Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Polyps Is Characterized by Increased Mucosal and Blood Th17 Effector Cytokine Producing Cells
- PMID: 29311948
- PMCID: PMC5742278
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00898
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Polyps Is Characterized by Increased Mucosal and Blood Th17 Effector Cytokine Producing Cells
Abstract
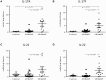
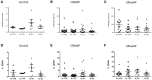
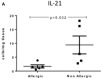
Background: Recent studies have implied a role for Th17 cells in CRS with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) patients. However, the capacity of these cells to produce Th17 cytokines is still unknown. Here we sought to quantify IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21, and IL-22 cytokines produced by Th17 cells in mucosal tissue and peripheral blood of CRSwNP, CRS without nasal polyps (CRSsNP) and control patients. Methods: Samples were prospectively collected from CRS patients and non-CRS controls. We used flow cytometry to characterize the Th17 cells and their cytokines in sinonasal tissue and peripheral blood. Results: A total of 36 patients were recruited to the study. CRSwNP patients had significantly more tissue IL-17A (9.53 ± 2.71 vs. 1.11 ± 0.43 vs. 0.77 ± 0.07), IL-17F (4.96 ± 1.48 vs. 0.88 ± 0.31 vs. 0.56 ± 0.04), IL-21 (5.55 ± 2.01 vs. 1.60 ± 0.71 vs. 1.53 ± 0.55) and IL-22 (4.73 ± 1.58 vs. 0.70 ± 0.28 vs. 0.88 ± 0.26) producing Th17 cells compared to CRSsNP and control mucosa per mg of tissue, respectively. Allergic CRSwNP patients had decreased numbers of IL-21 producing Th17 cells compared to non-Allergic CRSwNP. (1.69 ± 0.57 vs. 9.41 ± 3.23) per mg of tissue, respectively (Kruskal-Wallis p < 0.05). Conclusion: In summary our study identified increased numbers of IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-21 and IL-22 positive Th17 cells in CRSwNP patient polyps and peripheral blood suggesting an altered activation state of those cells both locally and systemically. Atopic CRSwNP had decreased amounts of tissue Th17 cell derived IL-21 implying a potential protective role for IL-21 in CRSwNP allergic inflammation.
Keywords: Th17; Th17 cytokines; chronic rhinosinusitis; flow cytometry; nasal polyps.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Naive and effector B-cell subtypes are increased in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018 Jan 1;32(1):3-6. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2018.32.4496. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29336281 Free PMC article.
-
T regulatory and Th17 cells in chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016 Aug;6(8):826-34. doi: 10.1002/alr.21742. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. PMID: 27012842
-
Mixed T helper cell signatures in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without polyps.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 9;9(6):e97581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097581. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24911279 Free PMC article.
-
Tc17/IL-17A Up-Regulated the Expression of MMP-9 via NF-κB Pathway in Nasal Epithelial Cells of Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Front Immunol. 2018 Sep 19;9:2121. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02121. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30283454 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting IL-25 as a novel therapy in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Feb;17(1):17-22. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000332. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27870664 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps as a Biomarker in Refractory Non-Type 2 CRSwNP.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024 Sep;16(5):473-489. doi: 10.4168/aair.2024.16.5.473. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 39363767 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of mucin hypersecretion in different inflammatory patterns based on endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis.Clin Transl Allergy. 2024 Jan;14(1):e12334. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12334. Clin Transl Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38282195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The correlation between FCER2 gene polymorphism and the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Nov;37(11):856-863. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.11.002. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37905480 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Psoriasis and Systemic Inflammatory Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 18;23(8):4457. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084457. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-infection of Malassezia sympodialis With Bacterial Pathobionts Pseudomonas aeruginosa or Staphylococcus aureus Leads to Distinct Sinonasal Inflammatory Responses in a Murine Acute Sinusitis Model.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Sep 4;10:472. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00472. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33014894 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


