Influence of Different Light Spectra on Melatonin Synthesis by the Pineal Gland and Influence on the Immune System in Chickens
- PMID: 37443893
- PMCID: PMC10340020
- DOI: 10.3390/ani13132095
Influence of Different Light Spectra on Melatonin Synthesis by the Pineal Gland and Influence on the Immune System in Chickens
Abstract
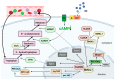
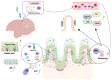
It is well known that the pineal gland in birds influences behavioural and physiological functions, including those of the immune system. The purpose of this research is to examine the endocrine-immune correlations between melatonin and immune system activity. Through a description of the immune-pineal axis, we formulated the objective to determine and describe: the development of the pineal gland; how light influences secretory activity; and how melatonin influences the activity of primary and secondary lymphoid organs. The pineal gland has the ability to turn light information into an endocrine signal suitable for the immune system via the membrane receptors Mel1a, Mel1b, and Mel1c, as well as the nuclear receptors RORα, RORβ, and RORγ. We can state the following findings: green monochromatic light (560 nm) increased serum melatonin levels and promoted a stronger humoral and cellular immune response by proliferating B and T lymphocytes; the combination of green and blue monochromatic light (560-480 nm) ameliorated the inflammatory response and protected lymphoid organs from oxidative stress; and red monochromatic light (660 nm) maintained the inflammatory response and promoted the growth of pathogenic bacteria. Melatonin can be considered a potent antioxidant and immunomodulator and is a critical element in the coordination between external light stimulation and the body's internal response.
Keywords: GALT; antioxidant; bursa of Fabricius; circadian rhythms; immune function; melatonin; spleen; thymus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Melatonin Nuclear Receptors Mediate Green-and-Blue-Monochromatic-Light-Combinations-Inhibited B Lymphocyte Apoptosis in the Bursa of Chickens via Reducing Oxidative Stress and Nfκb Expression.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Apr 8;11(4):748. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040748. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453433 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin mediates monochromatic light-induced proliferation of T/B lymphocytes in the spleen via the membrane receptor or nuclear receptor.Poult Sci. 2020 Sep;99(9):4294-4302. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867973 Free PMC article.
-
A Green and Blue Monochromatic Light Combination Therapy Reduces Oxidative Stress and Enhances B-Lymphocyte Proliferation through Promoting Melatonin Secretion.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Mar 19;2021:5595376. doi: 10.1155/2021/5595376. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 33828639 Free PMC article.
-
Localization and biological activities of melatonin in intact and diseased gastrointestinal tract (GIT).J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;58(3):381-405. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17928638 Review.
-
Human pineal physiology and functional significance of melatonin.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2004 Sep-Dec;25(3-4):177-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2004.08.001. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15589268 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Melatonin in the Inflammatory Process in Patients with Hyperglycemia and Leishmania Infection.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 6;14(8):950. doi: 10.3390/biom14080950. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199338 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapeutic Considerations on Telomere Biology: The Positive Effect of Pharmacologically Active Substances on Telomere Length.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 13;25(14):7694. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147694. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Light Mitigates Cyclic Chronic Heat-Stress-Induced Liver Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via NF-κB Pathway Inhibition in Geese.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;13(7):772. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070772. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061842 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Melatonin in Viral, Bacterial and Parasitic Infections.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 16;14(3):356. doi: 10.3390/biom14030356. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Falcón J., Gothilf Y., Coon S.L., Boeuf G., Klein D.C. Genetic, Temporal and Developmental Differences Between Melatonin Rhythm Generating Systems in the Teleost Fish Pineal Organ and Retina: Two melatonin rhythm generating systems in Teleost fish. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2003;15:378–382. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.00993.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


