Towards a better understanding of the cannabinoid-related orphan receptors GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12
- PMID: 29390908
- PMCID: PMC6093286
- DOI: 10.1080/03602532.2018.1428616
Towards a better understanding of the cannabinoid-related orphan receptors GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12
Abstract
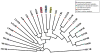
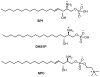
GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12 are three orphan receptors that belong to the Class A family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). These GPCRs share over 60% of sequence similarity among them. Because of their close phylogenetic relationship, GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12 share a high percentage of homology with other lipid receptors such as the lysophospholipid and the cannabinoid receptors. On the basis of sequence similarities at key structural motifs, these orphan receptors have been related to the cannabinoid family. However, further experimental data are required to confirm this association. GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12 are predominantly expressed in mammalian brain. Their high constitutive activation of adenylyl cyclase triggers increases in cAMP levels similar in amplitude to fully activated GPCRs. This feature defines their physiological role under certain pathological conditions. In this review, we aim to summarize the knowledge attained so far on the understanding of these receptors. Expression patterns, pharmacology, physiopathological relevance, and molecules targeting GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12 will be analyzed herein. Interestingly, certain cannabinoid ligands have been reported to modulate these orphan receptors. The current debate about sphingolipids as putative endogenous ligands will also be addressed. A special focus will be on their potential role in the brain, particularly under neurological conditions such as Parkinson or Alzheimer's disease. Reported physiological roles outside the central nervous system will also be covered. This critical overview may contribute to a further comprehension of the physiopathological role of these orphan GPCRs, hopefully attracting more research towards a future therapeutic exploitation of these promising targets.
Keywords: GPR12; GPR3; GPR6; Orphan receptors; cannabinoids; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a ligand of the human gpr3, gpr6 and gpr12 family of constitutively active G protein-coupled receptors.Cell Signal. 2002 Nov;14(11):941-53. doi: 10.1016/s0898-6568(02)00041-4. Cell Signal. 2002. PMID: 12220620
-
GPR3, GPR6, and GPR12 as novel molecular targets: their biological functions and interaction with cannabidiol.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019 Mar;40(3):300-308. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0031-9. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019. PMID: 29941868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Four Orphan Receptors (GPR3, GPR6, GPR12 and GPR12L) in Chickens and Ducks and Regulation of GPR12 Expression in Ovarian Granulosa Cells by Progesterone.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 27;12(4):489. doi: 10.3390/genes12040489. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801713 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for the Development of In Silico GPCR Models.Methods Enzymol. 2017;593:405-448. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28750813 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on Non-CB1, Non-CB2 Cannabinoid Related G-Protein-Coupled Receptors.Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017 Oct 1;2(1):265-273. doi: 10.1089/can.2017.0036. eCollection 2017. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017. PMID: 29098189 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New MiniPromoter Ple389 (ADORA2A) drives selective expression in medium spiny neurons in mice and non-human primates.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;14(1):28194. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79004-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39548191 Free PMC article.
-
CVN424, a GPR6 inverse agonist, for Parkinson's disease and motor fluctuations: a double-blind, randomized, phase 2 trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2024 Oct 18;77:102882. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.102882. eCollection 2024 Nov. EClinicalMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39469536 Free PMC article.
-
The Modulatory Effects and Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol in the Gut.Cells. 2024 Sep 26;13(19):1618. doi: 10.3390/cells13191618. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring orphan GPCRs in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jun 4;15:1394516. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394516. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38895631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional characterization of the endogenous agonist for orphan receptor GPR3.Cell Res. 2024 Mar;34(3):262-265. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00919-8. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 38287118 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Achiron A, Feldman A, Mandel M, Gurevich M. Impaired expression of peripheral blood apoptotic-related gene transcripts in acute multiple sclerosis relapse. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1107:155–167. - PubMed
-
- Adams ME, Brown JW, Hitchcock S, Kikuchi S, Lam B, Monenschein H, Reichard H, Sun H Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. Japan WO2015123533A1 Pyrazines as modulators of GPR6. 2015 Aug 20;
-
- Aldieri E, Riganti C, Polimeni M, Gazzano E, Lussiana C, Campia I, Ghigo D. Classical Inhibitors of NOX NAD(P)H Oxidases Are Not Specific. Curr Drug Metab. 2008;9:686–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

