The cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM251 increases paraoxon and chlorpyrifos oxon toxicity in rats
- PMID: 25447325
- PMCID: PMC4448943
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.11.001
The cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM251 increases paraoxon and chlorpyrifos oxon toxicity in rats
Abstract
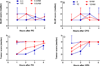
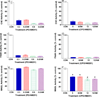
Organophosphorus anticholinesterases (OPs) elicit acute toxicity by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase (AChE), leading to acetylcholine accumulation and overstimulation of cholinergic receptors. Endocannabinoids (eCBs, e.g., arachidonoyl ethanolamide [AEA] and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol [2-AG]) are neuromodulators that regulate neurotransmission by reducing neurotransmitter release. The eCBs are degraded by the enzymes fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH, primarily involved in hydrolysis of AEA) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL, primarily responsible for metabolism of 2-AG). We previously reported that the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 reduced cholinergic toxicity after paraoxon exposure. This study compared the effects of the cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM251 on acute toxicity following either paraoxon (PO) or chlorpyrifos oxon (CPO). CPO was more potent in vitro than PO at inhibiting AChE (≈ 2 fold), FAAH (≈ 8 fold), and MAGL (≈ 19 fold). Rats were treated with vehicle, PO (0.3 and 0.6 mg/kg, sc) or CPO (6 and 12 mg/kg, sc) and subsets treated with AM251 (3mg/kg, ip; 30 min after OP). Signs of toxicity were recorded for 4h and rats were then sacrificed. OP-treated rats showed dose-related involuntary movements, with AM251 increasing signs of toxicity with the lower dosages. PO and CPO elicited excessive secretions, but AM251 had no apparent effect with either OP. Lethality was increased by AM251 with the higher dosage of PO, but no lethality was noted with either dosage of CPO, with or without AM251. Both OPs caused extensive inhibition of hippocampal AChE and FAAH (>80-90%), but only CPO inhibited MAGL (37-50%). These results provide further evidence that eCB signaling can influence acute OP toxicity. The selective in vivo inhibition of MAGL by CPO may be important in the differential lethality noted between PO and CPO with AM251 co-administration.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Endocannabinoids; Fatty acid amide hydrolase; Monoacylglycerol lipase; Organophosphate.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
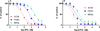
Similar articles
-
Comparative effects of parathion and chlorpyrifos on endocannabinoid and endocannabinoid-like lipid metabolites in rat striatum.Neurotoxicology. 2015 Sep;50:20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Neurotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 26215119 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of parathion and chlorpyrifos on extracellular endocannabinoid levels in rat hippocampus: influence on cholinergic toxicity.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 1;272(3):608-15. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.07.025. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23933531 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive toxicity of the organophosphorus insecticides chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion in adult rats.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004 Apr 15;196(2):183-90. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.014. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15081265
-
The toxicity of mixtures of specific organophosphate compounds is modulated by paraoxonase 1 status.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;660:47-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-350-3_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20221870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of the chemical families of fatty acid amide hydrolase and monoacylglycerol lipase inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2008;8(3):247-67. doi: 10.2174/156802608783498005. Curr Top Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18289091 Review.
Cited by
-
Retrograde activation of CB1R by muscarinic receptors protects against central organophosphorus toxicity.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Sep 1;155:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.028. Epub 2019 May 24. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 31132436 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of parathion and chlorpyrifos on endocannabinoid and endocannabinoid-like lipid metabolites in rat striatum.Neurotoxicology. 2015 Sep;50:20-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Neurotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 26215119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne JA, Fosbraey P, Halliday J. SCH 23390 affords protection against soman-evoked seizures in the freely moving guinea-pig: a concomitant neurochemical, electrophysiological and behavioural study. Neuropharmacology. 2001;40:279–288. - PubMed
-
- Casida JE, Gulevich AG, Sarpong R, Bunnelle EM. S-Arachidonoyl-2-thioglycerol synthesis and use for fluorimetric and colorimetric assays of monoacylglycerol lipase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010;18:1942–1947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous


