Aberrant RNA splicing and therapeutic opportunities in cancers
- PMID: 34812550
- PMCID: PMC8819303
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15213
Aberrant RNA splicing and therapeutic opportunities in cancers
Abstract
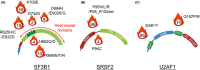
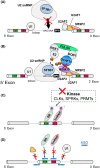
There has been accumulating evidence that RNA splicing is frequently dysregulated in a variety of cancers and that hotspot mutations affecting key splicing factors, SF3B1, SRSF2 and U2AF1, are commonly enriched across cancers, strongly suggesting that aberrant RNA splicing is a new class of hallmark that contributes to the initiation and/or maintenance of cancers. In parallel, some studies have demonstrated that cancer cells with global splicing alterations are dependent on the transcriptional products derived from wild-type spliceosome for their survival, which potentially creates a therapeutic vulnerability in cancers with a mutant spliceosome. It has been c. 10 y since the frequent mutations affecting splicing factors were reported in cancers. Based on these surprising findings, there has been a growing interest in targeting altered splicing in the treatment of cancers, which has promoted a wide variety of investigations including genetic, molecular and biological studies addressing how altered splicing promotes oncogenesis and how cancers bearing alterations in splicing can be targeted therapeutically. In this mini-review we present a concise trajectory of what has been elucidated regarding the pathogenesis of cancers with aberrant splicing, as well as the development of therapeutic strategies to target global splicing alterations in cancers.
Keywords: RNA binding protein; SF3b; antisense oligonucleotide; cancer; splicing factor.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Therapeutic targeting of splicing in cancer.Nat Med. 2016 Sep 7;22(9):976-86. doi: 10.1038/nm.4165. Nat Med. 2016. PMID: 27603132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[RNA splicing dysregulation in hematological malignancies].Rinsho Ketsueki. 2023;64(7):646-653. doi: 10.11406/rinketsu.64.646. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2023. PMID: 37544725 Japanese.
-
Targeting splicing abnormalities in cancer.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018 Feb;48:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.10.010. Epub 2017 Nov 12. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018. PMID: 29136527 Review.
-
Splicing factor mutations in the myelodysplastic syndromes: target genes and therapeutic approaches.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 Jan;67:13-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 28986033 Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of RNA Splicing in Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;14(7):1378. doi: 10.3390/genes14071378. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Upregulated Expression Mechanism of Apoptotic Chromatin Condensation Inducer 1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Bioinformatics.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr;35(4):307-315. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2024.23454. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39128105 Free PMC article.
-
SF3B3-regulated mTOR alternative splicing promotes colorectal cancer progression and metastasis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 26;43(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03053-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38671459 Free PMC article.
-
A-Z of Epigenetic Readers: Targeting Alternative Splicing and Histone Modification Variants in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 9;16(6):1104. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061104. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zygotic Splicing Activation of the Transcriptome is a Crucial Aspect of Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition and Required for the Conversion from Totipotency to Pluripotency.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Apr;11(14):e2308496. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308496. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38308190 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Drug Discovery for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2023 Nov 9;28(22):7513. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227513. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38005235 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Tokyo Biochemical Research Foundation
- Uehara Memorial Foundation
- 19K24691/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 21H04828/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Japanese Society of Hematology
- 2020-A-2/National Cancer Center Research and Development Funds
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Society
- JP20jm0210085h0002/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- Narishige Neuroscience Research Foundation
- The Japan Neurosurgical Society
- Brain Science Foundation
- Japanese Foundation for Multidisciplinary Treatment of Cancer
- Novartis Foundation
- Kato Memorial Bioscience Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


