Anthelmintic drugs for treating ascariasis
- PMID: 32289194
- PMCID: PMC7156140
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010599.pub2
Anthelmintic drugs for treating ascariasis
Abstract
Background: Ascaris lumbricoides is a common infection, and mainly affects children living in low-income areas. Water and sanitation improvement, health education, and drug treatment may help break the cycle of transmission, and effective drugs will reduce morbidity.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and safety of anthelmintic drugs (albendazole, mebendazole, ivermectin) for treating people with Ascaris infection.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Infectious Disease Group Specialized Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, LILACS, three other databases, and reference lists of included studies, without language restrictions, up to 4 July 2019.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials (RCT) that compared albendazole, mebendazole, and ivermectin in children and adults with confirmed Ascaris infection.
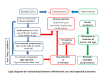
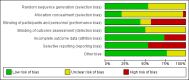
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed studies for inclusion, assessed risk of bias, and extracted data from the included trials. A third review author checked the quality of data extraction. We used the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' assessment tool to determine the risk of bias in included trials. We used risk ratios (RRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to compare dichotomous outcomes in treatment and control groups. We used the fixed-effect model for studies with low heterogeneity and the random-effects model for studies with moderate to high heterogeneity. We assessed the certainty of the evidence using the GRADE approach. We used the control rate average to provide illustrative cure rates in the comparison groups.
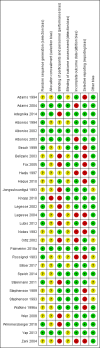
Main results: We included 30 parallel-group RCTs, which enrolled 6442 participants from 17 countries across Africa, Asia, Central America and the Caribbean, and South America. Participants were from 28 days to 82 years of age, recruited from school, communities, and health facilities. Twenty studies were funded or co-funded by manufacturers, while 10 studies were independent of manufacturer funding. Twenty-two trials had a high risk of bias for one or two domains (blinding, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting). Single dose of albendazole (four trials), mebendazole (three trials) or ivermectin (one trial) was compared to placebo. Parasitological cure at 14 to 60 days was high in all the studies (illustrative cure of 93.0% in the anthelmintic group and 16.1% in the placebo group; RR 6.29, 95% CI 3.91 to 10.12; 8 trials, 1578 participants; moderate-certainty evidence). Single dose of albendazole is as effective as multiple doses of albendazole (illustrative cure of 93.2% with single dose, 94.3% with multiple doses; RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.05; 3 trials, 307 participants; high-certainty evidence); or as single dose of mebendazole (illustrative cure of 98.0% with albendazole, 96.9% with mebendazole; RR 1.01, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.02; 6 trials, 2131 participants; high-certainty evidence). Studies did not detect a difference between a single dose of albendazole and a single dose of ivermectin (cure rates of 87.8% with albendazole, 90.2% with ivermectin; RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.08; 3 trials, 519 participants; moderate-certainty evidence). Across all the studies, failure after single dose of albendazole ranged from 0.0% to 30.3%, mebendazole from 0.0% to 22.2%, and ivermectin from 0.0% to 21.6%. The egg reduction rate (ERR) measured up to 60 days after the treatment was high in all treated groups, regardless of the anthelmintic used (range 96% to 100%). It was not possible to evaluate parasitological cure by classes of infection intensity. No included trials reported complication or serious adverse events. Other adverse events were apparently similar among the compared anthelmintic groups (moderate- to low-certainty evidence). The most commonly reported other adverse events were nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, headache, and fever.
Authors' conclusions: Single-dose of albendazole, mebendazole, and ivermectin all appeared effective against Ascaris lumbricoides infection, yielding high parasitological cure and large reductions in eggs excreted, with no differences detected between them. The drugs appear to be safe to treat children and adults with confirmed Ascaris infection. There is little to choose between drugs and regimens in terms of cure or adverse events.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
LOC has no known conflicts of interest.
MDT has no known conflicts of interest.
IC has no known conflicts of interest.
RAMBA has no known conflicts of interest.
Figures





Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010599
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin and permethrin for treating scabies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 2;4(4):CD012994. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012994. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29608022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthelmintics for people with neurocysticercosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jun 1;6(6):CD000215. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000215.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34060667 Free PMC article.
-
Ivermectin versus albendazole or thiabendazole for Strongyloides stercoralis infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 18;2016(1):CD007745. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007745.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26778150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Albendazole alone or in combination with microfilaricidal drugs for lymphatic filariasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 8;1(1):CD003753. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003753.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30620051 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
When Diagnosis Curls a Little: Partial Bowel Obstruction Due to Ascaris. L in a Young Man.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2024 Mar 4;14(2):87-90. doi: 10.55729/2000-9666.1317. eCollection 2024. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38966511 Free PMC article.
-
Ascaris suum infection in juvenile pigs elicits a local Th2 response in a setting of ongoing Th1 expansion.Front Immunol. 2024 May 10;15:1396446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396446. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38799456 Free PMC article.
-
Albendazole inhibits colon cancer progression and therapy resistance by targeting ubiquitin ligase RNF20.Br J Cancer. 2024 Apr;130(6):1046-1058. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02570-x. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38278978
-
In Vitro Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Ivermectin Interaction.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 16;24(22):16392. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216392. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003581 Free PMC article.
-
An unusual finding: Biliary ascariasis in a pregnant patient managed conservatively-a case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Aug 18;85(10):5200-5203. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001205. eCollection 2023 Oct. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37811107 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Adams 1994 {published data only}
-
- Adams EJ, Stephenson LS, Latham MC, Kinoti S. Physical activity and growth of Kenyan school children with hookworm, Trichuris trichiura and Ascaris lumbricoides infections are improved after treatment with albendazole. Journal of Nutrition 1994;124(8):1199‐206. - PubMed
Adams 2004 {published data only}
-
- Adams VJ, Lombard CJ, Dhansay MA, Markus MB, Fincham JE. Efficacy of albendazole against the whipworm Trichuris trichiura – a randomized, controlled trial. South African Medical Journal 2004;94(12):972‐6. - PubMed
Adegnika 2014 {published data only}
-
- Adegnika AA, Zinsou JF, Issifou S, Ateba‐Ngoa U, Kassa KF, Feuga LN, et al. Randomized, controlled, assessor‐blind clinical trial to assess the efficacy of single‐ versus repeated‐dose albendazole to treat Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura, and Hookworm Infection. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2014;58(5):2535‐40. - PMC - PubMed
Albonico 1994 {published data only}
-
- Albonico M, Smith PG, Hall A, Chwaya HM, Alawi KS, Savioli L. A randomized controlled trial comparing mebendazole and albendazole against Ascaris, Trichuris and hookworm infections. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1994;88(5):585‐9. - PubMed
Albonico 2002 {published data only}
Albonico 2003 {published data only}
-
- Albonico M, Bickle Q, Ramsan M, Montresor A, Savioli L, Taylor M. Efficacy of mebendazole and levamisole alone or in combination against intestinal nematode infections after repeated targeted mebendazole treatment in Zanzibar. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2003;81(5):343‐52. - PMC - PubMed
Beach 1999 {published data only}
-
- Beach MJ, Streit TG, Addiss DG, Prospere R, Roberts JM, Lammie PJ. Assessment of combined ivermectin and albendazole for treatment of intestinal helminth and Wuchereria bancrofti infections in Haitian schoolchildren. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1999;60(3):479‐86. - PubMed
Belizario 2003 {published data only}
-
- Belizario VY, Amarillo ME, Leon WU, Reyes AE, Bugayong MG, Macatangay BJ. A comparison of the efficacy of single doses of albendazole, ivermectin, and diethylcarbamazine alone or in combinations against Ascaris and Trichuris spp. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2003;81(1):35‐43. - PMC - PubMed
Fox 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fox LM, Furness BW, Haser JK, Desire D, Brissau JM, Milord MD, et al. Tolerance and efficacy of combined diethylcarbamazine and albendazole for treatment of Wuchereria bancrofti and intestinal helminth infections in Haitian children. Bulletin of the World Health Organization 2005;73(1):115‐21. - PubMed
Hadju 1997 {published data only}
-
- Hadju V, Satriono, Abadi K, Stephenson LS. Relationships between soil‐transmitted helminthiases and growth in urban slum schoolchildren in Ujung Pandang Indonesia. International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition 1997;48:85‐93. - PubMed
Haque 2010 {published data only}
Jongsuksuntigul 1993 {published data only}
-
- Jongsuksuntigul P, Jeradit C, Pornpattanakul S, Charanasri U. A comparative study on the efficacy of albendazole and mebendazole in the treatment of ascariasis, hookworm infection and trichuriasis. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1993;24(4):724‐9. - PubMed
Knopp 2010 {published data only}
-
- Knopp S, Mohammed KA, Speich B, Hattendorf J, Khamis S, Khamis AN, et al. Albendazole and mebendazole administered alone or in combination with ivermectin against Trichuris trichiura: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2010;51(12):1420‐8. - PubMed
Legesse 2002 {published data only}
-
- Legesse M, Erko B, Medhin G. Efficacy of albendazole and mebendazole in the treatment of Ascaris and Trichuris infections. Ethiopian Medical Journal 2002;40(4):335‐43. - PubMed
Legesse 2004 {published data only}
-
- Legesse M, Erko B, Medhin G. Comparative efficacy of albendazole and three brands of mebendazole in the treatment of ascariasis and trichuriasis. East African Medical Journal 2004;81(3):134‐8. - PubMed
Lubis 2012 {published data only}
-
- Lubis IN, Pasaribu S, Lubis CP. Current status of the efficacy and effectiveness of albendazole and mebendazole for the treatment of Ascaris lumbricoides in North‐Western Indonesia. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine 2012;2012(8):605‐9. - PubMed
Nokes 1992 {published data only}
-
- Nokes C, Grantham‐McGregor SM, Sawyer AW, Cooper ES, Robinson BA, Bundy DA. Moderate to heavy infections of Trichuris trichiura affect cognitive function in Jamaican school children. Parasitology 1992;104:539‐47. - PubMed
Ortiz 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ortiz JJ, Chegne NL, Gargala G, Favennec L. Comparative clinical studies of nitazoxanide, albendazole and praziquantel in the treatment of ascariasis, trichuriasis and hymenolepiasis in children from Peru. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2002;96(2):193‐6. - PubMed
Palmeirim 2018a {published data only}
Rossignol 1983 {published data only}
-
- Rossignol JF, Maisonneuve H. Albendazole: placebo controlled study in 870 patients with intestinal helminthiasis. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1983;77(5):707‐11. - PubMed
Silber 2017 {published data only}
-
- Silber SA, Diro E, Workneh N, Mekonnen Z, Levecke B, Steinmann P, et al. Efficacy and safety of a single‐dose mebendazole 500 mg chewable, rapidly‐disintegrating tablet for Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuris trichiura infection treatment in pediatric patients: a double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled, phase 3. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2017;97(6):1851‐6. - PMC - PubMed
Speich 2014 {published data only}
-
- Speich B, Ame SM, Ali SM, Alles R, Huwyler J, Hattendorf J, et al. Oxantel pamoate–albendazole for Trichuris trichiura infection. New England Journal of Medicine 2014;370(7):610‐20. - PubMed
Steinmann 2011 {published data only}
Stephenson 1989 {published data only}
-
- Stephenson LS, Latham MC, Kurz KM, Kinoti SN, Brigham H. Treatment with a single dose of albendazole improves growth of Kenyan schoolchildren with hookworm, Trichuris trichiura, and Ascaris lumbricoides infections. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1989;41(1):78‐87. - PubMed
Stephenson 1993 {published data only}
-
- Stephenson LS, Latham MD, Adams EJ, Perte A. Weight gain of Kenyan school children infected with hookworm, Trichuris trichiura and Ascaris lumbricoides is improved following once‐ or twice‐yearly treatment with albendazole. American Institute of Nutrition 1993;123(4):656‐65. - PubMed
Watkins 1996a {published data only}
-
- Watkins WE, Pollit E. Effect of removing Ascaris on the growth of Guatemalan schoolchildren. Pediatrics 1996;97(6):871‐6. - PubMed
Wen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wen LY, Yan XL, Sun FH, Fang YY, Yang MJ, Lou LJ. A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter clinical trial on the efficacy of ivermectin against intestinal nematode infections in China. Acta Tropica 2008;103(8):190‐4. - PubMed
Wimmersberger 2018 {published data only}
-
- Wimmersberger D, Coulibaly JT, Schulz J, Puchkow M, JörgHuwyler J, N'Gbesso Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of ivermectin against Trichuris trichiura in preschool‐ and school‐aged children: a randomized controlled dose‐finding trial. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2018;67(8):1247‐55. - PubMed
