Systemic serotonin inhibits brown adipose tissue sympathetic nerve activity via a GABA input to the dorsomedial hypothalamus, not via 5HT1A receptor activation in raphe pallidus
- PMID: 31599481
- PMCID: PMC7035194
- DOI: 10.1111/apha.13401
Systemic serotonin inhibits brown adipose tissue sympathetic nerve activity via a GABA input to the dorsomedial hypothalamus, not via 5HT1A receptor activation in raphe pallidus
Abstract
Aim: Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), an important neurotransmitter and hormone, modulates many physiological functions including body temperature. We investigated neural mechanisms involved in the inhibition of brown adipose tissue (BAT) sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) and BAT thermogenesis evoked by 5-HT.
Methods: Electrophysiological recordings, intravenous (iv) injections and nanoinjections in the brains of anaesthetized rats.
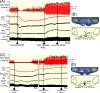
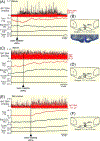
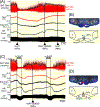
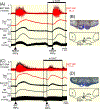
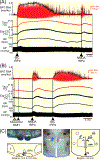
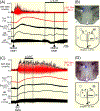
Results: Cooling-evoked increases in BAT SNA were inhibited by the intra-rostral raphé pallidus (rRPa) and the iv administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-OH-DPAT or 5-HT. The intra-rRPa 5-HT, the intra-rRPa and the iv 8-OH-DPAT, but not the iv 5-HT-induced inhibition of BAT SNA were prevented by nanoinjection of a 5-HT1A receptor antagonist in the rRPa. The increase in BAT SNA evoked by nanoinjection of NMDA in the rRPa was not inhibited by iv 5-HT, indicating that iv 5-HT does not inhibit BAT SNA by acting in the rRPa or in the sympathetic pathway distal to the rRPa. In contrast, under a warm condition, blockade of 5HT1A receptors in the rRPa increased BAT SNA and BAT thermogenesis, suggesting that endogenous 5-HT in the rRPa contributes to the suppression of BAT SNA and BAT thermogenesis. The increases in BAT SNA and BAT thermogenesis evoked by nanoinjection of NMDA in the dorsomedial hypothalamus (DMH) were inhibited by iv 5-HT, but those following bicuculline nanoinjection in the DMH were not inhibited.
Conclusions: The systemic 5-HT-induced inhibition of BAT SNA requires a GABAergic inhibition of BAT sympathoexcitatory neurones in the DMH. In addition, during warming, 5-HT released endogenously in rRPa inhibits BAT SNA.
Keywords: 5-hydroxytryptamine; brown adipose tissue; hypothalamus; raphé pallidus; thermoregulation.
© 2019 Scandinavian Physiological Society. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tonic inhibition of brown adipose tissue sympathetic nerve activity via muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in the rostral raphe pallidus.J Physiol. 2017 Dec 15;595(24):7495-7508. doi: 10.1113/JP275299. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29023733 Free PMC article.
-
Glycinergic inhibition of BAT sympathetic premotor neurons in rostral raphe pallidus.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):R919-R926. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00551.2016. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28254751 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic input from the posterior hypothalamus to the raphe pallidus area inhibits brown adipose tissue thermogenesis.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021 Dec 1;321(6):R938-R950. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00149.2021. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34704845 Free PMC article.
-
[Dapagliflozin, a Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitor, Acutely Reduces Energy Expenditure in Brown Adipose Tissue via Neural Signals in Mice].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018;138(7):945-954. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.17-00223-3. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2018. PMID: 29962474 Review. Japanese.
-
Central neural control of thermoregulation and brown adipose tissue.Auton Neurosci. 2016 Apr;196:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2016.02.010. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Auton Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26924538 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cell stabilizer, an anti-allergic drug, reduces ventricular arrhythmia risk via modulation of neuroimmune interaction.Basic Res Cardiol. 2024 Feb;119(1):75-91. doi: 10.1007/s00395-023-01024-y. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Basic Res Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38172251
-
Constitutive Serotonin Tone as a Modulator of Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis: A Rat Study.Life (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;13(7):1436. doi: 10.3390/life13071436. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37511811 Free PMC article.
-
Mediobasal hypothalamic neurons contribute to the control of brown adipose tissue sympathetic nerve activity and cutaneous vasoconstriction.J Therm Biol. 2023 May;114:103551. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2023.103551. Epub 2023 May 11. J Therm Biol. 2023. PMID: 37216765 Free PMC article.
-
High Fat Diet Suppresses Energy Expenditure Via Neurons in the Brainstem.Neuroscience. 2023 Jun 1;520:84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.04.006. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Neuroscience. 2023. PMID: 37054945 Free PMC article.
-
Acute deep brain stimulation of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus increases brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in rats.Neurosci Lett. 2023 Mar 16;799:137130. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2023.137130. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Neurosci Lett. 2023. PMID: 36792026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sevoz C, Callera JC, Machado BH, Hamon M, Laguzzi R. Role of serotonin3 receptors in the nucleus tractus solitarii on the carotid chemoreflex. Am J Physiol. 1997;272(3 Pt 2):H1250–1259. - PubMed
-
- Shajib MS, Khan WI. The role of serotonin and its receptors in activation of immune responses and inflammation. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015;213(3):561–574. - PubMed
-
- Marston OJ, Garfield AS, Heisler LK. Role of central serotonin and melanocortin systems in the control of energy balance. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;660(1):70–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials


