Pathogenic variants in human DNA damage repair genes mostly arose in recent human history
- PMID: 38575974
- PMCID: PMC10993466
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-12160-6
Pathogenic variants in human DNA damage repair genes mostly arose in recent human history
Abstract
Background: Genome stability is maintained by the DNA damage repair (DDR) system composed of multiple DNA repair pathways of hundreds of genes. Germline pathogenic variation (PV) in DDR genes damages function of the affected DDR genes, leading to genome instability and high risk of diseases, in particular, cancer. Knowing evolutionary origin of the PVs in human DDR genes is essential to understand the etiology of human diseases. However, answer to the issue remains largely elusive. In this study, we analyzed evolutionary origin for the PVs in human DDR genes.
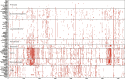
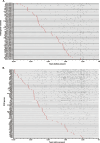
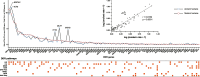
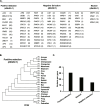
Methods: We identified 169 DDR genes by referring to various databases and identified PVs in the DDR genes of modern humans from ClinVar database. We performed a phylogenetic analysis to analyze the conservation of human DDR PVs in 100 vertebrates through cross-species genomic data comparison using the phyloFit program of the PHAST package and visualized the results using the GraphPad Prism software and the ggplot module. We identified DDR PVs from over 5000 ancient humans developed a database to host the DDR PVs ( https://genemutation.fhs.um.edu.mo/dbDDR-AncientHumans ). Using the PV data, we performed a molecular archeological analysis to compare the DDR PVs between modern humans and ancient humans. We analyzed evolution selection of DDR genes across 20 vertebrates using the CodeML in PAML for phylogenetic analysis.
Results: Our phylogenic analysis ruled out cross-species conservation as the origin of human DDR PVs. Our archeological approach identified rich DDR PVs shared between modern and ancient humans, which were mostly dated within the last 5000 years. We also observed similar pattern of quantitative PV distribution between modern and ancient humans. We further detected a set of ATM, BRCA2 and CHEK2 PVs shared between human and Neanderthals.
Conclusions: Our study reveals that human DDR PVs mostly arose in recent human history. We propose that human high cancer risk caused by DDR PVs can be a by-product of human evolution.
Keywords: Archaeological; DNA damage repair; Evolutionary origin; Pathogenic variants; Phylogenetic.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pathogenic variants in human DNA damage repair genes mostly arose after the latest human out-of-Africa migration.Front Genet. 2024 Jun 14;15:1408952. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1408952. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38948361 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary origin of germline pathogenic variants in human DNA mismatch repair genes.Hum Genomics. 2024 Jan 29;18(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00573-0. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38287404 Free PMC article.
-
Using Portuguese BRCA pathogenic variation as a model to study the impact of human admixture on human health.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 27;25(1):416. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10311-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38671360 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage response--a double-edged sword in cancer prevention and cancer therapy.Cancer Lett. 2015 Mar 1;358(1):8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.12.038. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25528631 Review.
-
Beyond BRCA: The Emerging Significance of DNA Damage Response and Personalized Treatment in Pancreatic and Prostate Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 24;23(9):4709. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094709. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Deciphering of the Potential Impact of Variants of Uncertain Significance in Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Syndromes.Cells. 2024 Aug 6;13(16):1314. doi: 10.3390/cells13161314. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39195204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive classification of TP53 somatic missense variants based on their impact on p53 structural stability.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jul 25;25(5):bbae400. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae400. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39140857 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic variants in human DNA damage repair genes mostly arose after the latest human out-of-Africa migration.Front Genet. 2024 Jun 14;15:1408952. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1408952. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38948361 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Origin of Human PALB2 Germline Pathogenic Variants.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 12;24(14):11343. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411343. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511102 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


