Brexpiprazole in patients with schizophrenia with or without substance use disorder: an observational study
- PMID: 38111619
- PMCID: PMC10725927
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1321233
Brexpiprazole in patients with schizophrenia with or without substance use disorder: an observational study
Abstract
Background: Partial dopamine D2 receptor agonists are used for psychotic symptoms in adults with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Recently, interest surged for partial dopamine D2 receptor agonists in substance use disorders (SUDs). Since it is believed that SUDs decrease the efficacy of pharmacotherapy of underlying psychiatric disorders, we tested the efficacy of the partial D2 agonist brexpiprazole in patients with schizophrenia who were either comorbid with a SUD (SUD group) or not comorbid (non-SUD) to assess treatment response and the effect of brexpiprazole on substance craving in SUD.
Methods: We included patients with DSM-5/DSM-5-TR schizophrenia (using SCID-5-CV) aged 18-66 years with either comorbid SUD or non-SUD to treat with brexpiprazole 4 mg/day for 6 months during February-October 2022. Patients were assessed with the Clinical Global Impressions-Severity (CGI-S) scale, the 24-item Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), and the Positive And Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) at baseline, weekly for the first 2 months and monthly for the next four. Furthermore, we assessed substance craving in SUD with a visual analog scale for craving (VAScrav) at the same timepoints.
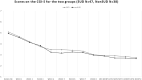
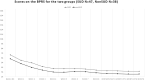
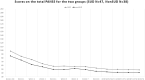
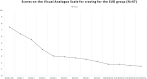
Results: The total sample was 86 (85 analysable) 18- to 64-year-old (mean 39.32 ± 14.09) patients with schizophrenia [51 men (59.3%) and 35 women (40.7%)], of whom 48 SUD (55.8%) (37 men and 11 women) and 38 non-SUD (44.2%) (14 men and 24 women). No serious or persistent adverse events developed over the study period, but one patient dropped out for subjective akathisia. Results indicated the main effects of time with improvements over the course of the study for CGI-S, BPRS, and PANSS in both SUD and non-SUD groups and the entire sample, and for VAScrav in SUD. Brexpiprazole was associated with similar significant improvements in both groups at the 6 month endpoint compared to baseline.
Conclusion: Treatment with brexpiprazole for 6 months improved psychotic symptoms in patients with schizophrenia, independently from whether they belonged to the SUD or the non-SUD group; hence, SUD comorbidity did not confer treatment resistance to brexpiprazole. Furthermore, in the SUD group, we observed reduced substance craving.
Keywords: antipsychotic medications; brexpiprazole; partial dopamine D2 receptor agonists; schizophrenia; substance use disorder.
Copyright © 2023 Lombardozzi, Trovini, Amici, Kotzalidis, Perrini, Giovanetti, Di Giovanni and De Filippis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating the Effectiveness of Brexpiprazole in Subjects with Schizophrenia Spectrum Illness and Co-Occurring Substance Use Disorder: A Prospective, Multicentric, Real-World Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 21;17(4):535. doi: 10.3390/ph17040535. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675495 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Brexpiprazole for the Treatment of Acute Schizophrenia: A 6-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Am J Psychiatry. 2015 Sep 1;172(9):870-80. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.14101275. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Am J Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25882325 Clinical Trial.
-
Brexpiprazole for the treatment of schizophrenia.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017 Feb;18(2):217-223. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2016.1274972. Epub 2017 Jan 16. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 27997809 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of brexpiprazole in acute management of psychiatric disorders: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020 May;35(3):119-128. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000308. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32141908 Review.
-
Brexpiprazole for the treatment of schizophrenia.Expert Rev Neurother. 2016;16(2):109-22. doi: 10.1586/14737175.2016.1129901. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Expert Rev Neurother. 2016. PMID: 26650624 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of schizophrenia and comorbid substance use disorders: expert review and guidance.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 30;23(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12991-024-00529-7. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39478536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Effectiveness of Brexpiprazole in Subjects with Schizophrenia Spectrum Illness and Co-Occurring Substance Use Disorder: A Prospective, Multicentric, Real-World Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 21;17(4):535. doi: 10.3390/ph17040535. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry. (2022) 9:137–50. 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Titulaer J, Radhe O, Danielsson K, Dutheil S, Marcus MM, Jardemark K, et al. . Lumateperone-mediated effects on prefrontal glutamatergic receptor-mediated neurotransmission: a dopamine D1 receptor dependent mechanism. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. (2022) 62:22–35. 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.06.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laborit H, Huguenard P, Alluaume R. Un nouveau stabilisateur végétatif; le 4560 RP [a new vegetative stabilizer; 4560 R.P.]. Presse Méd. (1893). (1952) 60:206–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


