Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Applications in Dermatology
- PMID: 35024683
- PMCID: PMC8669514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2021.100015
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Applications in Dermatology
Abstract
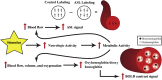
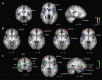
As a noninvasive imaging modality able to show the dynamic changes in neurologic activity, functional magnetic resonance imaging has revolutionized the ability to both map and further understand the functional regions of the brain. Current applications range from neurosurgical planning to an enormous variety of investigational applications across many diverse specialties. The main purpose of this article is to provide a foundational understanding of how functional magnetic resonance imaging is being used in research by outlining the underlying basic science, specific methods, and direct investigational and clinical applications. In addition, the use of functional magnetic resonance imaging in current dermatological research, especially in relation to studies concerning the skin‒brain axis, is explicitly addressed. This article also touches on the advantages and limitations concerning functional magnetic resonance imaging in comparison with other similar techniques.
Keywords: ASL, arterial spin labeling; BOLD, blood oxygenation level‒dependent; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Perfusion magnetic resonance imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling: methods and clinical applications in the central nervous system.Eur J Radiol. 1999 May;30(2):115-24. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(99)00050-9. Eur J Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10401592
-
Comparison of 3T and 7T ASL techniques for concurrent functional perfusion and BOLD studies.Neuroimage. 2017 Aug 1;156:363-376. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.05.038. Epub 2017 May 19. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 28528845
-
Technical aspects and utility of fMRI using BOLD and ASL.Clin Neurophysiol. 2002 May;113(5):621-34. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(02)00038-x. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11976042 Review.
-
Functional localization in the human brain: Gradient-Echo, Spin-Echo, and arterial spin-labeling fMRI compared with neuronavigated TMS.Hum Brain Mapp. 2011 Mar;32(3):341-57. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21024. Hum Brain Mapp. 2011. PMID: 20533563 Free PMC article.
-
Functional imaging of the human placenta with magnetic resonance.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Oct;213(4 Suppl):S103-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2015.06.045. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015. PMID: 26428488 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurosurgical robots in China: State of the art and future prospect.iScience. 2023 Sep 21;26(11):107983. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107983. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37867956 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguirre G.K., Detre J.A., Zarahn E., Alsop D.C. Experimental design and the relative sensitivity of BOLD and perfusion fMRI. Neuroimage. 2002;15:488–500. - PubMed
-
- Alsop D.C., Detre J.A., Golay X., Günther M., Hendrikse J., Hernandez-Garcia L., et al. Recommended implementation of arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI for clinical applications: a consensus of the ISMRM perfusion study group and the European consortium for ASL in dementia. Magn Reson Med. 2015;73:102–116. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apkarian A.V., Bushnell M.C., Treede R.D., Zubieta J.K. Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. Eur J Pain. 2005;9:463–484. - PubMed
-
- Babajani A., Soltanian-Zadeh H. Integrated MEG/EEG and fMRI model based on neural masses. IEEE Trans Bio med Eng. 2006;53:1794–1801. - PubMed
-
- Belliveau J.W., Kennedy D.N., Jr., McKinstry R.C., Buchbinder B.R., Weisskoff R.M., Cohen M.S., et al. Functional mapping of the human visual cortex by magnetic resonance imaging. Science. 1991;254:716–719. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials


