Pattern and Frequency of Seroreactivity to Routinely Used Serologic Tests in Early-Treated Infants With HIV
- PMID: 31917751
- PMCID: PMC7050817
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002254
Pattern and Frequency of Seroreactivity to Routinely Used Serologic Tests in Early-Treated Infants With HIV
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have shown low frequencies of seroreactivity to HIV diagnostic assays for infected infants treated with antiretroviral therapy (ART) early in infection.
Methods: Fifty-eight HIV-infected infants treated with ART at a median age of 1.9 months (range: 0.2-5.4) for up to 4 years of life were assessed for seroreactivity to 4 routinely used HIV clinical immunoassays (IA): Second-generation (2ndG) IA and 2 rapid diagnostic tests (RDT), based on third-generation principles, measuring antibody only and a fourth-generation (4thG) antigen/antibody IA. HIV Western blot assay was also performed to assess HIV-specific antibodies.
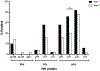
Results: The 2ndG IA demonstrated the highest frequency of seroreactivity in children (69%) followed by the 4thG IA (40%) and the RDT (26%) after one year of ART. Infants initiating ART during ages 3-6 months (N = 15) showed a greater frequency (range: 53%-93%) and breadth (median and range: 3 [1-4]) of reactivity across the assays compared with those treated within 3 months (N = 43):16%-61% and breadth (1 [0-4]). The 4thG IA showed significantly reduced reactivity relative to the 2ndG IA at one (P = 0.016) and 3 (P = 0.004) years of ART. Western blot profiles following 3 years of ART showed the highest frequency of reactivity to HIV Gag p24 (76%) and lowest reactivity to Env gp120 and gp41, with only 24% of children confirmed positive by the assay.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the use of 4thG IA and RDT test combination algorithms with limited HIV antigen breadth may not be adequate for diagnosis of HIV-infected children following early treatment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy During Acute HIV-1 Infection Leads to a High Rate of Nonreactive HIV Serology.Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Aug 15;63(4):555-61. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw365. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Clin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27317797
-
Decreased Seroreactivity in Individuals Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy during Acute HIV Infection.J Clin Microbiol. 2019 Sep 24;57(10):e00757-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00757-19. Print 2019 Oct. J Clin Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31217270 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivity of routine HIV antibody tests in children who initiated antiretroviral therapy in early infancy as part of the Children with HIV Early Antiretroviral Therapy (CHER) trial: a retrospective analysis.Lancet Infect Dis. 2015 Jul;15(7):803-9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00087-0. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26043884 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) for treating HIV infection in ART-eligible pregnant women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;(3):CD008440. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008440. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20238370 Review.
-
Effectiveness of antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected children under 2 years of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jul 11;(7):CD004772. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004772.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 22;(5):CD004772. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004772.pub4 PMID: 22786492 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
The contemporary immunoassays for HIV diagnosis: a concise overview.Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2023 Aug 7;17(1):3-12. doi: 10.2478/abm-2023-0038. eCollection 2023 Feb. Asian Biomed (Res Rev News). 2023. PMID: 37551202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Combination Antiretroviral Therapy on HIV-1 Serological Responses and Their Implications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 30;13:844023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.844023. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ananworanich J, Puthanakit T, Suntarattiwong P, et al. Reduced markers of HIV persistence and restricted HIV-specific immune responses after early antiretroviral therapy in children. AIDS (London, England). 2014;28(7):1015–1020. - PubMed
-
- de Souza MS, Pinyakorn S, Akapirat S, et al. Initiation of Antiretroviral Therapy During Acute HIV-1 Infection Leads to a High Rate of Nonreactive HIV Serology. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2016;63(4):555–561. - PubMed
-
- Payne H, Mkhize N, Otwombe K, et al. Reactivity of routine HIV antibody tests in children who initiated antiretroviral therapy in early infancy as part of the Children with HIV Early Antiretroviral Therapy (CHER) trial: a retrospective analysis. The Lancet Infectious diseases. 2015;15(7):803–809. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hainaut M, Peltier CA, Goetghebuer T, et al. Seroreversion in children infected with HIV type 1 who are treated in the first months of life is not a rare event. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2005;41(12):1820–1821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


