Loss of LGR4/GPR48 causes severe neonatal salt wasting due to disrupted WNT signaling altering adrenal zonation
- PMID: 36538378
- PMCID: PMC9927937
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI164915
Loss of LGR4/GPR48 causes severe neonatal salt wasting due to disrupted WNT signaling altering adrenal zonation
Abstract
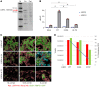
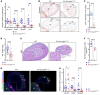
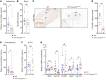
Disorders of isolated mineralocorticoid deficiency, which cause potentially life-threatening salt-wasting crisis early in life, have been associated with gene variants of aldosterone biosynthesis or resistance; however, in some patients no such variants are found. WNT/β-catenin signaling is crucial for differentiation and maintenance of the aldosterone-producing adrenal zona glomerulosa (zG). Herein, we describe a highly consanguineous family with multiple perinatal deaths and infants presenting at birth with failure to thrive, severe salt-wasting crises associated with isolated hypoaldosteronism, nail anomalies, short stature, and deafness. Whole exome sequencing revealed a homozygous splice variant in the R-SPONDIN receptor LGR4 gene (c.618-1G>C) regulating WNT signaling. The resulting transcripts affected protein function and stability and resulted in loss of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in vitro. The impact of LGR4 inactivation was analyzed by adrenal cortex-specific ablation of Lgr4, using Lgr4fl/fl mice mated with Sf1:Cre mice. Inactivation of Lgr4 within the adrenal cortex in the mouse model caused decreased WNT signaling, aberrant zonation with deficient zG, and reduced aldosterone production. Thus, human LGR4 mutations establish a direct link between LGR4 inactivation and decreased canonical WNT signaling, which results in abnormal zG differentiation and endocrine function. Therefore, variants in WNT signaling and its regulators should systematically be considered in familial hyperreninemic hypoaldosteronism.
Keywords: Endocrinology; Genetic diseases; Molecular biology; Mouse models.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-canonical Wnt signaling triggered by WNT2B drives adrenal aldosterone production.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 24:2024.08.23.609423. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.23.609423. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229119 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
LGR4 deficiency results in delayed puberty through impaired Wnt/β-catenin signaling.JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):e133434. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.133434. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32493844 Free PMC article.
-
LGR5 Activates Noncanonical Wnt Signaling and Inhibits Aldosterone Production in the Human Adrenal.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Jun;100(6):E836-44. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-1734. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25915569 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of LGR4 (GPR48) in Normal and Cancer Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 29;22(9):4690. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094690. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33946652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RSPO-LGR4/5-ZNRF3/RNF43 module in liver homeostasis, regeneration, and disease.Hepatology. 2022 Sep;76(3):888-899. doi: 10.1002/hep.32328. Epub 2022 Feb 20. Hepatology. 2022. PMID: 35006616 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and Genetics Perspectives on Primary Adrenocortical Hyperfunction Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 22;25(21):11341. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111341. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39518893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical Wnt signaling triggered by WNT2B drives adrenal aldosterone production.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 24:2024.08.23.609423. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.23.609423. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229119 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Letter to the Editor From Janot et al: « Single-Exon Deletions of ZNRF3 Exon 2 Cause Congenital Adrenal Hypoplasia ».J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Aug 13;109(9):e1808-e1809. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae229. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38589987 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Primary aldosteronism: molecular medicine meets public health.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023 Dec;19(12):788-806. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00753-6. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37612380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Splicing defects in rare diseases: transcriptomics and machine learning strategies towards genetic diagnosis.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Sep 20;24(5):bbad284. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad284. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37580177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miller WL, et al. In: Sperling MA, ed. Sperling - Pediatric Endocrinology. Elsevier; 2020.


