The translational revolution in atopic dermatitis: the paradigm shift from pathogenesis to treatment
- PMID: 36928371
- PMCID: PMC10203371
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-023-00992-4
The translational revolution in atopic dermatitis: the paradigm shift from pathogenesis to treatment
Abstract
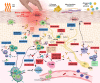
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is the most common inflammatory skin disease, and it is considered a complex and heterogeneous condition. Different phenotypes of AD, defined according to the patient age at onset, race, and ethnic background; disease duration; and other disease characteristics, have been recently described, underlying the need for a personalized treatment approach. Recent advancements in understanding AD pathogenesis resulted in a real translational revolution and led to the exponential expansion of the therapeutic pipeline. The study of biomarkers in clinical studies of emerging treatments is helping clarify the role of each cytokine and immune pathway in AD and will allow addressing the unique immune fingerprints of each AD subset. Personalized medicine will be the ultimate goal of this targeted translational research. In this review, we discuss the changes in the concepts of both the pathogenesis of and treatment approach to AD, highlight the scientific rationale behind each targeted treatment and report the most recent clinical efficacy data.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; biomarkers; eczema; translational revolution.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CSI and USTC.
Conflict of interest statement
EGY is an employee of Mount Sinai and has received research funds (grants paid to the institution) from AbbVie, Almirall, AnaptysBio, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Dermavant, DS Biopharma, Eli Lilly, Innovaderm, Janssen, Kiniska, KyowaKirin, Novan, Pfizer, Regeneron, Ralexar, Glenmark, Galderma, Asana, Innovaderm, Leo Pharma, Sienna Biopharm, Union Therapeutics, and UCB. EGY is also a consultant for Sanofi Aventis, Regeneron, Cara Therapeutics, Celgene, Concert, Amgen, Boehringer-Ingelheim, DBV, Dermira, DS Biopharma, EMD Serono, Escalier, Flx Bio, Galderma, Glenmark, Incyte, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis, Pfizer, Leo Pharma, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Kyowa, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Asana Biosciences, Sienna Biopharm, and Union Therapeutics. The rest of the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of biologics in atopic dermatitis.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020 May;20(5):525-538. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1722998. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32003247 Review.
-
Systemic therapies in atopic dermatitis: The pipeline.Clin Dermatol. 2017 Jul-Aug;35(4):387-397. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2017.03.012. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Clin Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28709570 Review.
-
Atopic dermatitis endotypes: knowledge for personalized medicine.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Jun 1;22(3):153-159. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000820. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35152229 Review.
-
Atopic dermatitis phenotypes and the need for personalized medicine.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Aug;17(4):309-315. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000376. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28582322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in atopic dermatitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 May;151(5):1163-1168. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.019. Epub 2023 Feb 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36792449 Review.
Cited by
-
Durable improvements in atopic dermatitis in the head and neck and across other anatomic regions with rocatinlimab.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Nov 6;316(10):747. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03426-x. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39503757 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The therapeutic effect of 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-3-acetyl-rac-glycerol on chemically induced atopic dermatitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 8;14(1):23402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73951-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39379428 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Biologic Therapies for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis.Drugs. 2024 Nov;84(11):1379-1394. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02095-4. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39365406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation and aging-related disease: A transdisciplinary inflammaging framework.Geroscience. 2024 Oct 1. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01364-0. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 39352664 Review.
-
[Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors in dermatology : Role in the treatment of skin diseases].Dermatologie (Heidelb). 2024 Oct;75(10):791-797. doi: 10.1007/s00105-024-05407-7. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Dermatologie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39212723 Review. German.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


