Central nervous system effects of 5-HT7 receptors: a potential target for neurodegenerative diseases
- PMID: 35725396
- PMCID: PMC9208181
- DOI: 10.1186/s10020-022-00497-2
Central nervous system effects of 5-HT7 receptors: a potential target for neurodegenerative diseases
Abstract
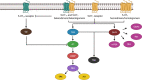
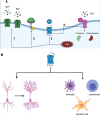
5-HT7 receptors (5-HT7R) are the most recently identified among the family of serotonin receptors. Their role in health and disease, particularly as mediators of, and druggable targets for, neurodegenerative diseases, is incompletely understood. Unlike other serotonin receptors, for which abundant preclinical and clinical data evaluating their effect on neurodegenerative conditions exist, the available information on the role of the 5-HT7R receptor is limited. In this review, we describe the signaling pathways and cellular mechanisms implicated in the activation of the 5-HT7R; also, we analyze different mechanisms of neurodegeneration and the potential therapeutic implications of pharmacological interventions for 5-HT7R signaling.
Keywords: 5-HT7; Alzheimer disease; Dementia; Neurodegeneration; Neuroprotection; Parkinson disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest while making this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the Serotonin 5-HT7 Receptor in the Search for Treatments for CNS Disorders: Rationale and Progress to Date.CNS Drugs. 2015 Apr;29(4):265-75. doi: 10.1007/s40263-015-0236-0. CNS Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25721336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-Activity Relationships and Therapeutic Potentials of 5-HT7 Receptor Ligands: An Update.J Med Chem. 2018 Oct 11;61(19):8475-8503. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01898. Epub 2018 Jun 5. J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29767995
-
Serotonin 5-HT7 receptor increases the density of dendritic spines and facilitates synaptogenesis in forebrain neurons.J Neurochem. 2017 Jun;141(5):647-661. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13962. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28122114
-
5-HT7 receptors increase the excitability of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons by inhibiting the A-type potassium current.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Oct 15;177:108248. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108248. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32736087
-
Role of 5-HT7 receptors in the immune system in health and disease.Mol Med. 2019 Dec 31;26(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s10020-019-0126-x. Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31892309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association between small intestine bacterial overgrowth and psychiatric disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 21;15:1438066. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1438066. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39497810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated Cellular Uptake of Succinimide- and Glucose-Modified Liposomes for Blood-Brain Barrier Transfer and Glioblastoma Therapy.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 20;12(9):2135. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092135. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335648 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective and Neurite Outgrowth Stimulating Effects of New Low-Basicity 5-HT7 Receptor Agonists: In Vitro Study in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.Neurochem Res. 2024 Aug;49(8):2179-2196. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04159-z. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 38834845 Free PMC article.
-
Psychedelics for acquired brain injury: a review of molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Mar;29(3):671-685. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02360-0. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38177350 Review.
-
Biological studies of clavine alkaloids targeting CNS receptors.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Nov 21;14:1286941. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1286941. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38076698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bard JA et al. Cloning of a novel human serotonin receptor (5-HT7) positively linked to adenylate cyclase. 1993;268: 23422–23426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


