Sequencing Y chromosomes resolves discrepancy in time to common ancestor of males versus females
- PMID: 23908239
- PMCID: PMC4032117
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1237619
Sequencing Y chromosomes resolves discrepancy in time to common ancestor of males versus females
Abstract
The Y chromosome and the mitochondrial genome have been used to estimate when the common patrilineal and matrilineal ancestors of humans lived. We sequenced the genomes of 69 males from nine populations, including two in which we find basal branches of the Y-chromosome tree. We identify ancient phylogenetic structure within African haplogroups and resolve a long-standing ambiguity deep within the tree. Applying equivalent methodologies to the Y chromosome and the mitochondrial genome, we estimate the time to the most recent common ancestor (T(MRCA)) of the Y chromosome to be 120 to 156 thousand years and the mitochondrial genome T(MRCA) to be 99 to 148 thousand years. Our findings suggest that, contrary to previous claims, male lineages do not coalesce significantly more recently than female lineages.
Figures

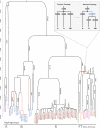
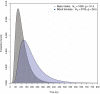
Comment in
-
Genetics. Y weigh in again on modern humans.Science. 2013 Aug 2;341(6145):465-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1242899. Science. 2013. PMID: 23908212 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
An unbiased resource of novel SNP markers provides a new chronology for the human Y chromosome and reveals a deep phylogenetic structure in Africa.Genome Res. 2014 Mar;24(3):535-44. doi: 10.1101/gr.160788.113. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24395829 Free PMC article.
-
A revised root for the human Y chromosomal phylogenetic tree: the origin of patrilineal diversity in Africa.Am J Hum Genet. 2011 Jun 10;88(6):814-818. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.05.002. Epub 2011 May 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21601174 Free PMC article.
-
A recent bottleneck of Y chromosome diversity coincides with a global change in culture.Genome Res. 2015 Apr;25(4):459-66. doi: 10.1101/gr.186684.114. Epub 2015 Mar 13. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 25770088 Free PMC article.
-
The study of human Y chromosome variation through ancient DNA.Hum Genet. 2017 May;136(5):529-546. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1773-z. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28260210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Y-chromosome variation in the genome-sequencing era.Nat Rev Genet. 2017 Aug;18(8):485-497. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.36. Epub 2017 May 30. Nat Rev Genet. 2017. PMID: 28555659 Review.
Cited by
-
Y chromosome sequencing data suggest dual paths of haplogroup N1a1 into Finland.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 Oct 28. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01707-7. Online ahead of print. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39465313
-
The role of emerging elites in the formation and development of communities after the fall of the Roman Empire.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Sep 3;121(36):e2317868121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2317868121. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39159385 Free PMC article.
-
A familial, telomere-to-telomere reference for human de novo mutation and recombination from a four-generation pedigree.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 5:2024.08.05.606142. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.05.606142. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39149261 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Multiple Human Population Movements and Cultural Dispersal Events Shaped the Landscape of Chinese Paternal Heritage.Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Jul 3;41(7):msae122. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae122. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 38885310 Free PMC article.
-
Human Y chromosome haplogroup L1-M22 traces Neolithic expansion in West Asia and supports the Elamite and Dravidian connection.iScience. 2024 May 17;27(6):110016. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110016. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38883810 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


