A High-Resolution In Vivo Atlas of the Human Brain's Serotonin System
- PMID: 28053035
- PMCID: PMC5214625
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2830-16.2016
A High-Resolution In Vivo Atlas of the Human Brain's Serotonin System
Abstract
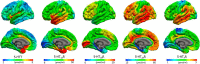
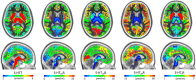
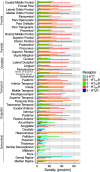
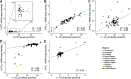
The serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) system modulates many important brain functions and is critically involved in many neuropsychiatric disorders. Here, we present a high-resolution, multidimensional, in vivo atlas of four of the human brain's 5-HT receptors (5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT4) and the 5-HT transporter (5-HTT). The atlas is created from molecular and structural high-resolution neuroimaging data consisting of positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans acquired in a total of 210 healthy individuals. Comparison of the regional PET binding measures with postmortem human brain autoradiography outcomes showed a high correlation for the five 5-HT targets and this enabled us to transform the atlas to represent protein densities (in picomoles per milliliter). We also assessed the regional association between protein concentration and mRNA expression in the human brain by comparing the 5-HT density across the atlas with data from the Allen Human Brain atlas and identified receptor- and transporter-specific associations that show the regional relation between the two measures. Together, these data provide unparalleled insight into the serotonin system of the human brain.
Significance statement: We present a high-resolution positron emission tomography (PET)- and magnetic resonance imaging-based human brain atlas of important serotonin receptors and the transporter. The regional PET-derived binding measures correlate strongly with the corresponding autoradiography protein levels. The strong correlation enables the transformation of the PET-derived human brain atlas into a protein density map of the serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) system. Next, we compared the regional receptor/transporter protein densities with mRNA levels and uncovered unique associations between protein expression and density at high detail. This new in vivo neuroimaging atlas of the 5-HT system not only provides insight in the human brain's regional protein synthesis, transport, and density, but also represents a valuable source of information for the neuroscience community as a comparative instrument to assess brain disorders.
Keywords: 5-HT; MRI; PET; atlas; autoradiography; mRNA.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/370120-09$15.00/0.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The structure of the serotonin system: A PET imaging study.Neuroimage. 2020 Jan 15;205:116240. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116240. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31600591 Free PMC article.
-
A high-resolution in vivo atlas of the human brain's benzodiazepine binding site of GABAA receptors.Neuroimage. 2021 May 15;232:117878. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.117878. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33610745 Free PMC article.
-
Autoradiographic distribution of serotonin transporters and receptor subtypes in human brain.Hum Brain Mapp. 2004 Jul;22(3):246-60. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20035. Hum Brain Mapp. 2004. PMID: 15195291 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin and molecular neuroimaging in humans using PET.Amino Acids. 2012 Jun;42(6):2039-57. doi: 10.1007/s00726-011-1078-9. Epub 2011 Sep 24. Amino Acids. 2012. PMID: 21947614 Review.
-
5-HT radioligands for human brain imaging with PET and SPECT.Med Res Rev. 2013 Jan;33(1):54-111. doi: 10.1002/med.20245. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Med Res Rev. 2013. PMID: 21674551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
OpenMAP-T1: A Rapid Deep-Learning Approach to Parcellate 280 Anatomical Regions to Cover the Whole Brain.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Nov;45(16):e70063. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70063. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39523990 Free PMC article.
-
How Psychedelics Modulate Multiple Memory Mechanisms in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder.Drugs. 2024 Nov;84(11):1419-1443. doi: 10.1007/s40265-024-02106-4. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39455547 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the neural correlates of working memory.BMC Biol. 2024 Oct 21;22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12915-024-02039-0. BMC Biol. 2024. PMID: 39428484 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating brainstem and cortical functional architectures.Nat Neurosci. 2024 Dec;27(12):2500-2511. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01787-0. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Nat Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39414973 Free PMC article.
-
Convergent functional effects of antidepressants in major depressive disorder: a neuroimaging meta-analysis.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 15. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02780-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39406999
References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Comtat C, Sureau FC, Sibomana M, Hong IK, Sjoholm N, Trebossen R. Image based resolution modeling for the HRRT OSEM reconstructions software. IEEE Nucl Sci Symp Conf Rec. 2008;2008:4120–4123.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

