The interplay between bicarbonate kinetics and gastrointestinal upset on ergogenic potential after sodium bicarbonate intake: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 37127791
- PMCID: PMC10151363
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-34343-0
The interplay between bicarbonate kinetics and gastrointestinal upset on ergogenic potential after sodium bicarbonate intake: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
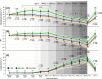
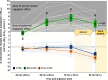
This double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over study utilized comprehensive monitoring of blood bicarbonate (HCO3¯) kinetics and evaluation of gastrointestinal (GI) upset to determine their impact on an ergogenic potential of sodium bicarbonate (SB) co-ingested with carbohydrate (CHO). Nineteen CrossFit athletes performed 6 bouts of 15 s Wingate Anaerobic Test (WAnT) 90 min post-ingestion of 0.4 g·kg-1 body mass (BM) of SB (SB + CHO treatment) or PLA (PLA + CHO treatment) with 15 g CHO. Blood HCO3¯ concentration was evaluated at baseline, 30-, 60-, 75- and 90 min post-ingestion, in between WAnT bouts, and 3 and 45 min post-exercise, while GI upset at 120 min after protocol started. Control (no supplementation; CTRL) procedures were also performed. An effective elevation of extra-cellular buffering capacity was observed 60-90 min post-ingestion of SB + CHO. At mean peak blood HCO3¯, or at start of exercise an increase > 6 mmol·L-1 in HCO3¯ was noted in 84% and 52.6% participants, respectively. SB + CHO did not prevent performance decrements in WAnT bouts. There were no significant relationships between changes in blood HCO3¯ and WAnTs' performance. Total GI was significantly higher in SB + CHO compared to CTRL, and stomach problems in SB + CHO compared to CTRL and PLA + CHO. There were inverse associations between peak- (p = 0.031; r = - 0.495), average- (p = 0.002; r = - 0.674) and minimum power (p = 0.008; r = - 0.585) and total GI upset, as well as average power and severe GI distress (p = 0.042; r = - 0.471) at SB + CHO. The implemented dose of SB + CHO was effective in improving buffering capacity, but did not prevent decrements in WAnTs' performance. GI side effects were crucial in affecting the ergogenic potential of SB and thus must be insightfully monitored in future studies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
I.Ł. is a shareholder of an alkali products distributor and has received honoraria from the Sanum Polska sp. z o. o. However, the content of this study was not constrained by this fact in absolutely no extend. K.D.-M., P.M.N., J.K., B.S., D.C., M.S., and T.P. report no conflicts of interest. The results of the present study do not constitute endorsement by the
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sex-dependent responses to acute sodium bicarbonate different dose treatment: A randomized double-blind crossover study.J Sci Med Sport. 2024 Sep 5:S1440-2440(24)00494-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2024.08.209. Online ahead of print. J Sci Med Sport. 2024. PMID: 39306577
-
The effects of enteric-coated sodium bicarbonate supplementation on 2 km rowing performance in female CrossFit® athletes.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023 Jun;123(6):1191-1198. doi: 10.1007/s00421-023-05140-4. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36705750 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of sodium bicarbonate supplementation at individual time-to-peak blood bicarbonate on 4-km cycling time trial performance in the heat.Eur J Sport Sci. 2022 Dec;22(12):1856-1864. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2021.1998644. Epub 2021 Nov 21. Eur J Sport Sci. 2022. PMID: 34704539 Clinical Trial.
-
Enhancing exercise performance and recovery through sodium bicarbonate supplementation: introducing the ingestion recovery framework.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024 Nov;124(11):3175-3190. doi: 10.1007/s00421-024-05578-0. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39177769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of acute alkalosis and acidosis on performance: a meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2011 Oct 1;41(10):801-14. doi: 10.2165/11591440-000000000-00000. Sports Med. 2011. PMID: 21923200 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


