Restless arms syndrome with oral olanzapine: case based review
- PMID: 36619467
- PMCID: PMC9816658
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12258
Restless arms syndrome with oral olanzapine: case based review
Abstract
Background: Restless arms syndrome (RAS) is a specific variant of restless legs syndrome (RLS). RAS is characterised by an uncomfortable, painful, burning or uneasy sensation confined to the arm.
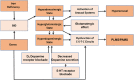
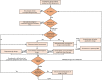
Case presentation: We report a case of RAS with oral olanzapine, which improved with medication reduction. In addition, all reported cases of RAS were reviewed to explore the underlying mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment for psychiatric drug-induced RAS. The literature review and new case suggest that iron deficiency may be a predisposing factor for RAS. Psychiatric medications are closely associated with RAS, especially olanzapine, quetiapine, and mirtazapine. Discontinuation is the recommended treatment for psychotropic drug-induced RAS, while α2δ calcium channel ligand drugs and benzodiazepines may be considered.
Conclusion: In conclusion, psychiatrists should be alert to the possibility of RAS when administering psychiatric medications for the first time to psychiatric patients with iron deficiency.
Keywords: Case report; Olanzapine; Restless arms syndrome (RAS); Review.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transitory restless arms syndrome in a patient with antipsychotics and antidepressants: a case report.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Sep 16;21(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03433-6. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34530775 Free PMC article.
-
Olanzapine-induced restless legs syndrome.J Clin Neurosci. 2014 Sep;21(9):1622-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2014.01.007. Epub 2014 May 27. J Clin Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24874697
-
Restless Legs Syndrome and the Use of Antipsychotic Medication: An Updated Literature Review.Cureus. 2022 Aug 9;14(8):e27821. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27821. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36134065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restless arms syndrome: prevalence, impact, and management strategies.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019 Jul 1;15:1737-1750. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S161583. eCollection 2019. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019. PMID: 31308668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olanzapine-induced restless leg syndrome: a case report and review of literature.Indian J Pharmacol. 2014 Jul-Aug;46(4):450-2. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.135965. Indian J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25097291 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Suspected duloxetine-induced restless legs syndrome phenotypic variant: a case report.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 May 10;24(1):349. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-05763-7. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38730422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suzuki K., et al. Involvement of legs and other body parts in patients with restless legs syndrome and its variants. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019;407 - PubMed
-
- Kay S.R., et al. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987;(13):261–276. - PubMed
-
- Sharon D., et al. Validation of the self-administered version of the international Restless Legs Syndrome study group severity rating scale - the sIRLS. Sleep Med. 2019;54:94–100. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


