Leptin treatment prevents impaired hypoglycemic counterregulation induced by exposure to severe caloric restriction or exposure to recurrent hypoglycemia
- PMID: 34358845
- PMCID: PMC8532139
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2021.102853
Leptin treatment prevents impaired hypoglycemic counterregulation induced by exposure to severe caloric restriction or exposure to recurrent hypoglycemia
Abstract
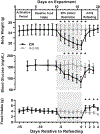
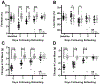
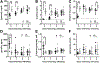
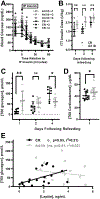
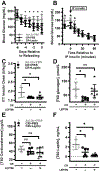
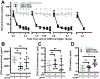
Hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure (HAAF) is a maladaptive failure in glucose counterregulation in persons with diabetes (PWD) that is caused by recurrent exposure to hypoglycemia. The adipokine leptin is known to regulate glucose homeostasis, and leptin levels fall following exposure to recurrent hypoglycemia. Yet, little is known regarding how reduced leptin levels influence glucose counterregulation, or if low leptin levels are involved in the development of HAAF. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of hypoleptinemia on the neuroendocrine responses to hypoglycemia. We utilized two separate experimental paradigms known to induce a hypoleptinemic state: 60% caloric restriction (CR) in mice and three days of recurrent hypoglycemia (3dRH) in rats. A sub-set of animals were also treated with leptin (0.5-1.0 μg/g) during the CR or 3dRH periods. Neuroendocrine responses to hypoglycemia were assessed 60 min following an IP insulin injection on the terminal day of the paradigms. CR mice displayed defects in hypoglycemic counterregulation, indicated by significantly lower glucagon levels relative to controls, 13.5 pmol/L (SD 10.7) versus 64.7 pmol/L (SD 45) (p = 0.002). 3dRH rats displayed reduced epinephrine levels relative to controls, 1900 pg/mL (SD 1052) versus 3670 pg/mL (SD 780) (p = 0.030). Remarkably, leptin treatment during either paradigm completely reversed this effect by normalizing glucagon levels in CR mice, 78.0 pmol/L (SD 47.3) (p = 0.764), and epinephrine levels in 3dRH rats, 2910 pg/mL (SD 1680) (p = 0.522). These findings suggest that hypoleptinemia may be a key signaling event driving the development of HAAF and that leptin treatment may prevent the development of HAAF in PWD.
Keywords: Diabetes complications; Hypoglycemia; Leptin; Recurrent hypoglycemia; Starvation.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures:
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure and its component syndromes in diabetes.Diabetes. 2005 Dec;54(12):3592-601. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3592. Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 16306382 Review.
-
Leptin acts in the brain to influence hypoglycemic counterregulation: disparate effects of acute and recurrent hypoglycemia on glucagon release.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec 15;309(12):E960-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00361.2015. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26506851 Free PMC article.
-
Blunted glucagon but not epinephrine responses to hypoglycemia occurs in youth with less than 1 yr duration of type 1 diabetes mellitus.Pediatr Diabetes. 2014 Mar;15(2):127-34. doi: 10.1111/pedi.12070. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 23992543 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impaired hormonal responses to hypoglycemia in spontaneously diabetic and recurrently hypoglycemic rats. Reversibility and stimulus specificity of the deficits.J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2667-74. doi: 10.1172/JCI116883. J Clin Invest. 1993. PMID: 8254023 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycemia in diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms and diurnal variation.Prog Brain Res. 2006;153:361-5. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)53021-3. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16876586 Review.
Cited by
-
Leptin receptor signaling is required for intact hypoglycemic counterregulation: A study in male Zucker rats.J Diabetes Complications. 2021 Oct;35(10):107994. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.107994. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J Diabetes Complications. 2021. PMID: 34325985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamson U, Lins PE, et al. (1989). "Fasting for 72 h decreases the responses of counterregulatory hormones to insulin-induced hypoglycaemia in normal man." Scandinavian journal of clinical and laboratory investigation 49(8): 751–756. - PubMed
-
- Ahren B (2000). "Diurnal variation in circulating leptin is dependent on gender, food intake and circulating insulin in mice." Acta physiologica Scandinavica 169(4): 325–331. - PubMed
-
- Allars J and York DA (1986). "The effects of 2-deoxy-D-glucose on brown adipose tissue of lean and obese Zucker rats." International journal of obesity 10(2): 147–158. - PubMed
-
- Bagnasco M, Kalra PS, et al. (2002). "Ghrelin and Leptin Pulse Discharge in Fed and Fasted Rats." Endocrinology 143(2): 726–729. - PubMed
-
- Beall C, Ashford ML, et al. (2012). "The physiology and pathophysiology of the neural control of the counterregulatory response." American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology 302(2): R215–R223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


