pH dependency of the structural and photophysical properties of the atypical 2',3-dihydroxyflavone
- PMID: 35515691
- PMCID: PMC9056863
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra06833k
pH dependency of the structural and photophysical properties of the atypical 2',3-dihydroxyflavone
Abstract
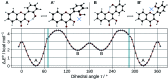
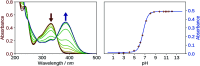
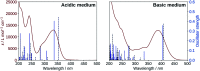
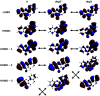
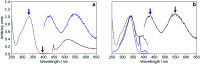
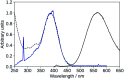
2',3-Dihydroxyflavone (2'3HF) is a natural flavonol that has barely ever been studied, however the scarce studies of its physico-chemical properties have highlighted its atypical behaviour. We present a structural and spectral study of 2'3HF, performed using UV-visible absorption and fluorescence spectroscopies, coupled with DFT and TD-DFT calculations. Although its structure is close to that of 3-hydroxyflavone, 2'3HF shows a much lower pK a value. We show that the origin of this particularity is the substitution by a hydroxyl group on position 2', that induces a stronger inter-ring interaction weakening the bonding of the proton at position 3. The main absorption band of the is red-shifted upon deprotonation. The remaining proton is highly bonded in between oxygen atoms 3 and 2', making the second deprotonation unattainable in methanol. The neutral form can undergo an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer to emit dual fluorescence by the normal and tautomer forms. We suggested five geometries to be the sources of the emission bands, and showed that the energy barriers to interconversions were almost null. The anion is also fluorescent. The Stokes shifts for the neutral normal and anion species are extremely high, that can be explained by the conformational rearrangement, as the species go from twisted in the ground-state, to planar in the excited-state. Finally, another emission band is evidenced when exciting in the vicinity of the absorption maximum of the anion species in acidic medium. We suggest an aggregate with the solvent to be the origin of the emission.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
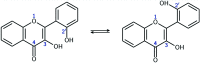
Similar articles
-
Electron spectroscopies of 3-hydroxyflavone and 7-hydroxyflavone in MCM-41 silica nanoparticles and in acetonitrile solutions. Experimental data and DFT/TD-DFT calculations.Data Brief. 2020 Dec 8;34:106630. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106630. eCollection 2021 Feb. Data Brief. 2020. PMID: 33409341 Free PMC article.
-
Triple Emission of 5'-(para-R-Phenylene)vinylene-2-(2'-hydroxyphenyl)benzoxazole (PVHBO). Part I: Dual Emission from the Neutral Species.J Phys Chem A. 2022 Feb 24;126(7):1033-1061. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.1c10165. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Phys Chem A. 2022. PMID: 35143188
-
Excited state intramolecular proton transfer in 2-(2'-arylsulfonamidophenyl)benzimidazole derivatives: insights into the origin of donor substituent-induced emission energy shifts.J Phys Chem A. 2007 May 31;111(21):4584-95. doi: 10.1021/jp068832s. Epub 2007 May 10. J Phys Chem A. 2007. PMID: 17489564
-
Rotamerism, tautomerism, and excited-state intramolecular proton transfer in 2-(4'-N,N-diethylamino-2'-hydroxyphenyl)benzimidazoles: novel benzimidazoles undergoing excited-state intramolecular coupled proton and charge transfer.J Phys Chem A. 2008 Jan 24;112(3):376-87. doi: 10.1021/jp076634a. Epub 2007 Dec 23. J Phys Chem A. 2008. PMID: 18154323
-
Experimental and DFT studies: novel structural modifications greatly enhance the solvent sensitivity of live cell imaging dyes.J Phys Chem A. 2007 Oct 25;111(42):10849-60. doi: 10.1021/jp073197r. Epub 2007 Oct 5. J Phys Chem A. 2007. PMID: 17918807 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
New insights for titanium(iv) speciation in acidic media based on UV-visible and 31P NMR spectroscopies and molecular modeling.RSC Adv. 2021 Aug 9;11(43):27059-27073. doi: 10.1039/d1ra04284j. eCollection 2021 Aug 2. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35480018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawabata K. Tanaka T. Honjo S. Kakumoto M. Hara A. Makita H. Tatematsu N. Ushida J. Tsuda H. Mori H. Chemopreventive effect of dietary flavonoid morin on chemically induced rat tongue carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer. 1999;83:381–386. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19991029)83:3<381::AID-IJC14>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


