PEGylation and folic-acid functionalization of cationic lipoplexes-Improved nucleic acid transfer into cancer cells
- PMID: 36619382
- PMCID: PMC9811411
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1066887
PEGylation and folic-acid functionalization of cationic lipoplexes-Improved nucleic acid transfer into cancer cells
Abstract
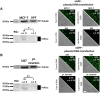
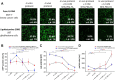
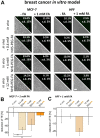
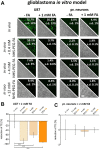
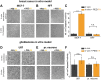
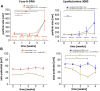
Efficient and reliable transfer of nucleic acids for therapy applications is a major challenge. Stabilization of lipo- and polyplexes has already been successfully achieved by PEGylation. This modification reduces the interaction with serum proteins and thus prevents the lipoplexes from being cleared by the reticuloendothelial system. Problematically, this stabilization of lipoplexes simultaneously leads to reduced transfer efficiencies compared to non-PEGylated complexes. However, this reduction in transfer efficiency can be used to advantage since additional modification of PEGylated lipoplexes with functional groups enables improved selective transfer into target cells. Cancer cells overexpress folate receptors because of a significantly increased need of folate due to high cell proliferation rates. Thus, additional folate functionalization of PEGylated lipoplexes improves uptake into cancer cells. We demonstrate herein that NHS coupling chemistries can be used to modify two commercially available transfection reagents (Fuse-It-DNA and Lipofectamine® 3000) with NHS-PEG-folate for increased uptake of nucleic acids into cancer cells. Lipoplex characterization and functional analysis in cultures of cancer- and healthy cells clearly demonstrate that functionalization of PEGylated lipoplexes offers a promising method to generate efficient, stable and selective nucleic acid transfer systems.
Keywords: DNA-transfer; PEGylation; biocompatibility; functionalized lipoplexes; selective nucleic acid transfer.
Copyright © 2022 Hoffmann, Gerlach, Hoffmann, Richter, Hersch, Csiszár, Merkel and Hoffmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Post-pegylated lipoplexes are promising vehicles for gene delivery in RPE cells.J Control Release. 2007 Aug 28;121(3):208-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.05.033. Epub 2007 Jun 5. J Control Release. 2007. PMID: 17630013
-
Gene delivery with active targeting to ovarian cancer cells mediated by folate receptor alpha.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013 May;9(5):833-44. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2013.1587. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23802413
-
Folate-associated lipoplexes mediate efficient gene delivery and potent antitumoral activity in vitro and in vivo.Int J Pharm. 2012 Feb 28;423(2):365-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.12.035. Epub 2011 Dec 29. Int J Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22209825
-
On the mechanism of cationic amphiphile-mediated transfection. To fuse or not to fuse: is that the question?J Membr Biol. 2002 Oct 1;189(3):167-79. doi: 10.1007/s00232-002-1015-7. J Membr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12395282 Review.
-
Structure and kinetics of lipid-nucleic acid complexes.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014 Mar;205:230-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2014. PMID: 24529969 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing the efficacy of letrozole-loaded PEGylated nanoliposomes against breast cancer cells: In vitro study.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 30;10(9):e30503. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30503. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38726203 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant Novel Nanocarrier-Based Targeted Therapy for Lung Cancer.Molecules. 2024 Feb 29;29(5):1076. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051076. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA Sonotransfection of Tumors with Polymeric Microbubbles: Co-Formulation versus Co-Administration.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(15):e2306139. doi: 10.1002/advs.202306139. Epub 2024 Feb 11. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38342634 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered smart materials for RNA based molecular therapy to treat Glioblastoma.Bioact Mater. 2023 Nov 27;33:396-423. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.11.007. eCollection 2024 Mar. Bioact Mater. 2023. PMID: 38059120 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Folate-Containing Liposomal Nucleic Acid Delivery Systems for Antitumor Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 3;15(5):1400. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051400. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242642 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allard-Vannier E., Herve-Aubert K., Kaaki K., Blondy T., Shebanova A., Shaitan K. V., et al. (2017). Folic acid-capped PEGylated magnetic nanoparticles enter cancer cells mostly via clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Biochimica Biophysica Acta - General Subj. 1861 (6), 1578–1586. 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.11.045 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chan C. L., Majzoub R. N., Shirazi R. S., Ewert K. K., Chen Y. J., Liang K. S., et al. (2012). Endosomal escape and transfection efficiency of PEGylated cationic liposome-DNA complexes prepared with an acid-labile PEG-lipid. Biomaterials 33 (19), 4928–4935. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.03.038 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


