The burden of health care costs for patients with dementia in the last 5 years of life
- PMID: 26502320
- PMCID: PMC4809412
- DOI: 10.7326/M15-0381
The burden of health care costs for patients with dementia in the last 5 years of life
Abstract
Background: Common diseases, particularly dementia, have large social costs for the U.S. population. However, less is known about the end-of-life costs of specific diseases and the associated financial risk for individual households.
Objective: To examine social costs and financial risks faced by Medicare beneficiaries 5 years before death.
Design: Retrospective cohort.
Setting: The HRS (Health and Retirement Study).
Participants: Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries, aged 70 years or older, who died between 2005 and 2010 (n = 1702), stratified into 4 groups: persons with a high probability of dementia or those who died because of heart disease, cancer, or other causes.
Measurements: Total social costs and their components, including Medicare, Medicaid, private insurance, out-of-pocket spending, and informal care, measured over the last 5 years of life; and out-of-pocket spending as a proportion of household wealth.
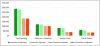
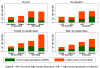
Results: Average total cost per decedent with dementia ($287 038) was significantly greater than that of those who died of heart disease ($175 136), cancer ($173 383), or other causes ($197 286) (P < 0.001). Although Medicare expenditures were similar across groups, average out-of-pocket spending for patients with dementia ($61 522) was 81% higher than that for patients without dementia ($34 068); a similar pattern held for informal care. Out-of-pocket spending for the dementia group (median, $36 919) represented 32% of wealth measured 5 years before death compared with 11% for the nondementia group (P < 0.001). This proportion was greater for black persons (84%), persons with less than a high school education (48%), and unmarried or widowed women (58%).
Limitation: Imputed Medicaid, private insurance, and informal care costs.
Conclusion: Health care expenditures among persons with dementia were substantially larger than those for other diseases, and many of the expenses were uncovered (uninsured). This places a large financial burden on families, and these burdens are particularly pronounced among the demographic groups that are least prepared for financial risk.
Primary funding source: National Institute on Aging.
Figures
Comment in
-
Health care costs for patients with dementia at the end of life.Ann Intern Med. 2015 Nov 17;163(10):I-28. doi: 10.7326/P15-9035. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Ann Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26502381 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Residential Setting and the Cumulative Financial Burden of Dementia in the 7 Years Before Death.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020 Jun;68(6):1319-1324. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16414. Epub 2020 Mar 18. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020. PMID: 32187655 Free PMC article.
-
Out-of-pocket health spending by poor and near-poor elderly Medicare beneficiaries.Health Serv Res. 1999 Apr;34(1 Pt 2):241-54. Health Serv Res. 1999. PMID: 10199672 Free PMC article.
-
Out-of-Pocket Spending and Financial Burden Among Medicare Beneficiaries With Cancer.JAMA Oncol. 2017 Jun 1;3(6):757-765. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.4865. JAMA Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27893028 Free PMC article.
-
Dollars and sight: the economics of ophthalmology.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004 Jun;15(3):173-80. doi: 10.1097/01.icu.0000120673.27548.52. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2004. PMID: 15118502 Review.
-
The costs of caring: medical costs of Alzheimer's disease and the managed care environment.J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2001 Winter;14(4):168-78. doi: 10.1177/089198870101400402. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11794445 Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between Race and Comorbid Conditions Among Older Adults with Dementia.J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 24;13(21):6368. doi: 10.3390/jcm13216368. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39518507 Free PMC article.
-
Ascertaining Out-of-Pocket Costs of Dementia Care: Feasibility Study of a Web-Based Weekly Survey.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Sep 25;8:e56878. doi: 10.2196/56878. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 39321453 Free PMC article.
-
Racial and Ethnic Disparities in the Monetary Value of Informal Caregiving for Non-Institutionalized People Living With Dementia.J Aging Health. 2024 Oct;36(9):570-582. doi: 10.1177/08982643241262917. Epub 2024 Jun 17. J Aging Health. 2024. PMID: 38887015 Free PMC article.
-
Hospitalization expenses of coronary heart disease inpatients in China: evidence from two hospitals in Ningxia Hui autonomous region.Front Public Health. 2024 May 2;12:1266456. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1266456. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38756881 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of outdoor activities on the medical expenditure of older people: multiple chain mediating effects of health benefits.BMC Public Health. 2024 May 3;24(1):1227. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18719-z. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38702631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamel MB, Blumenthal D, Stremikis K, Cutler D. Health Care Spending—A Giant Slain or Sleeping? New England Journal of Medicine. 2013;369(26):2551–7. - PubMed
-
- Baicker K, Elmendorf D. Comments and Discussion. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity. 2013:303–23.
-
- National Health Expenditures 2013 Highlights. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid; 2013.
-
- Graaff JdV. New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. London; 1987. Social Cost; pp. 393–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical