Antinociceptive effect of intermittent fasting via the orexin pathway on formalin-induced acute pain in mice
- PMID: 37985842
- PMCID: PMC10661460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-47278-3
Antinociceptive effect of intermittent fasting via the orexin pathway on formalin-induced acute pain in mice
Abstract
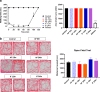
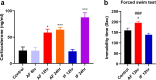
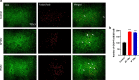
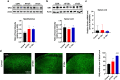
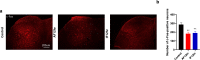
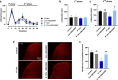
It has been suggested that stress responses induced by fasting have analgesic effects on nociception by elevating the levels of stress-related hormones, while there is limited understanding of pain control mechanisms. Here, we investigated whether acute or intermittent fasting alleviates formalin-induced pain in mice and whether spinal orexin A (OXA) plays a role in this process. 6, 12, or 24 h acute fasting (AF) and 12 or 24 h intermittent fasting (IF) decreased the second phase of pain after intraplantar formalin administration. There was no difference in walking time in the rota-rod test and distance traveld in the open field test in all groups. Plasma corticosterone level and immobility time in the forced swim test were increased after 12 h AF, but not after 12 h IF. 12 h AF and IF increased not only the activation of OXA neurons in the lateral hypothalamus but also the expression of OXA in the lateral hypothalamus and spinal cord. Blockade of spinal orexin 1 receptor with SB334867 restored formalin-induced pain and spinal c-Fos immunoreactivity that were decreased after 12 h IF. These results suggest that 12 h IF produces antinociceptive effects on formalin-induced pain not by corticosterone elevation but by OXA-mediated pathway.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The stress-induced antinociceptive responses to the persistent inflammatory pain involve the orexin receptors in the nucleus accumbens.Neuropeptides. 2023 Apr;98:102323. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2023.102323. Epub 2023 Jan 28. Neuropeptides. 2023. PMID: 36736068
-
Effects of intrathecal administration of orexin-1 receptor antagonist on antinociceptive responses induced by chemical stimulation of lateral hypothalamus in an animal model of tonic nociception.Neuropeptides. 2018 Jun;69:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Neuropeptides. 2018. PMID: 29735274
-
Blockade of the orexin receptors in the CA1 region of hippocampus decreased the lateral hypothalamic-induced antinociceptive responses in the model of orofacial formalin test in the rats.Peptides. 2018 Jan;99:217-222. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Peptides. 2018. PMID: 29042271
-
Orexins/hypocretins: pain regulation and cellular actions.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(28):3089-100. doi: 10.2174/138161210793292483. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20687883 Review.
-
The Orexinergic (Hypocretin) System and Nociception: An Update to Supraspinal Mechanisms.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(32):3917-3929. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170529072554. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28552056 Review.
References
-
- Donham KJ, Thelin A. Agricultural Medicine: Rural Occupational and Environmental Health, Safety, and Prevention. John Wiley & Sons; 2016.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


