Hepatic Diacylglycerol-Associated Protein Kinase Cε Translocation Links Hepatic Steatosis to Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Humans
- PMID: 28591572
- PMCID: PMC5469939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.035
Hepatic Diacylglycerol-Associated Protein Kinase Cε Translocation Links Hepatic Steatosis to Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Humans
Abstract
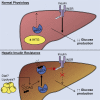
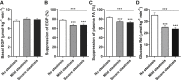
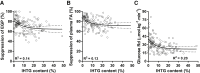
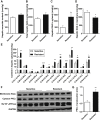
Hepatic lipid accumulation has been implicated in the development of insulin resistance, but translational evidence in humans is limited. We investigated the relationship between liver fat and tissue-specific insulin sensitivity in 133 obese subjects. Although the presence of hepatic steatosis in obese subjects was associated with hepatic, adipose tissue, and peripheral insulin resistance, we found that intrahepatic triglycerides were not strictly sufficient or essential for hepatic insulin resistance. Thus, to examine the molecular mechanisms that link hepatic steatosis to hepatic insulin resistance, we comprehensively analyzed liver biopsies from a subset of 29 subjects. Here, hepatic cytosolic diacylglycerol content, but not hepatic ceramide content, was increased in subjects with hepatic insulin resistance. Moreover, cytosolic diacylglycerols were strongly associated with hepatic PKCε activation, as reflected by PKCε translocation to the plasma membrane. These results demonstrate the relevance of hepatic diacylglycerol-induced PKCε activation in the pathogenesis of NAFLD-associated hepatic insulin resistance in humans.
Keywords: NAFLD; diacylglycerol; glucose clamp; hepatic glucose production; hepatic steatosis; human; insulin resistance; obesity; protein kinase Cε.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D on hepatic diacylglycerol accumulation, steatosis, and insulin resistance in diet-induced obesity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Feb 1;316(2):E239-E250. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00319.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30457913
-
Diacylglycerol activation of protein kinase Cε and hepatic insulin resistance.Cell Metab. 2012 May 2;15(5):574-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.03.005. Cell Metab. 2012. PMID: 22560210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ketogenic diet prevents steatosis and insulin resistance by reducing lipogenesis, diacylglycerol accumulation and protein kinase C activity in male rat liver.J Physiol. 2022 Sep;600(18):4137-4151. doi: 10.1113/JP283552. Epub 2022 Sep 4. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35974660
-
Hepatic steatosis by dietary-conjugated linoleic acid is accompanied by accumulation of diacylglycerol and increased membrane-associated protein kinase C ε in mice.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Jul;55(7):1010-7. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201000413. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21480517
-
Roles of Diacylglycerols and Ceramides in Hepatic Insulin Resistance.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Jul;38(7):649-665. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 May 24. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28551355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-fat-diet-induced hepatic insulin resistance per se attenuates murine de novo lipogenesis.iScience. 2024 Oct 15;27(11):111175. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111175. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39524330 Free PMC article.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Staging of Hepatic Fibrosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:539-574. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287864 Review.
-
Relationship of weight-adjusted waist index and developmental disabilities in children 6 to 17 years of age: a cross-sectional study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 4;15:1406996. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1406996. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39027477 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance in South Asian and Nordic Women after Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Metabolites. 2024 May 18;14(5):288. doi: 10.3390/metabo14050288. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38786765 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic glucose metabolism in the steatotic liver.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 May;21(5):319-334. doi: 10.1038/s41575-023-00888-8. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38308003 Review.
References
-
- Ackermans M.T., Pereira Arias A.M., Bisschop P.H., Endert E., Sauerwein H.P., Romijn J.A. The quantification of gluconeogenesis in healthy men by (2)H2O and [2-(13)C]glycerol yields different results: Rates of gluconeogenesis in healthy men measured with (2)H2O are higher than those measured with [2-(13)C]glycerol. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;86:2220–2226. - PubMed
-
- Buettner R., Ottinger I., Schölmerich J., Bollheimer L.C. Preserved direct hepatic insulin action in rats with diet-induced hepatic steatosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004;286:E828–E833. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


