Allosteric modulation of dopamine D2L receptor in complex with Gi1 and Gi2 proteins: the effect of subtle structural and stereochemical ligand modifications
- PMID: 35064921
- PMCID: PMC8964653
- DOI: 10.1007/s43440-021-00352-x
Allosteric modulation of dopamine D2L receptor in complex with Gi1 and Gi2 proteins: the effect of subtle structural and stereochemical ligand modifications
Abstract
Background: Allosteric modulation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is nowadays one of the hot topics in drug discovery. In particular, allosteric modulators of D2 receptor have been proposed as potential modern therapeutics to treat schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease.
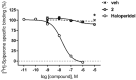
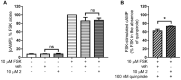
Methods: To address some subtle structural and stereochemical aspects of allosteric modulation of D2 receptor, we performed extensive in silico studies of both enantiomers of two compounds (compound 1 and compound 2), and one of them (compound 2) was synthesized as a racemate in-house and studied in vitro.
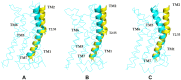
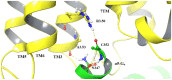
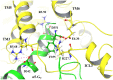
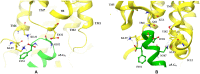
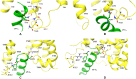
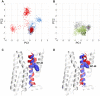
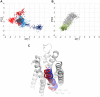
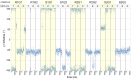
Results: Our molecular dynamics simulations confirmed literature reports that the R enantiomer of compound 1 is a positive allosteric modulator of the D2L receptor, while its S enantiomer is a negative allosteric modulator. Moreover, based on the principal component analysis (PCA), we hypothesized that both enantiomers of compound 2 behave as silent allosteric modulators, in line with our in vitro studies. PCA calculations suggest that the most pronounced modulator-induced receptor rearrangements occur at the transmembrane helix 7 (TM7). In particular, TM7 bending at the conserved P7.50 and G7.42 was observed. The latter resides next to the Y7.43, which is a significant part of the orthosteric binding site. Moreover, the W7.40 conformation seems to be affected by the presence of the positive allosteric modulator.
Conclusions: Our work reveals that allosteric modulation of the D2L receptor can be affected by subtle ligand modifications. A change in configuration of a chiral carbon and/or minor structural modulator modifications are solely responsible for the functional outcome of the allosteric modulator.
Keywords: Dopamine D2 receptor; GPCRs; Molecular dynamics; Molecular switches; Negative allosteric modulators; Positive allosteric modulators.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
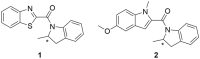

Similar articles
-
Allosteric Modulators of Dopamine D2 Receptors for Fine-Tuning of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in CNS Diseases: Overview, Pharmacology, Structural Aspects and Synthesis.Molecules. 2022 Dec 25;28(1):178. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010178. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Lipids in Allosteric Modulation of Dopamine D2 Receptor-In Silico Study.Molecules. 2022 Feb 16;27(4):1335. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041335. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209123 Free PMC article.
-
Preferential Coupling of Dopamine D2S and D2L Receptor Isoforms with Gi1 and Gi2 Proteins-In Silico Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 9;21(2):436. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020436. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31936673 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for modulation of a G-protein-coupled receptor by allosteric drugs.Nature. 2013 Nov 14;503(7475):295-9. doi: 10.1038/nature12595. Epub 2013 Oct 13. Nature. 2013. PMID: 24121438
-
The First Negative Allosteric Modulator for Dopamine D2 and D3 Receptors, SB269652 May Lead to a New Generation of Antipsychotic Drugs.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Jun;91(6):586-594. doi: 10.1124/mol.116.107607. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28265019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review on allosteric modulators of dopamine receptors so far.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 18;7(3):e1984. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1984. eCollection 2024 Mar. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38505681 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric Modulators of Dopamine D2 Receptors for Fine-Tuning of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in CNS Diseases: Overview, Pharmacology, Structural Aspects and Synthesis.Molecules. 2022 Dec 25;28(1):178. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010178. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Lipids in Allosteric Modulation of Dopamine D2 Receptor-In Silico Study.Molecules. 2022 Feb 16;27(4):1335. doi: 10.3390/molecules27041335. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35209123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giros B, Sokoloff P, Martres MP, Riou JF, Emorine LJ, Schwartz JC. Alternative splicing directs the expression of two D2 dopamine receptor isoforms. Nature. 1989;342(6252):923–926. - PubMed
-
- Guiramand J, Montmayeur JP, Ceraline J, Bhatia M, Borrelli E. Alternative splicing of the dopamine D2 receptor directs specificity of coupling to G-proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(13):7354–7358. - PubMed
-
- Jomphe C, Tiberi M, Trudeau L-E. Expression of D2 receptor isoforms in cultured neurons reveals equipotent autoreceptor function. Neuropharmacology. 2006;50(5):595–605. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

