Role of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/Negative Ratios in Regulating Breast Cancer
- PMID: 36118080
- PMCID: PMC9477638
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7833389
Role of Estrogen Receptor-Positive/Negative Ratios in Regulating Breast Cancer
Abstract
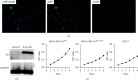
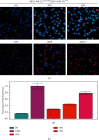
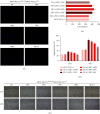
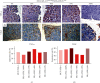
The alpha estrogen receptor (ERα) contributes to breast cancer progression and recent guidelines define ER positivity as ≥1% stained cells, and a few tumor tissues show no ERα expression at all or are at 100%. Although ER and aromatase inhibitors are widely used to treat hormone receptor-positive (HR+) breast cancer, their effect on tumor activity at different ERα levels remains unclear. Therefore, we investigated the role of ERα+/ERα- ratios in determining the ERα level. We used ERα stably transfected and wild-type MDA-MB-231 cells (MDA-MB-231Trans-ER and MDA-MB-231WT, respectively) as represented ER+ and ER- cells, respectively, and MCF-7 cells were the positive control. MDA-MB-231Trans-ER and MDA-MB-231WT cells were mixed and cocultured at a ratio of 0%, 20%, 40%, 70%, and 100%. Migration and invasion functions at different cell ratios were evaluated in vitro using the Transwell and scratch test. In a xenograft mouse model, the polarization of the tumor-associated (M2) macrophage and the expression of breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α were measured. The results showed that the cell invasion and migration were significantly higher at 40% and 70% than they were at other ratios. Additionally, in vivo, the 70% ERα+/ERα-ratio was a critical indicator of cell activity and cytokine expression. The highest M2 level and expression of VEGR, TNF-α, BRCA1, and HER2 were shown at a ratio of 70%. Moreover, the effects of ERα were not linear in breast cancer, indicating that the ERα status requires continuous monitoring during long-term endocrine treatment. These results indicate that during HR+ breast cancer treatment, the ERα+/ERα- ratio may be a useful predictor and should be evaluated further.
Copyright © 2022 Yanchu Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by estradiol and tamoxifen in breast cancer cells: a complex interplay between estrogen receptors alpha and beta.Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 1;62(17):4977-84. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12208749
-
[Study of the CpG methylation status of ER alpha gene in estrogen receptor alpha-negative breast cancer cell lines and the role of hydralazine demethylation].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005 May;34(5):283-7. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16181550 Chinese.
-
Estrogen Receptor α Mediates Doxorubicin Sensitivity in Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating E-Cadherin.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 4;9:583572. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.583572. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33614637 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen Receptor Is Required for Metformin-Induced Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells Under Hyperglycemic Conditions.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2024 Apr 8;18:11782234241240173. doi: 10.1177/11782234241240173. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 38779416 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor-α and sex steroid hormones regulate Toll-like receptor-9 expression and invasive function in human breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 Apr;132(2):411-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1590-3. Epub 2011 May 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21607583
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


