Mechanisms Underlying Serotonergic Excitation of Callosal Projection Neurons in the Mouse Medial Prefrontal Cortex
- PMID: 29422840
- PMCID: PMC5778113
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2018.00002
Mechanisms Underlying Serotonergic Excitation of Callosal Projection Neurons in the Mouse Medial Prefrontal Cortex
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Mechanisms Underlying Serotonergic Excitation of Callosal Projection Neurons in the Mouse Medial Prefrontal Cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2019 Apr 9;13:23. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00023. eCollection 2019. Front Neural Circuits. 2019. PMID: 31024266 Free PMC article.
Abstract
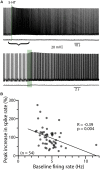
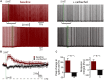
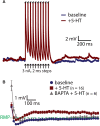
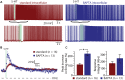
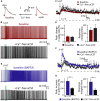
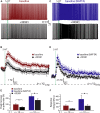
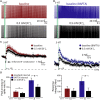
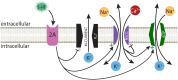
Serotonin (5-HT) selectively excites subpopulations of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex via activation of 5-HT2A (2A) receptors coupled to Gq subtype G-protein alpha subunits. Gq-mediated excitatory responses have been attributed primarily to suppression of potassium conductances, including those mediated by KV7 potassium channels (i.e., the M-current), or activation of non-specific cation conductances that underlie calcium-dependent afterdepolarizations (ADPs). However, 2A-dependent excitation of cortical neurons has not been extensively studied, and no consensus exists regarding the underlying ionic effector(s) involved. In layer 5 of the mouse medial prefrontal cortex, we tested potential mechanisms of serotonergic excitation in commissural/callosal (COM) projection neurons, a subpopulation of pyramidal neurons that exhibits 2A-dependent excitation in response to 5-HT. In baseline conditions, 5-HT enhanced the rate of action potential generation in COM neurons experiencing suprathreshold somatic current injection. This serotonergic excitation was occluded by activation of muscarinic acetylcholine (ACh) receptors, confirming that 5-HT acts via the same Gq-signaling cascades engaged by ACh. Like ACh, 5-HT promoted the generation of calcium-dependent ADPs following spike trains. However, calcium was not necessary for serotonergic excitation, as responses to 5-HT were enhanced (by >100%), rather than reduced, by chelation of intracellular calcium with 10 mM BAPTA. This suggests intracellular calcium negatively regulates additional ionic conductances gated by 2A receptors. Removal of extracellular calcium had no effect when intracellular calcium signaling was intact, but suppressed 5-HT response amplitudes, by about 50%, when BAPTA was included in patch pipettes. This suggests that 2A excitation involves activation of a non-specific cation conductance that is both calcium-sensitive and calcium-permeable. M-current suppression was found to be a third ionic effector, as blockade of KV7 channels with XE991 (10 μM) reduced serotonergic excitation by ∼50% in control conditions, and by ∼30% with intracellular BAPTA present. Together, these findings demonstrate a role for at least three distinct ionic effectors, including KV7 channels, a calcium-sensitive and calcium-permeable non-specific cation conductance, and the calcium-dependent ADP conductance, in mediating serotonergic excitation of COM neurons.
Keywords: 5-HT2A receptor; Kv7 channels; M-current; afterdepolarization; calcium; cortex; pyramidal neuron; serotonin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preferential cholinergic excitation of corticopontine neurons.J Physiol. 2018 May 1;596(9):1659-1679. doi: 10.1113/JP275194. Epub 2018 Feb 20. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29330867 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent serotonergic excitation of callosal projection neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Aug 26;8:97. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00097. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 25206322 Free PMC article.
-
A major role for thalamocortical afferents in serotonergic hallucinogen receptor function in the rat neocortex.Neuroscience. 2001;105(2):379-92. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(01)00199-3. Neuroscience. 2001. PMID: 11672605
-
Neural KCNQ (Kv7) channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;156(8):1185-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00111.x. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19298256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonergic regulation of neuronal excitability in the prefrontal cortex.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Sep;61(3):382-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.015. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21251917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Common and contrasting effects of 5-HTergic signaling in pyramidal cells and SOM interneurons of the mouse cortex.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Nov 7. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-02022-x. Online ahead of print. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39511335
-
Cellular rules underlying psychedelic control of prefrontal pyramidal neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 23:2023.10.20.563334. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.20.563334. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37961554 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Targeting 5-HT2A receptors and Kv7 channels in PFC to attenuate chronic neuropathic pain in rats using a spared nerve injury model.Neurosci Lett. 2022 Oct 15;789:136864. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.136864. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Neurosci Lett. 2022. PMID: 36063980 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin neurons modulate learning rate through uncertainty.Curr Biol. 2022 Feb 7;32(3):586-599.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.12.006. Epub 2021 Dec 21. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 34936883 Free PMC article.
-
NRG1, PIP4K2A, and HTR2C as Potential Candidate Biomarker Genes for Several Clinical Subphenotypes of Depression and Bipolar Disorder.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 25;11:936. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00936. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33193575 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Almada R. C., Coimbra N. C., Brandao M. L. (2015). Medial prefrontal cortex serotonergic and GABAergic mechanisms modulate the expression of contextual fear: intratelencephalic pathways and differential involvement of cortical subregions. Neuroscience 284 988–997. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.11.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