Yap 2013 {published data only}
Zani 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zani LC, Favre TC, Piere OS, Barbosa CS. Impact of antihelminthic treatment on infection by Ascaris lumbricoides, Trichuris trichiura e Hookworm in Covas, a rural community of Pernambuco Brazil. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo 2004;46(2):63‐71. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Adriko 2018 {published data only}
-
- Adriko M, Tinkitina B, Arinaitwe M, Kabatereine NB, Nanyunja M, Tukahebwa E. Impact of a national deworming campaign on the prevalence of soil‐transmitted helminthiasis in Uganda (2004‐2016): implications for national control programs. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2018;12(7):e0006520. - PMC - PubMed
Alavi Majd 2014 {published data only}
Albonico 1995 {published data only}
-
- Albonico M, Smith PG, Ercole E, Hall A, Chwaya HM, Alawi KS, et al. Rate of reinfection with intestinal nematodes after treatment of children with mebendazole or albendazole in a highly endemic area. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1995;89(5):538‐41. - PubMed
Albonico 1999 {published data only}
-
- Albonico M, Stoltzfus RJ, Savioli L, Chwaya HM, d'Harcourt E, Tielsch JM. A controlled evaluation of two school‐based anthelminthic chemotherapy regimens on intensity of intestinal helminth infections. International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28(3):591‐6. - PubMed
Albonico 2013 {published data only}
-
- Albonico M, Rinaldi L, Sciascia S, Morgoglione ME, Piemonte M, Maurelli MP, et al. Comparison of three copromicroscopic methods to assess albendazole efficacy against soil‐transmitted helminth infections in school‐aged children on Pemba Island. Transaction of Real Society of Tropical Medicine Hygiene 2013;107(8):493‐501. - PubMed
Al‐Mekhlafi 2014 {published data only}
Amato 1983 {published data only}
-
- Amato NV, Moreira AA, Campos R, Lazzaro ES, Chiaramelli MC, Pinto PL, et al. Tratamento da ancilostomiase, ascaridiase e tricocefaliase por meio do albendazol ou do mebendazol. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo 1983;25(6):294‐9. - PubMed
Anto 2019 {published data only}
Awasthi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Awasthi S, Pande VK, Fletcher RH. Effectiveness and cost‐effectiveness of albendazole in improving nutritional status of pre‐school children in urban slums. Indian Pediatrics 2000;37(1):19‐29. - PubMed
Awasthi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Awasthi S, Pande VK. Six‐monthly de‐worming in infants to study effects on growth. Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2001;68(9):823‐7. - PubMed
Bartoloni 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bartoloni A, Guglielmetti P, Cancrini G, Gamboa H, Roselli M, Nicoletti A, et al. Comparative efficacy of a single 400 mg dose of albendazole or mebendazole in the treatment of nematode infections in children. Tropical and Geographical Medicine 1993;45(3):114‐6. - PubMed
Bassily 1984 {published data only}
-
- Bassily S, El‐Masry NA, Trabolsi B, Farid Z. Treatment of ancylostomiasis and ascariasis with albendazole. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 1984;78(1):81‐2. - PubMed
Behnke 1994 {published data only}
-
- Behnke JM, Pritchard DI, Wakelin D, Park JR, McNicholas AM, Gilbert FS. Effect of ivermectin on infection with gastro‐intestinal nematodes in Sierra Leone. Journal of Helminthology 1994;68(3):187‐95. - PubMed
Belew 2015 {published data only}
Bell 1971 {published data only}
-
- Bell WJ, Nassif S. Comparison of pyrantel pamoate and piperazine phosphate in the treatment of ascariasis. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1971;20(4):584‐8. - PubMed
Boivin 1993 {published data only}
-
- Boivim MJ, Giordani B. Improvements in cognitive performance for schoolchildren in Zaire, Africa, following an iron supplement and treatment for intestinal parasites. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1993;18(2):249‐64. - PubMed
Brutus 2006 {published data only}
-
- Brutus L, Watier L, Briand V, Hanitrasoamampionona V, Razanatsoarilala H, Cot M. Parasitic co‐infections: does Ascaris lumbricoides protect against Plasmodium falciparum infection?. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2006;75(2):194‐8. - PubMed
Brutus 2007 {published data only}
-
- Brutus L, Watier L, Hanitrasoamampionona V, Razanatsoarilala H, Cot M. Confirmation of the protective effect of Ascaris lumbricoides on Plasmodium falciparum infection: results of a randomized trial in Madagascar. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2007;77(6):1091‐5. - PubMed
Campbell 2014 {published data only}
Carmona‐Fonseca 2015 {published data only}
-
- Carmona‐Fonseca J, Correa‐Botero A. Effect of albendazole and vitamin A treatment on intestinal helminths and anaemia in children from Urabá (Antioquia, Colombia) [Effecto del albendazol y la vitamina A periódicos sobre helmintos intestinales y anemia em niños del Urabá Antioqueño (Colombia)]. Biosalud 2015;14(1):9‐25.
Cervoni 1971 {published data only}
-
- Cervoni WA, Oliver‐Gonzçalez J. Clinical evaluation of pyrantel pamoate in helminthiasis. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1971;20(4):589‐91. - PubMed
Clarke 2016 {published data only}
-
- Clarke NE, Clements AC, Doi SA, Wang D, Campbell SJ, Gray D, et al. Differential effect of mass deworming and targeted deworming for soil‐transmitted helminth control in children: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet 2016;389(10066):287‐97. - PubMed
Cleary 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cleary JD, Graham D, Lushbaugh WB, Nolan RL, Chapman SW. Single low‐dose mebendazole administered quarterly for ascaris treatment. American Journal of Medical Science 2007;333(6):340‐5. - PubMed
Coulaud 1984 {published data only}
-
- Coulaud JP, Rossignol JF. Albendazole: a new single dose anthelmintic‐study in 1455 patients. Acta Tropica 1984;41:87‐90. - PubMed
Coulibaly 2018 {published data only}
De Guimaraes 2001 {published data only}
-
- Guimaraes DL, Llanos RS, Acevedo JH. Ascariasis: comparison of the therapeutic efficacy between paico and albendazole in children from Huaraz [Ascaridiasis: comparación de la eficacia terapeutica entre paico y albendazol en niños de Huaraz]. Revista de Gastroenterología del Perú 2001;21(3):212‐19. - PubMed
Donnen 1998 {published data only}
-
- Donnen P, Brasseur D, Dramaix M, Vertongen F, Zihindula M, Muhamiriza M, et al. Vitamin A supplementation but not deworming improves growth of malnourished preschool children in eastern Zaire. Journal of Nutrition 1998;128(8):1320‐7. - PubMed
Dossa 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dossa RA, Ategbo EA, Koning FL, Raaij JM, Hautvast JG. Impact of iron supplementation and deworming on growth performance in preschool Beninese children. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2001;55:223‐8. - PubMed
Ebenezer 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ebenezer R, Gunawardena K, Kumarendran B, Pathmeswaran A, Jukes MC, Drake LJ, et al. Cluster‐randomised trial of the impact of school‐based deworming and iron supplementation on the cognitive abilities of schoolchildren in Sri Lanka's plantation sector. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2013;18(8):942‐51. - PubMed
Edelduok 2013 {published data only}
-
- Edelduok EG, Eke FN, Evelyn NE, Atama CI, Eyo JE. Efficacy of a single dose albendazole chemotherapy on human intestinal helminthiasis among school children in selected rural tropical communities. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Public Heath 2013;6(4):413‐7.
El‐Masry 1983 {published data only}
-
- El‐Masry NA, Trabolsi B, Bassily S, Farid Z. Albendazole in the treatment of Ancylostoma duodenale and Ascaris lumbricoides infections. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1983;77(2):160‐1. - PubMed
Farahmandian 1972 {published data only}
-
- Farahmandian I, Sahba GH, Arfaa F, Jalali H. A comparative evaluation of the therapeutic effect of pyrantel pamoate and bephenium hydroxynaphthoate on Ancylostoma duodenale and other intestinal helminths. Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1972;75(10):205‐7. - PubMed
Farahmandian 1977 {published data only}
-
- Farahmandian I, Arfaa F, Jalali H, Reza M. Comparative studies on the evaluation of the effect of new anthelminthics on various intestinal helminthiasis in Iran. Effects of anthelminthics on intestinal helminthiasis. Chemotherapy 1977;23(2):98‐105. - PubMed
Fernandes 1981 {published data only}
-
- Fernandes P, Baranski MC. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of mebendazole of different origin [Comparação da eficácia terapêutica de diferentes preparados de mebendazol]. Folha Médica 1981;82(4):431‐3.
Freeman 2013 {published data only}
Friis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Friis H, Mwaniki D, Omondi B, Muniu E, Thiong'o F, Ouma J, et al. Effects on haemoglobin of multi‐micronutrient supplementation and multi‐helminth chemotherapy: a randomized, controlled trial in Kenyan school children. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2003;57(4):573‐9. - PubMed
Gilgen 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gilgen DD, Mascie‐Taylor CG, Rosetta LL. Intestinal helminth infections, anaemia and labour productivity of female tea pluckers in Bangladesh. Tropical Medicine and International Health 2001;6(6):449‐57. - PubMed
Gizaw 2019 {published data only}
Goodwin 1954 {published data only}
Goodwin 1958 {published data only}
Greemberg 1981 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg BL, Gilman RH, Shapiro H, Gilman JB, Mondal G, Maksud M, et al. Single dose piperazine therapy for Ascaris lumbricoides: an unsuccessful method of promoting growth. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1981;34(11):2508‐15. - PubMed
Gupta 1982 {published data only}
-
- Gupta MC, Urrutia JJ. Effect of periodic anti ascaris and anti giardia treatment on nutritional status of preschool children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1982;36(1):79‐86. - PubMed
Gutierrez 1986 {published data only}
-
- Gutierrez FP, Solís JM, Delgado GL. Single dose antihelmintic: comparative study with single dose, between oxantel/pyrantel and albendazole in ascariasis, trochocephalus and hookworm [Dosis unica antihelmintica: estudio comparativo con dosis unica, entre oxantel/pirantel y albendazol en ascariasis, tricocefalosis y uncinarias]. Revista Medica de Costa Rica 1986;53(494):5‐12.
Gyorkos 2013a {published data only}
-
- Gyorkos TW, Maheu‐Giroux M, Blouin B, Saavedra L, Casapía M. Efficacy of a single dose of albendazole for soil‐transmitted helminth infections in school children of a village in Iquitos, Perú [Eficacia del Albendazol en dosis única sobre las infecciones por helmintos transmitidos por el suelo en escolares de una comunidad de Iquitos, Perú]. Revista Peruana de Medicina Experimental y Salud Publica 2013;30(4):601‐7. - PubMed
Gyorkos 2013b {published data only}
Hadidjaja 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hadidjaja P, Bonang E, Suyardi MA, Abidin SA, Ismid IS, Margono SS. The effect of intervention methods on nutritional status and cognitive function of primary school children infected with Ascaris lumbricoides. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1998;59(5):791‐5. - PubMed
Hadju 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hadju V, Stephenson LS, Abadi K, Mohammed HO, Bowman DD, Parker RS. Improvements in appetite and growth in helminth‐infected schoolboys three and seven weeks after a single dose of pyrantel pamoate. Parasitology 1996;113(Pt 5):497‐504. - PubMed
Hall 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hall A, Nahar Q. Albendazole and infections with Ascaris lumbricoides and Trichuris trichiura in children in Bangladesh. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1994;88(1):110‐2. - PubMed
Hatchuel 1973 {published data only}
-
- Hatchuel W, Isaãcson M, Villiers DJ. Pyrantel pamoate in roundworm infestations: a comparative trial with piperazine citrate given in a single dose. South African Medical Journal 1973;47(3):91‐3. - PubMed
Hoang 1993 {published data only}
-
- Hoang TK, Bronshtein AM, Zang NT, Nguyen VT, Sabgaida TP. The first experience with embovin therapy of intestinal nematodes in a focus of the disease in Vietnam. Meditsinskaya Parazitologiya i Parazitarnye Bolezni 1993;0(2):27‐8. - PubMed
Holland 1996 {published data only}
-
- Holland CV, Asaolu SO, Crompton DW, Whitehead RR, Coombs I. Targeted anthelminthic treatment of school children: effect of frequency of application on the intensity of Ascaris lumbricoides infection in children from rural Nigerian villages. Parasitology 1996;113:87‐95. - PubMed
Hurlimann 2018 {published data only}
-
- Hurlimann E, Silué KD, Zouzou F, Ouattara M, Schmidlin T, Yapi RB, et al. Effect of an integrated intervention package of preventive chemotherapy, community‐led total sanitation and health education on the prevalence of helminth and intestinal protozoa infections in Cote d'Ivoire. Parasites & Vectors 2018;11(1):115. - PMC - PubMed
Islam 1976 {published data only}
-
- Islam N, Chowdhury NA. Mebendazole and pyrantel pamoate as broad spectrum anthelmintics. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1976;1:81‐4. - PubMed
Jalal 1998 {published data only}
-
- Jalal F, Nesheim MC, Agus Z, Sanjur D, Habicht JP. Serum retinol concentrations in children are affected by food sources of beta‐carotene, fat intake, and anthelmintic drug treatment. American Journal of Clinical and Nutrition 1998;68(3):623‐9. - PubMed
Jancloes 1979 {published data only}
-
- Jancloes MF, Cornet P, Thienpont D. Mass control of ascariasis with single oral doses of levamisole. A controlled comparison in 3,056 subjects between three incomplete population coverage. Tropical and Geographic Medicine 1979;31(1):111‐21. - PubMed
Jinabhai 2001 {published data only}
-
- Jinabhai CC, Taylor M, Coutsoudis A, Coovadia HM, Tomkins AM, Sullivan KR. Epidemiology of helminth infections: implications for parasite control programmes, a South African perspective. Public Health and Nutrition 2001;4(6):1211‐9. - PubMed
Joseph 2015 {published data only}
Kale 1981 {published data only}
-
- Kale OO. Controlled comparative study of the efficacy of pyrantel pamoate and a combined regimen of piperazine citrate and bephenium hydroxynaphthoate in the treatment of intestinal nemathelminthiases. African Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 1981;10(1‐2):63‐7. - PubMed
Kale 1982 {published data only}
-
- Kale OO, Bammeke AO, Nwankwo EO. Field trials of pyrantel pamoate (Combantrin) in Ascaris, hookworm and Trichuris infections. African Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences 1982;11(1):23‐31. - PubMed
Karyadi 1996 {published data only}
-
- Karyadi E, Gross R, Sastroamidjojo S, Dillon D, Richards AL, Sutanto I. Anthelminthic treatment raises plasma iron levels but does not decrease the acute‐phase response in Jakarta school children. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1996;4(6):742‐53. - PubMed
Kepha 2017 {published data only}
-
- Kepha S, Mwandawiro CS, Anderson RM, Pullan RL, Nuwaha F, Cano J, et al. Impact of single annual treatment and four‐monthly treatment for hookworm and Ascaris lumbricoides, and factors associated with residual infection among Kenyan school children. Infectious Diseases of Poverty 2017;6(1):30. - PMC - PubMed
Kirwan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kirwan P, Asaolu SO, Molloy SF, Abiona TC, Jackson AL, Holland CV. Patterns of soil‐transmitted helminth infection and impact of four‐monthly albendazole treatments in preschool children from semi‐urban communities in Nigeria: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled randomised trial. BMC Infectious Diseases 2009;9:20. - PMC - PubMed
Kirwan 2010 {published data only}
Kugo 2018 {published data only}
Lai 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lai KP, Kaur H, Mathias RG, Ow‐Yang CK. Ascaris and Trichuris do not contribute to growth retardation in primary school children. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1995;26(2):322‐8. - PubMed
Lechat 1974 {published data only}
-
- Lechat MF, Jancloes MF, Galambos F, Cornet P, Thienpont D. Control by levamisole of ascariasis and ancylostomiasis in rural areas. Tropical and Geographical Medicine 1974;26(4):441‐5. - PubMed
Le Huong 2007 {published data only}
-
- Huong T, Brouwer ID, Nguyen KC, Burema J, Kok FJ. The effect of iron fortification and de‐worming on anaemia and iron status of Vietnamese schoolchildren. British Journal of Nutrition 2007;97:955‐62. - PubMed
Lionel 1969 {published data only}
Lynch 1997 {published data only}
-
- Lynch NR, Palenque M, Hagel I, DiPrisco MC. Clinical improvement of asthma after anthelminthic treatment in a tropical situation. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 1997;156(1):50‐4. - PubMed
Maipanich 1997 {published data only}
-
- Maipanich W, Pubampen S, Sa‐nguankiat S, Nontasut P, Waikagul J. Effect of albendazole and mebendazole on soil‐transmitted helminth eggs. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1997;28(2):321‐5. - PubMed
Mani 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mani TR, Rajendran R, Munirathinam A, Sunish IP, Md Abdulla, Augustin DJ, et al. Efficacy of co‐administration of albendazole and diethylcarbamazine against geohelminthiases: a study from South India. Tropical Medicine and International Health 2002;7(6):541‐8. - PubMed
Marti 1996 {published data only}
-
- Marti H, Haji HJ, Savioli L, Chwaya HM, Mgeni AF, Ameir JS, et al. A comparative trial of a single‐dose ivermectin versus three days of albendazole for treatment of Strongyloides stercoralis and other soil‐transmitted helminth infections in children. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;55(5):477‐81. - PubMed
Martin 2018 {published data only}
Mascie‐Taylor 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mascie‐Taylor CG, Alam M, Montanari RM, Karim R, Ahmed T, Karim E, et al. A study of the cost effectiveness of selective health interventions for the control of intestinal parasites in rural Bangladesh. Journal of Parasitology 1999;85(1):6‐11. - PubMed
Means 2018 {published data only}
Meyrowitsch 2001 {published data only}
-
- Meyrowitsch DW, Simonsen PE. Efficacy of DEC against Ascaris and hookworm infections in schoolchildren. Tropical Medicine and International Health 2001;6(9):739‐42. - PubMed
Miller 1978 {published data only}
-
- Miller MJ, Farahmandian I, Arfaa F, Katz N, Winsor E, Bennett E. An evaluation of levamisole for treatment of ascariasis. Southern Medical Journal 1978;71(2):137‐40. - PubMed
Moens 1978 {published data only}
-
- Moens M, Dom J, Burke WE, Schlossberg S, Schuermans V. Levamisole in ascariasis. A multicenter controlled evaluation. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1978;27(5):897‐904. - PubMed
Moser 2017a {published data only}
-
- Moser W, Coulibaly JT, Ali SM, Ame SM, Amour AK, Yapi RB, et al. Efficacy and safety of tribendimidine, tribendimidine plus ivermectin, tribendimidine plus oxantel pamoate, and albendazole plus oxantel pamoate against hookworm and concomitant soil‐transmitted helminth infections in Tanzania and Côte d'Ivoire: a randomized, controlled, single‐blinded, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2017;17(11):1162‐71. - PubMed
Muchiri 2001 {published data only}
-
- Muchiri EM, Thiong'o FW, Magnussen P, Ouma JH. A comparative study of different albendazole and mebendazole regimens for the treatment of intestinal infections in school children of Usigu Division, western Kenya. Journal of Parasitology 2001;87(2):413‐9. - PubMed
Murray 1978 {published data only}
-
- Murray J, Murray A, Murray M, Murray C. The biological suppression of malaria: an ecological and nutritional interrelationship of a host and two parasites. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1978;31(8):1363‐6. - PubMed
Naquira 1989 {published data only}
-
- Naquira C, Jimenez G, Guerra JG, Bernal R, Nalin DR, Neu D, et al. Ivermectin for human strongyloidiasis and other intestinal helminths. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1989;40(3):304‐9. - PubMed
Ndibazza 2010 {published data only}
Ndibazza 2012 {published data only}
Ndyomugyenyi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ndyomugyenyi R, Kabatereine N, Olsen A, Magnussen P. Efficacy of ivermectin and albendazole alone and in combination for treatment of soil‐transmitted helminths in pregnancy and adverse events: a randomised open label controlled intervention trial in Masindi district, western Uganda. Americam Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2008;79(6):856‐63. - PubMed
Newlove 2011 {published data only}
-
- Newlove T, Guimaraes LH, Morgan DJ, Alcantara L, Glesby MJ, Carvalho EM, et al. Antihelminthic therapy and antimony in cutaneous leishmaniasis: a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial in patients co‐infected with helminths and leishmania braziliensis. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2011;84(4):551‐5. - PMC - PubMed
Nokes 1999 {published data only}
-
- Nokes C, McGarvey ST, Shiue L, Wu G, Wu H, Bundy DA, et al. Evidence for an improvement in cognitive function following treatment of Schistosoma japonicum infection in Chinese primary schoolchildren. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1999;60(4):556‐65. - PubMed
Nontasut 1997 {published data only}
-
- Nontasut P, Waikagul J, Muennoo C, Sanguankait, N, Maipanich W. Minimum effective doses of mebendazole in treatment of soil‐transmitted helminths. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1997;28(2):326‐8. - PubMed
Northrop‐Clewes 2001 {published data only}
-
- Northrop‐Clewes CA, Rousham EK, Mascie‐Taylor CN, Lunn PG. Anthelmintic treatment of rural Bangladeshi children: effect on host physiology, growth, and biochemical status. Americam Journal of Nutrition 2001;73(1):53‐60. - PubMed
Okoyo 2016 {published data only}
Pene 1982 {published data only}
-
- Pene P, Mojon M, Garin JP, Coulaud JP, Rossignol JF. Albendazole : a new broad spectrum anthelmintic. Double‐blind multicenter clinical trial. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1982;31(2):236‐66. - PubMed
Persson 2001 {published data only}
-
- Persson V, Ahmed F, Gebre‐Medhin M, Greiner T. Increase in serum beta‐carotene following dark green leafy vegetable supplementation in mebendazole‐treated school children in Bangladesh. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2001;55(1):1‐9. - PubMed
Pickering 2019 {published data only}
-
- Pickering AJ, Njenga SM, Steinbaum L, Stwarthout J, Lin A, Arnold BF, et al. Effects of single and integrated water, sanitation, handwashing, and nutrition interventions on child soil‐transmitted helminth and Giardia infections: a cluster‐randomized controlled trial in rural Kenya. PLoS Medicine 2019;16(6):e1002841. - PMC - PubMed
Pond 1970 {published data only}
-
- Pond HS, Bokat RB, Johnson JP, Knight JL, Healy GR, Gleason NN, et al. Mass treatment for ascariasis: value of prophylactic use of piperazine in groups heavily infected with Ascaris lumbricoides. Southern Medical Association 1970;63(5):599‐602. - PubMed
Pullan 2019 {published data only}
Rahman 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rahman WA. Comparative trials using albendazole and mebendazole in treatment of soil‐transmitted helminths in schoolchildren on Penang, Malaysia. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1996;27(4):765‐7. - PubMed
Rahman 1998 {published data only}
-
- Rahman WA. Helminthic infections of urban and rural school children in Penang Island, Malasia: implications for control. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1998;29(3):596‐8. - PubMed
Raj 1998 {published data only}
-
- Raj SM, Naing NN. Ascariasis, trichuriasis, and growth of schoolchildren in Northeastern Peninsular Malaysia. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1998;29(4):729‐34. - PubMed
Reddy 1986 {published data only}
-
- Reddy V, Vijayaraghsvsn K, Mathur KK. Effect of deworming and vitamin A administration on serum vitamin A levels in preschool children. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics 1986;32(4):196‐9. - PubMed
Restrepo 1987 {published data only}
-
- Restrepo M, Isaza D. Estudio comparativo de flubendazol, oxantel‐pirantel, albendazol y mebendazol en el tratamiento de helmintos transmitidos por el suelo. Acta Médica Colombiana 1987;12(5):344‐51.
Rousham 1994 {published data only}
-
- Rousham EK, Mascie‐Taylor CG. An 18‐month study of the effect of periodic anthelminthic treatment on the growth and nutritional status of pre‐school children in Bangladesh. Annals of Human Biology 1994;21(4):315‐24. - PubMed
Sarmah 1988 {published data only}
-
- Sarmah HC. A randomised controlled trial of pyrantel and mebendazole in children with enterobiasis and concomitant ascariasis. Indian Pediatrics 1988;25(6):544‐7. - PubMed
Seftel 1968 {published data only}
Seo 1980 {published data only}
-
- Seo BS, Cho SY, Chai JY, Hong ST. Comparative efficacy of various interval mass treatment of Ascaris lumbricoides infection in Korea. Kisaengch'unghak Chapchi [Korean Journal of Parasitology] 1980;18(2):145‐51. - PubMed
Sileshi 2017 {published data only}
-
- Sileshi B, Suleman S, Wynendaele E, Kosgei A, Duchateau L, Siegeleer B, et al. Poor dissolution of anthelminthic medicines: a risk for reduced efficacy. Tropical Medicine and International Health 2017;22(S1):353.
Sinniah 1981 {published data only}
-
- Sinniah B, Sinniah D. The anthelmintic effects of pyrantel pamoate, oxantel‐pyrantel pamoate, levamisole and mebendazole in the treatment of intestinal nematodes. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology 1981;75(3):315‐21. - PubMed
Sood 1975 {published data only}
-
- Sood S, Kini AS, Master J. Comparison of pyrantel and tetramisole in ascariasis. Indian Pediatrics 1975;12(8):689‐92. - PubMed
Speich 2016 {published data only}
Staal 2018 {published data only}
Steinmann 2008 {published data only}
Stephenson 1990 {published data only}
-
- Stephenson LS, Latham MC, Kinoti SN, Kurz KM, Brigham H. Improvements in physical fitness of Kenyan schoolboys infected with hookworm, Trichuris trichiura and Ascaris lumbricoides following a single dose of albendazole. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1990;84(2):277‐82. - PubMed
Stoltzfus 1997 {published data only}
-
- Stoltzfus RJ, Albonico M, Tielsch JM, Chwaya HM, Savioli L. School‐based deworming program yields small improvement in growth of Zanzibari school children after one year. Journal of Nutrition 1997;127(11):2187‐93. - PubMed
Stoltzfus 2001 {published data only}
-
- Stoltzfus RJ, Kvalsvig JD, Chwaya HW, Montresor A, Albonico M. Effects of iron supplementation and anthelmintic treatment on motor and language development of preschool children in Zanzibar: double blind placebo controlled study. British Medical Journal (Clinical Research Ed.) 2001;323(7326):1389‐93. - PMC - PubMed
Supali 2017 {published data only}
-
- Supali T, Djuardi Y, Christian M, Iskandar E, Maylasari R, Wondmeneh S, et al. A single dose of ivermectin, dec plus albendazole is superior to dec plus albendazole for treatment of Trichuris trichiura in Indonesia. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2017;97:614.
Tankhiwale 1989 {published data only}
-
- Tankhiwale SR, Kukade AL, Sarmah HC, Salunkhe DS, Kulkarni AS. Single dose therapy of ascariasis – a randomized comparison of mebendazole and pyrantel. Journal of Communicable Diseases 1989;21(1):71‐4. - PubMed
Tanumihardjo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Tanumihardjo SA, Permaesih D, Muhilal. Vitamin A status and hemoglobin concentrations are improved in Indonesian children with vitamin A and deworming interventions. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2004;58(9):1223‐30. - PubMed
Taylor 2001 {published data only}
-
- Taylor M, Jinabhai CC, Couper I, Kleinschmidt I, Jogessar VB. The effect of different anthelmintic treatment regimens combined with iron supplementation on the nutritional status of schoolchildren in KwaZulu‐Natal, South Africa: a randomized controlled trial. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2001;95(2):211‐6. - PubMed
Thein‐Hlaing 1991a {published data only}
-
- Thein‐Hlaing, Than‐Saw, Myat‐Lay‐Kyin. The impact of three‐monthly age‐targeted chemotherapy on Ascaris lumbricoides infection. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1991;85(4):519‐22. - PubMed
Thein‐Hlaing 1991b {published data only}
-
- Thein‐Hlaing, Thane‐Toe, Than‐Saw, Myat‐Lay‐Kyin, Myint‐Lwin. A controlled chemotherapeutic intervention trial on the relationship between Ascaris lumbricoides infection and malnutrition in children. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1991;85(4):523‐8. - PubMed
Urjel 1985 {published data only}
-
- Urjel D, Recacoechea SM, Darras C, Zuna V, Cardozo C, Carrasco J. Efficacy after 6 months of different therapeutic schedules of mebendazole in infections by A. lumbricoides, Ancylostomidae sp and T. trichiura in school children [Eficacia a los seis meses de diferentes esquemas terapeuticos de mebendazol en las infecciones por A. lumbricoides, ancylostomidae SP y T. trichiura en niños de edad escolar]. Boletín Científico del CENETROP 1985;11(1):13‐20.
