Immunomodulatory Role of Interferons in Viral and Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 37373262
- PMCID: PMC10298684
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms241210115
Immunomodulatory Role of Interferons in Viral and Bacterial Infections
Abstract
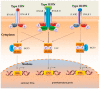
Interferons are a group of immunomodulatory substances produced by the human immune system in response to the presence of pathogens, especially during viral and bacterial infections. Their remarkably diverse mechanisms of action help the immune system fight infections by activating hundreds of genes involved in signal transduction pathways. In this review, we focus on discussing the interplay between the IFN system and seven medically important and challenging viruses (herpes simplex virus (HSV), influenza, hepatitis C virus (HCV), lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and SARS-CoV coronavirus) to highlight the diversity of viral strategies. In addition, the available data also suggest that IFNs play an important role in the course of bacterial infections. Research is currently underway to identify and elucidate the exact role of specific genes and effector pathways in generating the antimicrobial response mediated by IFNs. Despite the numerous studies on the role of interferons in antimicrobial responses, many interdisciplinary studies are still needed to understand and optimize their use in personalized therapeutics.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus; IFN-α; IFN-β; IFN-γ; SARS-CoV coronavirus; bacterial infections; hepatitis C virus; herpes simplex virus; immune system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Suppression of JAK-STAT Signaling by Epstein-Barr Virus Tegument Protein BGLF2 through Recruitment of SHP1 Phosphatase and Promotion of STAT2 Degradation.J Virol. 2021 Sep 27;95(20):e0102721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01027-21. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34319780 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
Lambda interferon (IFN-lambda), a type III IFN, is induced by viruses and IFNs and displays potent antiviral activity against select virus infections in vivo.J Virol. 2006 May;80(9):4501-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.9.4501-4509.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16611910 Free PMC article.
-
Induction and regulation of IFNs during viral infections.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004 Aug;24(8):439-54. doi: 10.1089/1079990041689665. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004. PMID: 15320958 Review.
-
Innate immunity and HCV.J Hepatol. 2013 Mar;58(3):564-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.10.005. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23063572 Review.
Cited by
-
Interplay between Lung Diseases and Viral Infections: A Comprehensive Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Oct 8;12(10):2030. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12102030. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is There such a Thing as Post-Viral Depression?: Implications for Precision Medicine.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024 Nov 1;32(6):659-684. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2024.170. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 39428555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demystifying the Role of Neuroinflammatory Mediators as Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: A Review.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Sep 26;7(10):2987-3003. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00457. eCollection 2024 Oct 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39416969 Review.
-
Aging mitochondria in the context of SARS-CoV-2: exploring interactions and implications.Front Aging. 2024 Sep 24;5:1442323. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2024.1442323. eCollection 2024. Front Aging. 2024. PMID: 39380657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulation in Non-traditional Therapies for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Management.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Sep 6;81(10):346. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03875-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39240286 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous


