Prevention of cisplatin-induced hearing loss by extended release fluticasone propionate intracochlear implants
- PMID: 30913504
- PMCID: PMC6502669
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.03.021
Prevention of cisplatin-induced hearing loss by extended release fluticasone propionate intracochlear implants
Abstract
Objective: Cisplatin is a chemotherapeutic drug known to induce hearing loss. Although corticosteroids may help to mitigate the ototoxic side effects of cisplatin, there are complications associated with their systemic and prolonged use. The goal of this study is to test the efficacy of extended-release fluticasone propionate intracochlear implant particles to protect against cisplatin-induced hearing loss.
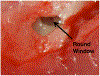
Methods: We used guinea pigs (n = 9) injected with cisplatin (IP, 12 mg/kg weight). Fluticasone particles were delivered to the cochlear scala tympani through the round window membrane into the right ears of the guinea pigs (left ears being used as a control) two weeks prior to cisplatin administration, and hearing function was evaluated by ABR and DPOAE before implantation, immediately before cisplatin administration, and 2 weeks after the challenge with cisplatin. Data was statistically evaluated using paired t-test analysis.
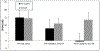
Results: No significant differences were observed in ABR threshold between control and implanted ears on day 14 (23.9 ± 2.3 dB vs. 25.6 ± 1.3 dB, P = 0.524), whereas the significant cisplatin-induced hearing loss in control animals (23.9 ± 2.3 dB at day 14 vs. 40.7 ± 2.5 dB at day 28, P ≤ 0.0001) was prevented in implanted animals (25.6 ± 1.3 dB at day 14 vs. 25.0 ± 3.1 at day 28, P ≥ 0.85). A similar, though not statistically significant, trend was observed in DPOAE responses in untreated ears (7.9 ± 5.8 dB at day14 vs. -0.5 ± 5.3 dB at day 28, P = 0.654) as compared to treatment (11.1 ± 3.4 dB at day 14 vs. 13.6 ± 4.8 dB at day 28, P = 0.733).
Conclusion: These results suggest that fluticasone intracochlear implants are safe and able to provide effective otoprotection against cisplatin-induced hearing loss in the guinea pig model.
Keywords: Cisplatin; Cochlea; Corticosteroids; Implantation; Ototoxicity.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
E.P. and W.S. own stock in O-Ray Pharma.
Figures





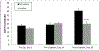
Similar articles
-
Dexamethasone-loaded chitosan-based genipin-cross-linked hydrogel for prevention of cisplatin induced ototoxicity in Guinea pig model.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Jul;122:60-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.04.003. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30974336
-
A Polymer-Based Extended Release System for Stable, Long-term Intracochlear Drug Delivery.Otol Neurotol. 2018 Oct;39(9):1195-1202. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001977. Otol Neurotol. 2018. PMID: 30199502 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a dexamethasone-releasing implant on cochleae: A functional, morphological and pharmacokinetic study.Hear Res. 2015 Sep;327:89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.04.019. Epub 2015 May 15. Hear Res. 2015. PMID: 25987502
-
Protective effect of thymoquinone against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013 Aug;270(8):2231-7. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-2254-6. Epub 2012 Nov 17. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2013. PMID: 23161274
-
Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: Updates on molecular mechanisms and otoprotective strategies.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Jun;163:60-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 33775853 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogel Matrix Containing Microcarriers for Dexamethasone Delivery to Protect Against Cisplatin-Induced Hearing Loss.Cureus. 2024 Oct 9;16(10):e71142. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71142. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39386930 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of an optimized guinea pig model of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Apr 13;10:1112857. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1112857. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37124562 Free PMC article.
-
Low-intensity low-frequency pulsed ultrasound ameliorates sciatic nerve dysfunction in a rat model of cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy.Sci Rep. 2022 May 17;12(1):8125. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11978-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35581281 Free PMC article.
-
Current Strategies to Combat Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 3;11:999. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00999. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32719605 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trzaska S, Cisplatin. Chemical & Engineering News. 83(25) (2005).
-
- Frisina RD, Wheeler HE, Fossa SD, Kerns SL, Fung C, Sesso HD, Monahan PO, Feldman DR, Hamilton R, Vaughn DJ, Beard CJ, Budnick A, Johnson EM, Ardeshir-Rouhani-Fard S, Einhorn LH, Lipshultz SE, Dolan ME, Travis LB, Comprehensive Audiometric Analysis of Hearing Impairment and Tinnitus After Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Survivors of Adult-Onset Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 34(23) (2016) 2712–20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kopelman J, Budnick AS, Sessions RB, Kramer MB, Wong GY, Ototoxicity of high-dose cisplatin by bolus administration in patients with advanced cancers and normal hearing. Laryngoscope. 98(8 Pt 1) (1988) 858–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


