Role of the Transcriptional Regulator ArgR in the Connection between Arginine Metabolism and c-di-GMP Signaling in Pseudomonas putida
- PMID: 35254100
- PMCID: PMC9004404
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.00064-22
Role of the Transcriptional Regulator ArgR in the Connection between Arginine Metabolism and c-di-GMP Signaling in Pseudomonas putida
Abstract
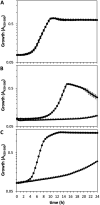
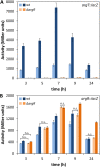
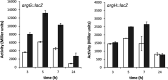
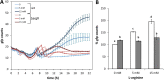
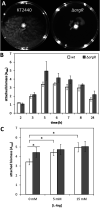
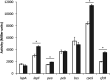
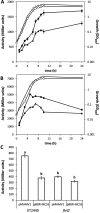
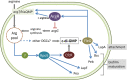
The second messenger cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP) is a key molecule that controls different physiological and behavioral processes in many bacteria, including motile-to-sessile lifestyle transitions. Although the external stimuli that modulate cellular c-di-GMP contents are not fully characterized, there is growing evidence that certain amino acids act as environmental cues for c-di-GMP turnover. In the plant-beneficial bacterium Pseudomonas putida KT2440, both arginine biosynthesis and uptake influence second messenger contents and the associated phenotypes. To further understand this connection, we have analyzed the role of ArgR, which in different bacteria is the master transcriptional regulator of arginine metabolism but had not been characterized in P. putida. The results show that ArgR controls arginine biosynthesis and transport, and an argR-null mutant grows poorly with arginine as the sole carbon or nitrogen source and also displays increased biofilm formation and reduced surface motility. Modulation of c-di-GMP levels by exogenous arginine requires ArgR. The expression of certain biofilm matrix components, namely, the adhesin LapF and the exopolysaccharide Pea, as well as the diguanylate cyclase CfcR is influenced by ArgR, likely through the alternative sigma factor RpoS. Our data indicate the existence of a regulatory feedback loop between ArgR and c-di-GMP mediated by FleQ. IMPORTANCE Identifying the molecular mechanisms by which metabolic and environmental signals influence the turnover of the second messenger c-di-GMP is key to understanding the regulation of bacterial lifestyles. The results presented here point at the transcriptional regulator ArgR as a central node linking arginine metabolism and c-di-GMP signaling and indicate the existence of a complex balancing mechanism that connects cellular arginine contents and second messenger levels, ultimately controlling the lifestyles of Pseudomonas putida.
Keywords: Pseudomonas; amino acid biosynthesis; amino acid transport; arginine synthesis; biofilm; c-di-GMP; cell signaling; gene regulation; metabolism; second messenger; transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The phosphodiesterase RmcA contributes to the adaptation of Pseudomonas putida to l-arginine.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023 Jan 17;370:fnad077. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnad077. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37550221 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient Sensing and Biofilm Modulation: The Example of L-arginine in Pseudomonas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 15;23(8):4386. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084386. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arginine as an environmental and metabolic cue for cyclic diguanylate signalling and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas putida.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 12;10(1):13623. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70675-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32788689 Free PMC article.
-
FleQ of Pseudomonas putida KT2440 is a multimeric cyclic diguanylate binding protein that differentially regulates expression of biofilm matrix components.Res Microbiol. 2017 Jan;168(1):36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Aug 5. Res Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27503246
-
c-di-GMP signaling in Pseudomonas syringae complex.Microbiol Res. 2023 Oct;275:127445. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127445. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Microbiol Res. 2023. PMID: 37450986 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene expression reprogramming of Pseudomonas alloputida in response to arginine through the transcriptional regulator ArgR.Microbiology (Reading). 2024 Mar;170(3):001449. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001449. Microbiology (Reading). 2024. PMID: 38511653 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning analysis of RB-TnSeq fitness data predicts functional gene modules in Pseudomonas putida KT2440.mSystems. 2024 Mar 19;9(3):e0094223. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00942-23. Epub 2024 Feb 7. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38323821 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphodiesterase RmcA contributes to the adaptation of Pseudomonas putida to l-arginine.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023 Jan 17;370:fnad077. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnad077. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37550221 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient Sensing and Biofilm Modulation: The Example of L-arginine in Pseudomonas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 15;23(8):4386. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084386. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


