Investigating the Nexus of NLRP3 Inflammasomes and COVID-19 Pathogenesis: Unraveling Molecular Triggers and Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 38399989
- PMCID: PMC10892947
- DOI: 10.3390/v16020213
Investigating the Nexus of NLRP3 Inflammasomes and COVID-19 Pathogenesis: Unraveling Molecular Triggers and Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
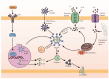
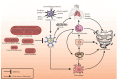
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) global pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has been marked by severe cases demonstrating a "cytokine storm", an upsurge of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream. NLRP3 inflammasomes, integral to the innate immune system, are speculated to be activated by SARS-CoV-2 within host cells. This review investigates the potential correlation between NLRP3 inflammasomes and COVID-19, exploring the cellular and molecular mechanisms through which SARS-CoV-2 triggers their activation. Furthermore, promising strategies targeting NLRP3 inflammasomes are proposed to mitigate the excessive inflammatory response provoked by SARS-CoV-2 infection. By synthesizing existing studies, this paper offers insights into NLRP3 as a therapeutic target, elucidating the interplay between COVID-19 and its pathophysiology. It serves as a valuable reference for future clinical approaches in addressing COVID-19 by targeting NLRP3, thus providing potential avenues for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: COVID-19; NLRP3 inflammasome; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine storm; therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Da Hu, as an employee of Sinopharm Animal Health Corporation Ltd, participated in the early writing work, and Da Hu stated that there was no business relationship or economic interest with the company that might constitute a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The NLRP3 inflammasome and COVID-19: Activation, pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Oct;61:2-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.06.002. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 34183243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in diabetes and COVID-19 role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis and treatment of COVID-19 and diabetes NLRP3 inflammasome in diabetes and COVID-19 intervention.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 5;14:1203389. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1203389. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37868953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection and development of their corresponding inhibitors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jun 9;13:1218039. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1218039. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37360532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Severe COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 23;11:1518. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01518. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32655582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting autophagy regulation in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated lung inflammation in COVID-19.Clin Immunol. 2022 Nov;244:109093. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109093. Epub 2022 Aug 6. Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35944881 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Pathophysiology of Long COVID: The Central Role of Low-Grade Inflammation and Multisystem Involvement.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 9;25(12):6389. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126389. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous


