The continuum of carbon-hydrogen (C-H) activation mechanisms and terminology
- PMID: 36697593
- PMCID: PMC9814233
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-021-00611-1
The continuum of carbon-hydrogen (C-H) activation mechanisms and terminology
Abstract
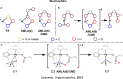
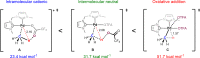
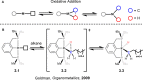
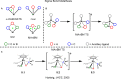
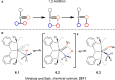
As a rapidly growing field across all areas of chemistry, C-H activation/functionalisation is being used to access a wide range of important molecular targets. Of particular interest is the development of a sustainable methodology for alkane functionalisation as a means for reducing hydrocarbon emissions. This Perspective aims to give an outline to the community with respect to commonly used terminology in C-H activation, as well as the mechanisms that are currently understood to operate for (cyclo)alkane activation/functionalisation.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Challenges and opportunities for alkane functionalisation using molecular catalysts.Chem Sci. 2017 Nov 9;9(2):288-299. doi: 10.1039/c7sc03610h. eCollection 2018 Jan 14. Chem Sci. 2017. PMID: 29629098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective functionalisation of saturated C-H bonds with metalloporphyrin catalysts.Chem Soc Rev. 2011 Apr;40(4):1950-75. doi: 10.1039/c0cs00142b. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Chem Soc Rev. 2011. PMID: 21387046 Review.
-
Arene C-H functionalisation using a removable/modifiable or a traceless directing group strategy.Chem Soc Rev. 2014;43(20):6906-19. doi: 10.1039/c4cs00137k. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Chem Soc Rev. 2014. PMID: 24983866 Review.
-
Recent advances using [Cp*Co(CO)I2] catalysts as a powerful tool for C-H functionalisation.Dalton Trans. 2017 Aug 14;46(30):9721-9739. doi: 10.1039/c7dt01980g. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Dalton Trans. 2017. PMID: 28661519
-
Visible light photoredox-catalysed remote C-H functionalisation enabled by 1,5-hydrogen atom transfer (1,5-HAT).Chem Soc Rev. 2021 Jul 7;50(13):7359-7377. doi: 10.1039/d0cs00774a. Epub 2021 May 20. Chem Soc Rev. 2021. PMID: 34013927
Cited by
-
Deuteration of Arenes via Pd-Catalyzed C-H Activation: A Lesson in Nondirected C-H Activation, Isotopic Labeling, and NMR Characterization.J Chem Educ. 2024 Jul 16;101(8):3410-3417. doi: 10.1021/acs.jchemed.4c00270. eCollection 2024 Aug 13. J Chem Educ. 2024. PMID: 39157437 Free PMC article.
-
Electron Dynamics in Alkane C-H Activation Mediated by Transition Metal Complexes.J Phys Chem A. 2024 Jun 13;128(23):4638-4650. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.4c01131. Epub 2024 Jun 4. J Phys Chem A. 2024. PMID: 38832757 Free PMC article.
-
Photochemical Formation and Electronic Structure of an Alkane σ-Complex from Time-Resolved Optical and X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 May 22;146(20):14000-14011. doi: 10.1021/jacs.4c02077. Epub 2024 May 7. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38713061 Free PMC article.
-
Derivatization of 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole via Regioselective C-H Functionalization and Aryne Reactivity.J Org Chem. 2024 May 3;89(9):6138-6148. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.4c00122. Epub 2024 Apr 22. J Org Chem. 2024. PMID: 38648018 Free PMC article.
-
LED-induced Ru-photoredox Pd-catalyzed C-H arylation of (6-phenylpyridin-2-yl)pyrimidines and heteroaryl counterparts.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 16;14(17):12179-12191. doi: 10.1039/d4ra02173h. eCollection 2024 Apr 10. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38628490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arndtsen BA, Bergman RG, Mobley TA, Peterson TH. Selective intermolecular carbon-hydrogen bond activation by synthetic metal complexes in homogeneous solution. Acc. Chem. Res. 1995;28:154–162.
-
- Goldberg KI, Goldman AS. Large-scale selective functionalization of alkanes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017;50:620–626. - PubMed
-
- Kakiuchi F, Chatani N. Catalytic methods for C-H bond functionalization: application in organic synthesis. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2003;345:1077–1101.
-
- Godula K, Sames D. C-H bond functionalization in complex organic synthesis. Science. 2006;312:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Ritleng V, Sirlin C, Pfeffer M. Ru-, Rh-, and Pd-catalyzed C−C bond formation involving C−H activation and addition on unsaturated substrates: reactions and mechanistic aspects. Chem. Rev. 2002;102:1731–1770. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials


