gemini, built on artificial intelligence, hold immense potential to support, augment, or even eventually automate psychotherapy. Enthusiasm about such applications is mounting in the field as well as industry. These developments promise to address insufficient mental healthcare system capacity and scale individual access to personalized treatments. However, clinical psychology is an uncommonly high stakes application domain for AI systems, as responsible and evidence-based therapy requires nuanced expertise. This paper provides a roadmap for the ambitious yet responsible application of clinical LLMs in psychotherapy. First, a technical overview of clinical LLMs is presented. Second, the stages of integration of LLMs into psychotherapy are discussed while highlighting parallels to the development of autonomous vehicle technology. Third, potential applications of LLMs in clinical care, training, and research are discussed, highlighting areas of risk given the complex nature of psychotherapy. Fourth, recommendations for the responsible development and evaluation of clinical LLMs are provided, which include centering clinical science, involving robust interdisciplinary collaboration, and attending to issues like assessment, risk detection, transparency, and bias. Lastly, a vision is outlined for how LLMs might enable a new generation of studies of evidence-based interventions at scale, and how these studies may challenge assumptions about psychotherapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: receiving consultation fees from Jimini Health (E.C.S., L.H.U., H.A.S., and J.C.E.).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current safeguards, risk mitigation, and transparency measures of large language models against the generation of health disinformation: repeated cross sectional analysis.BMJ. 2024 Mar 20;384:e078538. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-078538. BMJ. 2024. PMID: 38508682 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing prognosis in depression: comparing perspectives of AI models, mental health professionals and the general public.Fam Med Community Health. 2024 Jan 9;12(Suppl 1):e002583. doi: 10.1136/fmch-2023-002583. Fam Med Community Health. 2024. PMID: 38199604 Free PMC article.
-
The role of large language models in medical image processing: a narrative review.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):1108-1121. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-892. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38223123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large language models: a primer and gastroenterology applications.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 22;17:17562848241227031. doi: 10.1177/17562848241227031. eCollection 2024. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38390029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Alignment of Large Language Models With Human Values for Mental Health Integration: Cross-Sectional Study Using Schwartz's Theory of Basic Values.JMIR Ment Health. 2024 Apr 9;11:e55988. doi: 10.2196/55988. JMIR Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 38593424 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
"It happened to be the perfect thing": experiences of generative AI chatbots for mental health.Npj Ment Health Res. 2024 Oct 27;3(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s44184-024-00097-4. Npj Ment Health Res. 2024. PMID: 39465310 Free PMC article.
-
Large Language Models for Mental Health Applications: Systematic Review.JMIR Ment Health. 2024 Oct 18;11:e57400. doi: 10.2196/57400. JMIR Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 39423368 Free PMC article.
-
Describing the Framework for AI Tool Assessment in Mental Health and Applying It to a Generative AI Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Platform: Tutorial.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Oct 18;8:e62963. doi: 10.2196/62963. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 39423001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Impact of ChatGPT in Dermatology: A Comprehensive Rapid Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 3;13(19):5909. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195909. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Cognitive Behavioral Therapy-Based Generative AI Tool (Socrates 2.0) to Facilitate Socratic Dialogue: Protocol for a Mixed Methods Feasibility Study.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Oct 10;13:e58195. doi: 10.2196/58195. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39388255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bubeck, S. et al. Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4. Preprint at http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.12712 (2023).
-
- Broderick, R. People are using AI for therapy, whether the tech is ready for it or not. Fast Company (2023).
-
- Weizenbaum J. ELIZA—a computer program for the study of natural language communication between man and machine. Commun. ACM. 1966;9:36–45. doi: 10.1145/365153.365168. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