Vaz Nery 2019 {published data only}
-
- Vaz Nery S, Traub RJ, McCarthy JS, Clarke NE, Amaral S, Llewellyn S, et al. WASH for WORMS: a cluster‐randomized controlled trial of the impact of a community integrated water, sanitation, and hygiene and deworming intervention on soil‐transmitted helminth infections. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2019;100(3):750‐61. - PMC - PubMed
Walson 2008 {published data only}
Walson 2010 {published data only}
Wang 1987 {published data only}
-
- Wang BR, Wang HC, Li LW, Zhang XL, Yue JQ, Wang GX, et al. Comparative efficacy of thienpydin, pyrantel pamoate, mebendazole and albendazole in treating ascariasis and enterobiasis. Chinese Medical Journal 1987;100(11):928‐30. - PubMed
Watkins 1996b {published data only}
-
- Watkins WE, Cruz JR, Pollitt E. The effects of deworming on indicators of school performance in Guatemala. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1996;90(2):156‐60. - PubMed
Wesche 1994 {published data only}
-
- Wesche D, Lutz S, Barnish G. Comparative study of chewable pyrantel pamoate: should standards for chewable tablets be revised?. Papua and New Guinea Medical Journal 1994;37(1):12‐4. - PubMed
Whitworth 1991 {published data only}
-
- Whitworth JA, Morgan D, Maude GH, McNicholas AM, Taylor DW. A field study of the effect of ivermectin on intestinal helminths in man. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 1991;85(2):232‐4. - PubMed
Willett 1979 {published data only}
Williams 1997 {published data only}
-
- Williams RA, Koroma MM, Hodges M. Comparison of albendazole and levamisole chemotherapy on prevalence and intensity of common soil‐transmitted helminth infection in school children, Sierra Leone. West African Journal of Medicine 1997;16(3):179‐83. - PubMed
Wright 2009 {published data only}
Yangco 1981 {published data only}
-
- Yangco BG, Klein TW, Deresinski SC, Vickery AC, Craig CP. Flubendazole and mebendazole in the treatment of trichuriasis and other helminthiases. Clinical Therapeutics 1981;4(4):285‐90. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT02636803 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT02636803. Study of the efficacy of oxfendazole compared to albendazole in the treatment of Trichuris trichiura infection in adults. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02636803 (first received 22 December 2015).
TCTR20190111001 {unpublished data only}
-
- Sanprasert V. Assessment of efficacy of anthelmintic drugs against soil‐transmitted helminths in Thailand. www.clinicaltrials.in.th/index.php?tp=regtrials&menu=trialsearch&smenu=f... (first received 10 January 2019).
Additional references
Asaolu 1991
-
- Asaolu SO, Holland CV, Crompton DW. Community control of Ascaris lumbricoides in rural Oyo State, Nigeria: mass, targeted and selective treatment with levamisole. Parasitology 1991;103(Pt 2):291‐8. - PubMed
Ayana 2019
Bell 1975
-
- Bell DR. Diagnosis of parasitic diseases by filtration. Annales de la Société Belge de la Médicine Tropicale 1975;55(5):489‐96. - PubMed
Bennett 2000
-
- Bennett A, Guyatt H. Reducing intestinal nematode infection: efficacy of albendazole and mebendazole. Parasitology Today 2000;16(2):71‐4. - PubMed
Bergquist 2009
-
- Bergquist R, Johansen MV, Utzinger J. Diagnostic dilemmas in helminthology: what tools to use and when?. Trends in Parasitology 2009;25(4):151‐6. - PubMed
Bethony 2006
-
- Bethony J, Brooker S, Albonico M, Geiger SM, Loukas A, Diemert D, et al. Soil‐transmitted helminth infections: ascariasis, trichuriasis, and hookworm. Lancet 2006;367(9521):1521‐32. - PubMed
Campbell 2016
CDC 2009
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites and health: ascariasis. dpd.cdc.gov/DPDx/HTML/Ascariasis.htm. Atlanta, GA, U.S., (accessed 5 December 2011).
Clarke 2017
-
- Clarke NE, Clements AC, Doi SA, Wang D, Campbell SJ, Gray D, et al. Differential effect of mass deworming and targeted deworming for soil‐transmitted helminth control in children: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Lancet 2017;389(10066):287‐97. - PubMed
Cools 2019
-
- Cools P, Vlaminck J, Albonico M, Ame S, Ayana M, José Antonio BP, et al. Diagnostic performance of a single and duplicate Kato‐Katz, Mini‐FLOTAC, FECPAKG2 and qPCR for the detection and quantification of soil‐transmitted helminths in three endemic countries. PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2019;13(8):e0007446. - PMC - PubMed
Cooper 2009
Crompton 1989
-
- Crompton DW, Nesheim MC, Pawlowski ZS, editor(s). Biology of Ascaris lumbricoides. Ascariasis and Its Prevention and Control. London: Taylor and Francis, 1989:9‐44.
de Silva 2015
Degarege 2016
del Castillo 1964
Diaz 2003
-
- Diaz E, Mondragon J, Ramirez E, Bernal R. Epidemiology and control of intestinal parasites with nitazoxanide in children in Mexico. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2003;68(4):384‐5. - PubMed
Ehrhardt 2008
Fenton 2013
Flohr 2007
-
- Flohr C, Tuyen LN, Lewis S, Minh TT, Campbell J, Britton J, et al. Low efficacy of mebendazole against hookworm in Vietnam: two randomised controlled trials. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 2007;76(4):732‐6. - PubMed
Galvan‐Ramirez 2007
-
- Galvan‐Ramirez ML, Rivera N, Loeza ME, Avila X, Acero J, Troyo R, et al. Nitazoxanide in the treatment of Ascaris lumbricoides in a rural zone of Colima, Mexico. Journal of Helminthology 2007;81(3):255‐9. - PubMed
GBD 2017
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990‐2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017;390(10100):1211‐59. - PMC - PubMed
Geary 2010
-
- Geary TG, Woo K, McCarthy JS, Mackenzie CD, Horton J, Prichard RK, et al. Unresolved issues in anthelmintic pharmacology for helminthiases of humans. International Journal for Parasitology 2010;40(1):1‐13. - PubMed
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro. Version 3.2 for Windows. GRADE Working Group, 2008.
Hall 2008
Hefny 2009
-
- Hefny AF, Saadeldin YA, Abu‐Zidan FM. Management algorithm for intestinal obstruction due to ascariasis: a case report and review of the literature. Turkish Journal of Trauma & Emergency Surgery 2009;15(3):301‐5. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s).Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Holland 2009
-
- Holland CV. Predisposition to ascariasis: patterns, mechanisms and implications. Parasitology 2009;136(12):1537‐47. - PubMed
Jardim‐Botelho 2008
Katz 1972
-
- Katz N, Chaves A, Pellegrino J. A simple device for quantitative stool thick‐smear technique in Schistosomiasis mansoni. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de São Paulo 1972;14(6):397‐400. - PubMed
Keiser 2008
-
- Keiser J, Utzinger J. Efficacy of current drugs against soil‐transmitted helminth infections: systematic review and meta‐analysis. Journal of the American Medical Association 2008;299(16):1937‐48. - PubMed
Khurana 2017
Khuroo 1985
-
- Khuroo MS, Zargar SA. Biliary ascariasis. A common cause of biliary and pancreatic disease in an endemic area. Gastroenterology 1985;88(2):418‐23. - PubMed
Khuroo 1990
-
- Khuroo MS, Zargar SA, Mahajan R. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic ascariasis in India. Lancet 1990;335(8704):1503‐6. - PubMed
Kofie 1983
-
- Kofie BA, Dipeolu OO. A study of human and porcine ascariasis in a rural area of South‐West Nigeria. International Journal of Zoonoses 1983;10(1):66‐70. - PubMed
Leonardi‐Bee 2006
-
- Leonardi‐Bee J, Pritchard D, Britton J. Asthma and current intestinal parasite infection: systematic review and meta‐analysis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;174(5):514‐23. - PubMed
Levecke 2014
Long 2007
-
- Long KZ, Rosado JL, Montoya Y, de Lourdes Solano M, Hertzmark E, DuPont HL, et al. Effect of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on gastrointestinal parasitic infections among Mexican children. Pediatrics 2007;120(4):e846‐55. - PubMed
Maruyama 1997
-
- Maruyama H, Nawa Y, Noda S, Mimori T. An outbreak of ascariasis with marked eosinophilia in the southern part of Kyushu District, Japan, caused by infection with swine ascaris. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 1997;28(Suppl 1):194‐6. - PubMed
Montresor 2015
Montresor 1998
-
- Montresor A, Crompton DW, Hall A, Bundy DA, Savioli L. Guidelines for the evaluation of soil‐transmitted helminthiasis and schistosomiasis at community level. whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/1998/WHO_CTD_SIP_98.1.pdf (accessed prior to 31 January 2020).
Moser 2017b
Mrus 2017
-
- Mrus J, Baeten B, Engelen M, Silber SA. Efficacy of single‐dose 500 mg mebendazole in soil‐transmitted helminth infections: a review. Journal of Helminthology 2017;18:1‐10. - PubMed
O'Connell 2016
Palmeirim 2018b
-
- Palmeirim MS, Hürlimann E, Knopp S, Speich B, Belizario V Jr, Joseph SA, et al. Efficacy and safety of co‐administered ivermectin plus albendazole for treating soil‐transmitted helminths: a systematic review meta‐analysis and individual patient data analysis. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 2018;12(4):e0006458. - PMC - PubMed
Papaiakovou 2019
Pawlowski 1985
-
- Pawlowski ZS. Public health practice: ascariasis control. World Health Forum 1985;6(3):254‐6.
Pullan 2014
Reeder 1998
-
- Reeder MM. The radiological and ultrasound evaluation of ascariasis of the gastrointestinal, biliary, and respiratory tracts. Seminars in Roentgenology 1998;33(1):57‐78. - PubMed
Review Manager 2014 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Salam 2015
-
- Salam RA, Haider BA, Humayun Q, Bhutta ZA. Effect of administration of antihelminthics for soil‐transmitted helminths during pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Online) 2015;6:CD005547. - PubMed
Santos 2005
-
- Santos FL, Cerqueira EJ, Soares NM. Comparison of the thick smear and Kato‐Katz techniques for diagnosis of intestinal helminth infections. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Medecina Tropical 2005;38(2):196‐8. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org. The Cochrane Collaboration.
Stelekati 2012
Stepek 2006
Stephenson 2000
-
- Stephenson LS, Latham MC, Ottesen EA. Malnutrition and parasitic helminth infections. Parasitology 2000;121(Suppl):S23‐38. - PubMed
Taylor‐Robinson 2019
Utzinger 2004
-
- Utzinger J, Keiser J. Schistosomiasis and soil‐transmitted helminthiasis: common drugs for treatment and control. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy 2004;5(2):263‐85. - PubMed
Venkatesan 1998
-
- Venkatesan P. Albendazole. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1998;41(2):145‐7. - PubMed
Vercruysse 2011a
Vercruysse 2011b
WHO 2000
-
- World Health Organization. The use of essential drugs. Ninth report of the WHO Expert Committee. WHO Technical Report Series, No. 895 2000:1‐61. - PubMed
WHO 2001
-
- World Health Organization. Water related diseases: ascariasis. www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/diseases/ascariasis/en/ (accessed 20 September 2010).
WHO 2002
-
- World Health Organization. Prevention and control of schistosomiasis and soil‐transmitted helminthiasis: report of a WHO expert committee. WHO Technical Report Series No. 912 2002:1‐63. - PubMed
WHO 2005
-
- World Health Organization. Deworming for health and development. Report of the third global meeting of the partners for parasite control. Geneva, 29‐30 November 2004. apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/69005/WHO_CDS_CPE_PVC_2005.14.pdf (accessed prior to 31 January 2020).
WHO 2011
-
- World Health Organization. Helminth control in school‐age children: a guide for managers of control programmes. WHO Technical Report Series 2011:1‐90.
WHO 2012
-
- World Health Organization. Soil‐transmitted helminthiases: eliminating soil‐transmitted helminthiases as a public health problem in children. Progress report 2001‐2010 and strategic plan 2011‐2020. whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2012/9789241503129_eng.pdf (accessed prior to 31 January 2020.
WHO 2017a
-
- World Health Organization. Soil‐transmitted helminth infections. www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs366/en/ (accessed 19 August 2017).
WHO 2017b
-
- World Health Organization. The selection and use of essential medicines. WHO Technical Report Series 2017;1006:1‐604. - PubMed
Wolstenholme 2004
-
- Wolstenholme AJ, Fairweather I, Prichard R, Samson‐Himmelstjerna G, Sangster NC. Drug resistance in veterinary helminths. Trends in Parasitology 2004;20(10):469‐76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


